Tulipwood features a fine grain and light pinkish-brown color, offering a cost-effective and durable option for cabinets. Walnut is prized for its rich, dark brown tones and exceptional strength, providing a luxurious and long-lasting cabinet material.
Table of Comparison
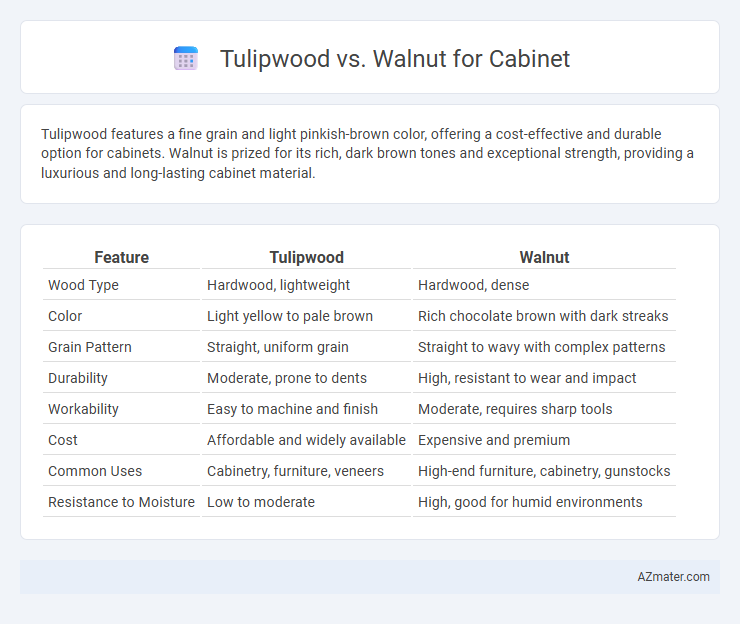
| Feature | Tulipwood | Walnut |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood, lightweight | Hardwood, dense |
| Color | Light yellow to pale brown | Rich chocolate brown with dark streaks |
| Grain Pattern | Straight, uniform grain | Straight to wavy with complex patterns |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to dents | High, resistant to wear and impact |
| Workability | Easy to machine and finish | Moderate, requires sharp tools |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available | Expensive and premium |
| Common Uses | Cabinetry, furniture, veneers | High-end furniture, cabinetry, gunstocks |
| Resistance to Moisture | Low to moderate | High, good for humid environments |
Introduction to Tulipwood and Walnut for Cabinetry
Tulipwood, known for its pale, creamy color with subtle pink or orange hues, offers a smooth grain ideal for bright, modern cabinetry. Walnut stands out with its rich, dark brown tones and striking grain patterns, lending warmth and elegance to traditional and contemporary cabinets alike. Both woods provide durability and workability, making them popular choices for high-quality cabinetry projects.
Appearance and Color Differences
Tulipwood offers a lighter, reddish-pink tone with subtle grain patterns, creating a warm and inviting appearance ideal for modern and contemporary cabinet designs. Walnut features a deep, rich brown color with pronounced, swirling grain that adds sophistication and timeless elegance to cabinetry. These distinct color and grain contrasts make tulipwood suitable for bright, airy spaces, while walnut suits traditional or luxurious settings.
Grain Patterns and Texture Comparison
Tulipwood features a straight to slightly wavy grain with a smooth, uniform texture that creates a clean and contemporary look for cabinets. Walnut displays a more varied grain pattern, including straight, curly, and wavy grains, offering rich, dynamic visual interest and a luxurious, deep texture. The finer, consistent texture of Tulipwood contrasts with Walnut's coarser, more pronounced grain, making each wood suited to different design aesthetics and tactile experiences in cabinetry.
Durability and Hardness
Tulipwood offers a moderate hardness rating of 830 on the Janka scale, making it a durable choice for cabinets but less resistant to dents compared to walnut. Walnut exhibits a higher Janka hardness of approximately 1,010, providing superior durability and better impact resistance for long-lasting cabinet surfaces. For projects demanding robust wear resistance, walnut is generally preferred due to its enhanced hardness and ability to withstand daily use.
Workability and Machinability
Tulipwood offers moderate workability with a fine, even texture that allows for smooth cutting and shaping, making it suitable for detailed cabinet components. Walnut exhibits excellent machinability due to its consistent grain and density, enabling precise milling, sanding, and finishing with minimal tool wear. Both woods respond well to hand and power tools, but walnut's superior stability and finish quality often make it the preferred choice for high-end cabinetry.
Cost and Availability
Tulipwood offers a cost-effective option for cabinet construction, typically priced lower than walnut due to its faster growth rate and wider availability in North America. Walnut, prized for its rich color and durability, commands a higher price and can be less accessible, especially in large, clear cuts needed for cabinetry. The choice between tulipwood and walnut often hinges on budget constraints and regional supply, with tulipwood providing a budget-friendly alternative without sacrificing strength.
Environmental Sustainability
Tulipwood cabinets offer a sustainable option due to faster growth rates and responsible forestry practices compared to walnut, which is slower growing and often sourced from older, less renewable forests. Walnut's environmental impact is higher because harvesting older trees contributes to habitat loss and carbon release. Choosing Tulipwood promotes reduced deforestation and supports eco-friendly building practices in cabinetry.
Finishing and Maintenance
Tulipwood cabinets provide a smooth surface ideal for staining and finishing, offering vibrant color absorption that enhances the wood's natural grain, while walnut cabinets feature a rich, dark tone that often requires oil-based finishes to maintain their deep luster. Tulipwood finishes typically need more frequent reapplication to protect against moisture and wear, whereas walnut's dense grain structure offers greater durability and resistance to dents and scratches. Regular dusting and the use of gentle wood cleaners preserve the finish quality for both, but walnut demands less intensive maintenance over time due to its natural hardness and oil content.
Best Applications in Cabinet Design
Tulipwood offers a light, creamy color with fine grain, making it ideal for modern or Scandinavian-style cabinets that emphasize brightness and subtle texture. Walnut provides rich, dark tones and pronounced grain patterns, perfect for traditional or luxury cabinet designs where warmth and elegance are desired. The choice depends on the aesthetic goal: tulipwood suits minimalist, airy spaces, while walnut enhances sophisticated, classic interiors.
Conclusion: Which Wood is Better for Cabinets?
Tulipwood offers a lighter, more affordable option with good durability and a smooth grain, making it ideal for bright, contemporary cabinet designs. Walnut provides superior strength, rich dark hues, and natural resistance to wear, making it a premium choice for high-end, classic cabinetry. The best wood for cabinets depends on budget, desired aesthetic, and usage, with walnut favored for luxury and longevity and tulipwood suited for cost-effective, stylish solutions.
Infographic: Tulipwood vs Walnut for Cabinet
 azmater.com
azmater.com