Yew wood offers a fine, smooth grain with yellowish-brown tones ideal for decorative cabinet work, while mahogany provides a rich reddish-brown color and exceptional durability suited for high-end cabinetry. Mahogany's superior resistance to warping and splitting makes it preferable for long-lasting cabinets compared to the softer, more porous yew.
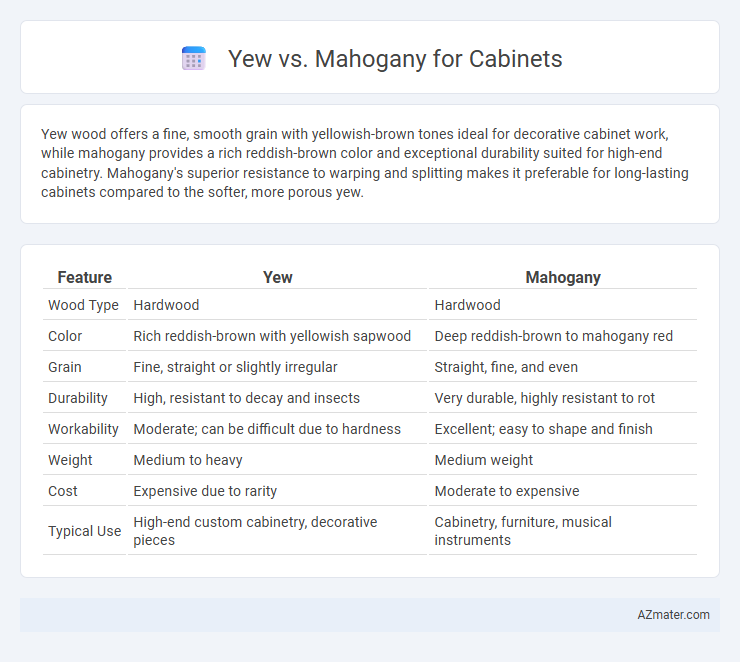
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Yew | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Hardwood |
| Color | Rich reddish-brown with yellowish sapwood | Deep reddish-brown to mahogany red |
| Grain | Fine, straight or slightly irregular | Straight, fine, and even |
| Durability | High, resistant to decay and insects | Very durable, highly resistant to rot |
| Workability | Moderate; can be difficult due to hardness | Excellent; easy to shape and finish |
| Weight | Medium to heavy | Medium weight |
| Cost | Expensive due to rarity | Moderate to expensive |
| Typical Use | High-end custom cabinetry, decorative pieces | Cabinetry, furniture, musical instruments |
Introduction: Comparing Yew and Mahogany for Cabinetry
Yew and mahogany are popular hardwoods known for their durability and unique grain patterns, making them ideal choices for cabinetry. Yew offers a warm, reddish-brown hue with fine grain, while mahogany boasts a rich, deep reddish-brown color and exceptional workability. Both woods provide strong resistance to wear, but mahogany is often preferred for its smoother finish and superior stability in humidity variations.
Origin and Botanical Differences
Yew (Taxus baccata) is a slow-growing conifer native to Europe and parts of Asia, prized for its fine grain and rich, reddish-brown hue with occasional darker streaks. Mahogany, primarily from the genus Swietenia, originates in Central and South America, known for its sturdy hardwood with a deep reddish-brown color and a more uniform grain pattern. Botanically, Yew is a softwood from an evergreen coniferous tree, whereas Mahogany is a hardwood derived from tropical deciduous trees, influencing their durability and workability in cabinetry.
Appearance: Color, Grain, and Texture
Yew wood features a pale yellow to light reddish-brown color with a fine, straight grain and a smooth texture that adds a subtle elegance to cabinets. Mahogany displays a rich reddish-brown hue with deep, interlocking grain patterns and a naturally lustrous, smooth texture, enhancing cabinetry with warmth and luxury. Both woods offer unique aesthetic qualities, but Mahogany's pronounced grain and richer color make it a preferred choice for striking, high-end cabinetry.
Durability and Hardness
Yew wood offers moderate hardness with a Janka rating of approximately 1,130, making it suitable for cabinetry that requires some resistance to dents but remains relatively easy to work with. Mahogany is significantly harder and more durable, featuring a Janka hardness of around 1,070 to 1,220 depending on the species, providing excellent longevity and resistance to wear for cabinets in high-use areas. Both woods exhibit good dimensional stability, but mahogany's superior hardness generally ensures greater durability for cabinetry subjected to daily stress.
Workability and Machining
Yew wood offers excellent workability due to its fine grain and moderate density, making it easy to shape and carve for detailed cabinetry. Mahogany, renowned for its smooth texture and uniform grain, provides superior machinability with minimal wear on tools, resulting in clean cuts and a polished finish. Both woods respond well to hand and machine tools, but mahogany's stability and resistance to chipping often make it the preferred choice for intricate cabinet components.
Maintenance and Longevity
Yew wood cabinets require moderate maintenance with regular sealing to prevent moisture damage and preserve their natural golden hue, offering good durability in low-humidity environments. Mahogany cabinets boast superior longevity due to their dense hardwood structure and resistance to warping, needing minimal upkeep beyond occasional polishing to maintain their rich, deep reddish-brown color. Both woods benefit from protection against extreme humidity but mahogany typically outperforms yew in long-term resilience and structural stability.
Cost and Availability
Yew wood is generally more affordable and easier to source regionally compared to mahogany, which is often pricier due to its exotic status and limited supply. Mahogany's higher cost reflects its durability, rich grain, and demand in luxury cabinetry, making it less accessible for budget-conscious projects. Availability of yew is typically steadier in temperate regions, while mahogany relies on tropical imports, influencing both price and delivery times.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Yew wood, known for its slow growth and limited availability, poses sustainability challenges due to overharvesting and habitat disruption. Mahogany, especially from unmanaged rainforest sources, often contributes to deforestation and biodiversity loss, though certified sustainable mahogany options exist, promoting responsible forestry. Choosing reclaimed or FSC-certified yew and mahogany significantly reduces environmental impact and supports sustainable cabinet production.
Popular Uses in Cabinetmaking
Yew wood is prized in cabinetmaking for its fine grain and warm, golden hue, making it ideal for decorative panels, intricate moldings, and custom furniture with a traditional aesthetic. Mahogany stands out for its durability, deep reddish-brown color, and workability, commonly used in high-end cabinetry, luxury kitchen installations, and heirloom-quality furniture pieces. Both woods offer excellent stability, but mahogany is favored for its resistance to swelling and warping, enhancing long-term performance in cabinetry exposed to varying humidity.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Yew and Mahogany
Yew offers a lighter, more durable wood with a fine grain ideal for cabinets requiring a natural, rustic aesthetic, while mahogany provides a rich, reddish-brown hue with exceptional stability and workability suited for high-end, elegant cabinetry. Mahogany's resistance to warping and fine finish make it preferable for long-lasting, luxurious pieces, whereas yew is favored for its unique texture and distinct appearance. Selecting between yew and mahogany depends on the desired cabinet style, durability requirements, and budget considerations.
Infographic: Yew vs Mahogany for Cabinet
 azmater.com
azmater.com