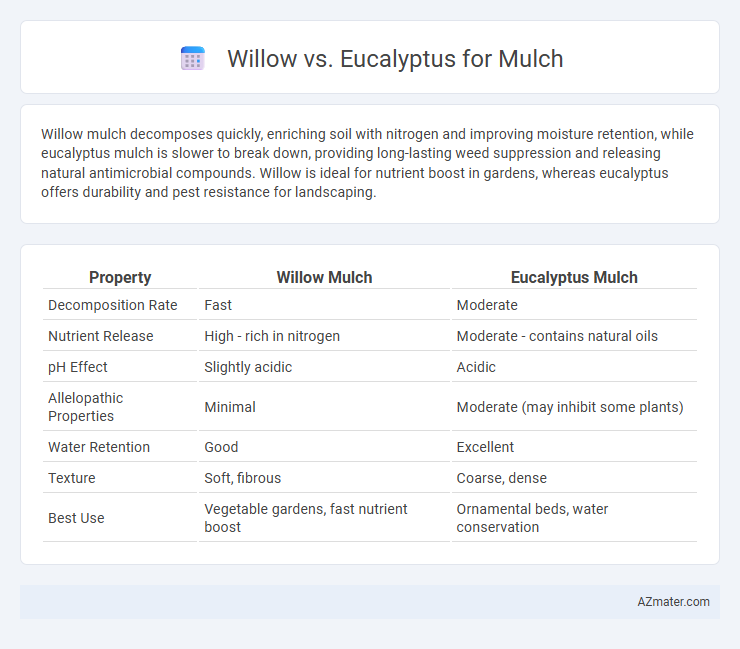
Willow mulch decomposes quickly, enriching soil with nitrogen and improving moisture retention, while eucalyptus mulch is slower to break down, providing long-lasting weed suppression and releasing natural antimicrobial compounds. Willow is ideal for nutrient boost in gardens, whereas eucalyptus offers durability and pest resistance for landscaping.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Willow Mulch | Eucalyptus Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Decomposition Rate | Fast | Moderate |
| Nutrient Release | High - rich in nitrogen | Moderate - contains natural oils |
| pH Effect | Slightly acidic | Acidic |
| Allelopathic Properties | Minimal | Moderate (may inhibit some plants) |
| Water Retention | Good | Excellent |
| Texture | Soft, fibrous | Coarse, dense |
| Best Use | Vegetable gardens, fast nutrient boost | Ornamental beds, water conservation |
Introduction to Mulch Materials
Willow and eucalyptus mulch both offer unique benefits for soil health and plant growth, with willow mulch providing rich organic matter that decomposes quickly to improve nutrient availability. Eucalyptus mulch is known for its natural pest-repellent properties and slower decomposition rate, making it ideal for long-term weed suppression and moisture retention. Choosing between willow and eucalyptus mulch depends on garden needs such as nutrient supplementation speed, pest control, and soil moisture management.
Key Differences Between Willow and Eucalyptus Mulch
Willow mulch decomposes quickly, enriching soil with nitrogen and improving moisture retention, while eucalyptus mulch breaks down slowly and has natural oils that may inhibit weed growth but can also affect seed germination. Willow mulch tends to be softer and lighter, making it ideal for garden beds, whereas eucalyptus mulch is denser, providing longer-lasting coverage and better erosion control. The choice depends on desired decomposition rate, impact on soil nutrients, and specific plant tolerance to eucalyptus oils.
Nutrient Composition: Willow vs Eucalyptus
Willow mulch is rich in nitrogen and potassium, promoting soil fertility and enhancing plant growth, while eucalyptus mulch contains natural oils with antimicrobial properties but has a lower nutrient content, particularly nitrogen. The high tannin levels in eucalyptus can inhibit nitrogen availability, making willow a more nutrient-dense option for enriching soil. Willow's faster decomposition rate releases nutrients quickly, whereas eucalyptus mulch breaks down slower, contributing to longer-lasting soil coverage but less immediate nutrient input.
Soil Health and Microorganism Impact
Willow mulch enhances soil health by promoting microbial activity due to its high nitrogen content and natural growth hormones, which stimulate beneficial soil organisms and improve nutrient cycling. In contrast, eucalyptus mulch contains allelopathic compounds that can inhibit certain soil microorganisms, potentially reducing microbial diversity and slowing organic matter decomposition. Selecting willow mulch supports a thriving soil microbiome and faster nutrient availability, crucial for plant growth and long-term soil fertility.
Weed Suppression Effectiveness
Willow mulch exhibits moderate weed suppression due to its moderate allelopathic properties and ability to retain soil moisture, which limits weed seed germination. Eucalyptus mulch provides superior weed suppression by releasing strong allelochemicals such as cineole, which inhibit weed growth and reduce seed viability effectively. Selecting eucalyptus mulch enhances garden weed control while improving soil conditions through its dense coverage and antimicrobial effects.
Moisture Retention Capabilities
Willow mulch excels in moisture retention due to its high water absorption capacity and slow decomposition rate, helping soil remain consistently damp. Eucalyptus mulch, while offering moderate moisture retention, can sometimes create hydrophobic soil layers that reduce water infiltration. Choosing willow mulch is generally more effective for maintaining soil moisture in garden beds and around plants.
Decomposition Rate and Longevity
Willow mulch decomposes rapidly due to its high moisture content and soft wood fibers, making it ideal for improving soil organic matter quickly. Eucalyptus mulch breaks down more slowly because of its dense, oily leaves and hardwood composition, offering longer-lasting weed suppression and moisture retention. Choosing between willow and eucalyptus mulch depends on whether fast nutrient cycling or extended ground coverage is prioritized in landscape management.
Potential Toxicity and Allelopathic Effects
Willow mulch is generally safe and beneficial, releasing natural growth hormones like salicylic acid that promote soil health without significant toxicity or allelopathic effects. Eucalyptus mulch contains compounds such as cineole, which can be toxic to certain plants and inhibit seed germination due to strong allelopathic properties. Choosing willow over eucalyptus for mulch reduces the risk of negative impacts on surrounding vegetation and supports a more balanced garden ecosystem.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Willow mulch is generally more affordable due to the widespread availability of willow branches in temperate regions, making it a cost-effective choice for gardeners. Eucalyptus mulch tends to be pricier, primarily sourced from eucalyptus plantations concentrated in specific areas like Australia and parts of California, affecting its overall market availability. Both mulches offer benefits, but willow's lower cost and easier accessibility often make it the preferred option for large-scale mulching projects.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Willow mulch excels in moisture retention and nutrient release, making it ideal for vegetable gardens and young plants requiring consistent hydration and nutrient-rich soil. Eucalyptus mulch offers strong antifungal and antibacterial properties, suited for ornamental gardens and areas prone to pests and diseases. For long-term weed suppression and soil acidity management, eucalyptus mulch is recommended, while willow mulch suits rapid nutrient cycling and organic matter enrichment.
Infographic: Willow vs Eucalyptus for Mulch
 azmater.com
azmater.com