Yew wood offers exceptional durability and a rich reddish-brown color, making it ideal for high-end panels, while Alder provides a softer texture with a light tan hue, suitable for budget-friendly and versatile paneling options. Yew's natural resistance to decay outperforms Alder, which requires additional treatment for moisture-prone environments.
Table of Comparison
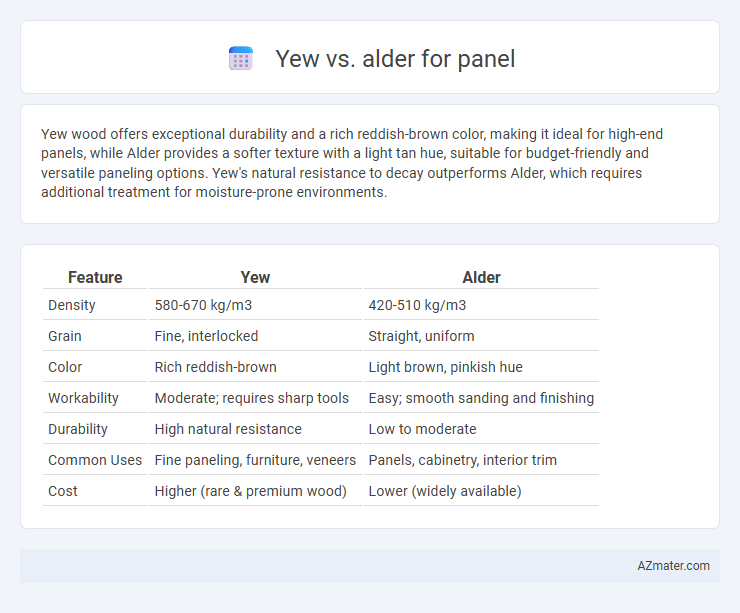
| Feature | Yew | Alder |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 580-670 kg/m3 | 420-510 kg/m3 |
| Grain | Fine, interlocked | Straight, uniform |
| Color | Rich reddish-brown | Light brown, pinkish hue |
| Workability | Moderate; requires sharp tools | Easy; smooth sanding and finishing |
| Durability | High natural resistance | Low to moderate |
| Common Uses | Fine paneling, furniture, veneers | Panels, cabinetry, interior trim |
| Cost | Higher (rare & premium wood) | Lower (widely available) |
Introduction: Comparing Yew and Alder for Paneling
Yew wood offers exceptional durability, rich reddish-brown hues, and fine grain, making it ideal for high-quality paneling in luxurious interiors. Alder, by contrast, provides a lighter tone with subtle grain patterns, offering an affordable and versatile option for paneling that easily takes stains and finishes. Comparing Yew and Alder for paneling highlights the trade-off between Yew's distinctive elegance and Alder's cost-effective adaptability.
Wood Characteristics: Yew vs Alder
Yew wood is dense, durable, and features a fine, smooth grain with a reddish-brown hue, making it highly resistant to decay and ideal for high-quality panels. Alder wood is softer and lighter with a more uniform, straight grain and a pale brown to reddish color, offering ease of workability but less durability compared to Yew. Yew's natural oils provide enhanced resistance to insects and moisture, whereas Alder is more prone to denting and requires finishing to improve its longevity for panel use.
Appearance and Grain Differences
Yew wood features a rich golden to reddish-brown hue with a distinctive fine, straight grain that often includes attractive knots and resin canals, giving it a striking and decorative appearance ideal for paneling. Alder wood displays a lighter, more uniform tan to reddish-brown color with a straight grain that is smooth and consistent, offering a subtler and more understated aesthetic. The contrast between Yew's dramatic, textured grain and Alder's even, mellow pattern makes Yew preferable for statement panels, while Alder suits applications demanding a softer, more neutral backdrop.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Yew wood exhibits superior durability and strength compared to alder, making it an ideal choice for high-quality panels that require long-lasting performance. Yew's dense grain structure provides exceptional resistance to wear, decay, and impact, whereas alder is softer and more prone to dents and scratches. For applications demanding robust and resilient paneling, yew offers enhanced structural integrity and longevity over alder.
Workability and Machinability
Yew wood offers excellent workability with its fine grain and moderate density, making it easy to cut, shape, and finish for panel applications. Alder, known for its softer texture and uniform grain, provides superior machinability, allowing precise routing and sanding without tear-out. Both woods perform well, but Alder typically requires less effort in machining processes, while Yew delivers a more durable and aesthetically rich panel surface.
Cost and Availability
Yew wood generally commands a higher price due to its limited availability and slower growth rate, making it a premium choice for paneling. Alder wood is more cost-effective and widely accessible, benefiting from faster growth and sustainable harvesting practices. For budget-conscious projects requiring consistent supply, alder panels offer a practical and economical alternative to yew.
Finishing and Staining Qualities
Yew wood offers a smooth, fine-grained surface that accepts finishes and stains evenly, highlighting its warm reddish-brown tones and intricate grain patterns. Alder paneling provides a softer texture with a consistent grain, making it highly receptive to stains and finishes that enhance its natural light brown to reddish hue. Both woods respond well to finishing products, but Yew's denser grain often results in a richer, more durable finish ideal for elegant interior panels.
Best Uses in Paneling Projects
Yew wood, prized for its rich color and fine grain, excels in decorative paneling projects requiring elegance and durability, often used in high-end interiors and furniture. Alder, with its softer texture and moderate hardness, is ideal for painted or stained paneling where cost-effectiveness and ease of work are priorities. Both woods offer unique aesthetic and functional benefits, with Yew favored for luxury finishes and Alder chosen for versatile, budget-friendly applications in paneling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Yew wood is highly valued for its durability and resistance to decay, contributing to long-lasting panels that reduce the need for frequent replacement, thereby minimizing resource consumption. Alder, being fast-growing and widely available, offers a more sustainable option with a smaller carbon footprint due to quicker replenishment rates and efficient carbon sequestration. Both woods have low environmental impact when sourced responsibly, but Alder's rapid growth and renewability make it a preferred choice for environmentally-conscious panel production.
Choosing the Right Wood: Yew or Alder
Yew wood offers a dense, fine grain with natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for high-quality, long-lasting panels that require a luxurious appearance. Alder wood is a softer hardwood with a uniform texture and excellent workability, providing a cost-effective and versatile option for smooth, stable panels. Choosing between yew and alder depends on the desired durability, visual appeal, and project budget, with yew favored for premium finishes and alder preferred for affordable, easy-to-finish surfaces.
Infographic: Yew vs Alder for Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com