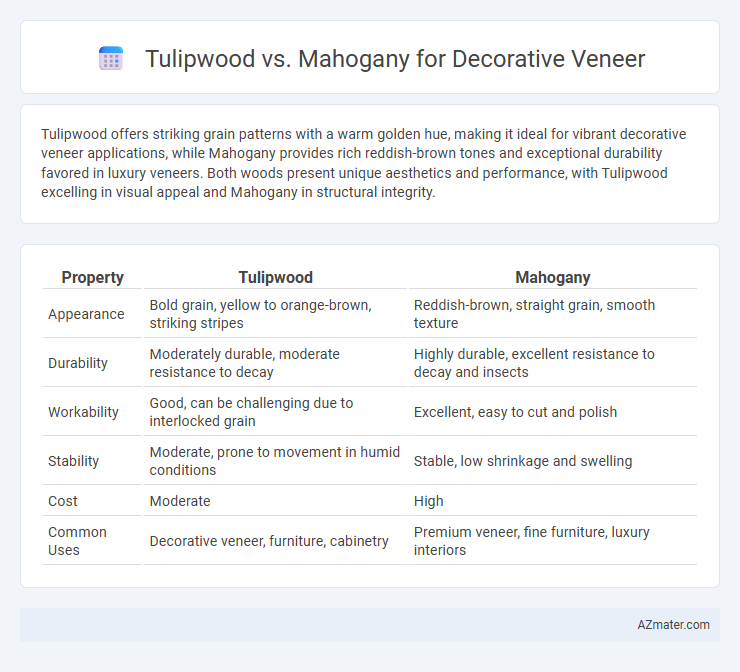
Tulipwood offers striking grain patterns with a warm golden hue, making it ideal for vibrant decorative veneer applications, while Mahogany provides rich reddish-brown tones and exceptional durability favored in luxury veneers. Both woods present unique aesthetics and performance, with Tulipwood excelling in visual appeal and Mahogany in structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tulipwood | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Bold grain, yellow to orange-brown, striking stripes | Reddish-brown, straight grain, smooth texture |
| Durability | Moderately durable, moderate resistance to decay | Highly durable, excellent resistance to decay and insects |
| Workability | Good, can be challenging due to interlocked grain | Excellent, easy to cut and polish |
| Stability | Moderate, prone to movement in humid conditions | Stable, low shrinkage and swelling |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Common Uses | Decorative veneer, furniture, cabinetry | Premium veneer, fine furniture, luxury interiors |
Introduction: Tulipwood and Mahogany in Decorative Veneers
Tulipwood and Mahogany are popular choices in decorative veneers due to their distinct grain patterns and rich color tones, offering unique aesthetic appeal in interior design. Tulipwood features a striking, streaked appearance with hues ranging from golden brown to reddish pink, while Mahogany is prized for its deep, reddish-brown color and smooth, fine grain. Both woods provide durability and elegance, making them ideal for high-end furniture, cabinetry, and paneling applications.
Botanical Origins and Species Overview
Tulipwood, derived primarily from the Brazilian species Dalbergia decipularis, is valued for its vibrant, reddish-gold hues and intricate grain patterns, making it a popular choice for decorative veneer. Mahogany, sourced mainly from several species including Swietenia macrophylla (Honduran mahogany) and Khaya spp. (African mahogany), offers deep reddish-brown tones and a fine, straight grain that enhance luxury veneers. Both woods belong to the Fabaceae family for tulipwood and Meliaceae family for mahogany, contributing distinct botanical characteristics that influence their texture, durability, and aesthetic appeal in veneering applications.
Color and Grain Characteristics
Tulipwood features a vibrant range of colors from bright yellow to deep orange with striking reddish streaks, offering a bold and dynamic appearance in decorative veneer applications. Its grain is typically fine and straight but can also appear wavy or interlocked, providing a unique texture that enhances visual interest. Mahogany, in contrast, displays a rich reddish-brown to deep mahogany hue with a consistent fine grain pattern, prized for its smooth texture and elegant, uniform aesthetic in high-end veneers.
Workability and Machining Properties
Tulipwood offers excellent workability with a fine, even texture and a straight grain, making it ideal for intricate decorative veneer applications. Mahogany also exhibits superior machining properties, including smooth cutting and minimal tear-out, but its interlocked grain can sometimes pose challenges during fine detailing. Both woods respond well to sanding and finishing, but Tulipwood's consistent grain pattern generally allows for more precise and clean machining in veneer production.
Durability and Longevity
Tulipwood offers moderate durability with good resistance to wear, making it suitable for decorative veneer applications that demand aesthetic appeal and consistent performance. Mahogany is renowned for its exceptional hardness and natural resistance to decay, providing superior longevity and enduring beauty in high-traffic or environmentally challenging conditions. Both woods deliver distinctive grains and tones, but mahogany generally outperforms tulipwood in durability for long-term veneer projects.
Cost and Availability
Tulipwood offers a more affordable option for decorative veneer compared to mahogany, which tends to be pricier due to its rich color and durability. Availability of tulipwood is generally higher as it is sourced from faster-growing trees, making it a sustainable choice for large projects. Mahogany's limited supply and slower growth rates contribute to its higher cost and less consistent availability in the veneer market.
Environmental Considerations
Tulipwood offers a more sustainable option for decorative veneer due to its faster growth rate and availability from managed plantations, reducing pressure on natural forests. Mahogany, often sourced from slower-growing tropical hardwoods, faces challenges related to deforestation and illegal logging, impacting biodiversity and carbon sequestration negatively. Choosing certified tulipwood veneers can support environmentally responsible woodworking practices while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Popular Applications in Veneering
Tulipwood and mahogany are both favored for decorative veneer due to their distinctive grain patterns and color variations, enhancing the visual appeal of furniture and cabinetry. Tulipwood's vibrant reddish-orange hues and fine, straight grain make it popular in luxury veneers for tabletops, paneling, and instrument cases. Mahogany's rich, deep reddish-brown tones and smooth texture are widely used in high-end veneering for doors, wall panels, and classic furniture pieces, offering durability and timeless elegance.
Aesthetic Appeal: Style and Design Trends
Tulipwood offers a vibrant, reddish-pink hue with subtle veining that enhances contemporary decorative veneer designs, creating bold, eye-catching surfaces. Mahogany provides a rich, deep brown color with a fine, straight grain that aligns with classic and traditional styles, adding warmth and elegance to interiors. Current design trends favor Tulipwood for modern, eclectic aesthetics while Mahogany remains a preferred choice for timeless, sophisticated decor.
Choosing Between Tulipwood and Mahogany
Tulipwood offers a vibrant, golden-yellow hue with distinctive grain patterns, making it ideal for bold decorative veneer applications, while mahogany provides a rich, reddish-brown color with a smoother, more uniform grain ideal for classic, high-end finishes. Tulipwood's hardness and durability suit projects requiring resilience, whereas mahogany's stability and workability make it preferable for intricate veneer designs. Selecting between tulipwood and mahogany hinges on desired aesthetic impact, project durability needs, and compatibility with existing decor styles.
Infographic: Tulipwood vs Mahogany for Decorative Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com