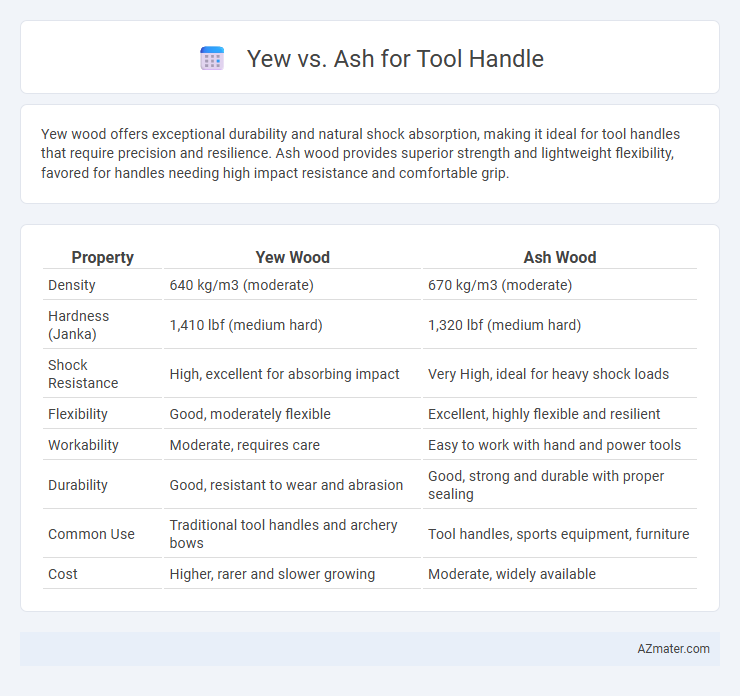
Yew wood offers exceptional durability and natural shock absorption, making it ideal for tool handles that require precision and resilience. Ash wood provides superior strength and lightweight flexibility, favored for handles needing high impact resistance and comfortable grip.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Yew Wood | Ash Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 640 kg/m3 (moderate) | 670 kg/m3 (moderate) |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1,410 lbf (medium hard) | 1,320 lbf (medium hard) |
| Shock Resistance | High, excellent for absorbing impact | Very High, ideal for heavy shock loads |
| Flexibility | Good, moderately flexible | Excellent, highly flexible and resilient |
| Workability | Moderate, requires care | Easy to work with hand and power tools |
| Durability | Good, resistant to wear and abrasion | Good, strong and durable with proper sealing |
| Common Use | Traditional tool handles and archery bows | Tool handles, sports equipment, furniture |
| Cost | Higher, rarer and slower growing | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Yew and Ash Wood
Yew wood, prized for its exceptional elasticity and durability, offers a dense grain structure that provides excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for tool handles requiring resilience. Ash wood features a lighter, straight-grained texture known for its strength and ability to withstand heavy impact while maintaining flexibility. The natural hardness and ease of machining in both yew and ash make them favored choices, balancing comfort and longevity in tool handle craftsmanship.
Botanical Characteristics and Growth Habits
Yew (Taxus baccata) features dense, fine-grained wood with high natural elasticity, making it ideal for shock-resistant tool handles; it thrives in shaded, well-drained soils and grows slowly, reaching heights of 10-20 meters. Ash (Fraxinus excelsior) offers straight-grained, tough, and flexible timber with excellent impact resistance, commonly found in mixed woodlands across Europe, growing rapidly to heights of 20-30 meters with a broad, open canopy. The contrasting growth rates and wood structures reflect Yew's slower maturation with tighter grain versus Ash's faster growth producing lighter, yet strong handles favored in ergonomic tool design.
Historical Use in Tool Handles
Yew wood has been historically prized for tool handles due to its exceptional elasticity and resistance to splitting, making it ideal for tools requiring shock absorption like bows and hammers. Ash wood, commonly used in tool handles since ancient times, offers superior strength and flexibility, providing durability and comfort in hand tools such as axes and shovels. Both woods were crucial in traditional craftsmanship, with yew favored for precision tools and ash preferred for heavy-duty implements.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Yew wood exhibits exceptional strength and flexibility, making it highly resistant to splitting and ideal for tool handles that require shock absorption. Ash wood is celebrated for its superior toughness and resilience, providing durable support under heavy usage with enhanced wear resistance. Comparing the two, yew offers better elasticity and impact resistance, while ash delivers greater hardness and long-term durability for demanding tool applications.
Flexibility and Shock Absorption
Yew wood offers exceptional flexibility and natural shock absorption, making it ideal for tool handles that require resilience under stress. Ash wood provides strong flexibility with a slightly higher stiffness, delivering reliable shock absorption suited for heavy-duty tools. Comparing the two, yew excels in dampening vibrations, while ash balances durability and comfort for prolonged use.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Yew wood offers exceptional workability due to its fine grain and moderate hardness, allowing for smooth shaping and detailed carving, which is ideal for intricate tool handles. Ash wood, known for its straight grain and excellent shock resistance, provides ease of shaping with minimal effort while maintaining durability under heavy use. Both woods perform well, but Yew excels in fine detailing whereas Ash is favored for its balance of toughness and machinability in tool handle applications.
Resistance to Weather and Decay
Yew wood offers exceptional resistance to weather and decay, making it highly durable for tool handles exposed to outdoor elements, due to its dense grain and natural oils. Ash, while strong and shock-resistant, is more susceptible to moisture damage and requires regular treatment to prevent rot and decay when used in wet or humid conditions. Choosing yew for tool handles ensures longer-lasting performance with minimal maintenance compared to ash in environments prone to weather variations.
Weight and Balance in Hand Tools
Yew wood offers a lightweight yet dense composition, providing excellent balance and reduced fatigue for tool handles. Ash, known for its straight grain and shock resistance, tends to be heavier but delivers superior durability and stability in hand tools. Comparing the two, Yew excels in weight-sensitive applications, while Ash provides robust balance for heavy-duty use.
Cost and Availability
Yew tool handles generally cost more than ash due to their denser grain and limited supply, making yew a premium choice for specialized tools. Ash is widely available and more affordable, favored for its strength and shock resistance in mass-produced handles. Availability of yew is often restricted to certain regions, while ash is common in North America and Europe, ensuring consistent supply and lower prices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wood
Selecting the right wood for a tool handle depends on balancing durability, shock absorption, and weight. Yew offers excellent flexibility and shock resistance, making it ideal for tools that require precision and comfort during extended use, while ash provides superior strength and impact resistance, suited for heavy-duty applications. Consider specific tool requirements and user preference to determine whether yew's elasticity or ash's robustness best enhances performance and longevity.
Infographic: Yew vs Ash for Tool Handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com