Sycamore offers a fine, consistent grain and light color ideal for smooth finishes in furniture making, while Hemlock features a straight grain with a slightly coarse texture and is valued for its strength and affordability. Sycamore provides better workability and aesthetic appeal, whereas Hemlock is preferred for structural pieces where durability is essential.
Table of Comparison
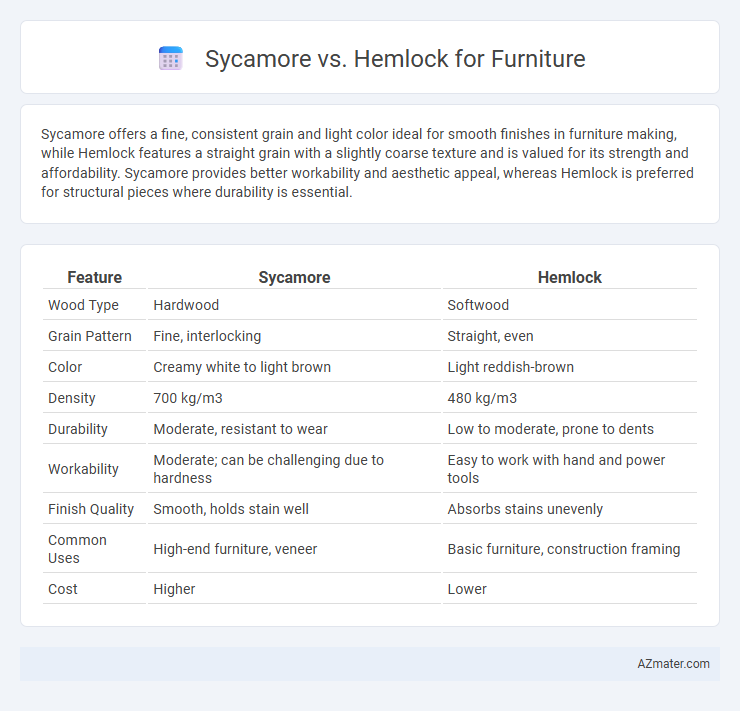
| Feature | Sycamore | Hemlock |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Softwood |
| Grain Pattern | Fine, interlocking | Straight, even |
| Color | Creamy white to light brown | Light reddish-brown |
| Density | 700 kg/m3 | 480 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to wear | Low to moderate, prone to dents |
| Workability | Moderate; can be challenging due to hardness | Easy to work with hand and power tools |
| Finish Quality | Smooth, holds stain well | Absorbs stains unevenly |
| Common Uses | High-end furniture, veneer | Basic furniture, construction framing |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction: Sycamore vs Hemlock in Furniture Making
Sycamore wood offers a fine, even grain and light color ideal for crafting elegant furniture with a smooth finish, while hemlock provides a softer texture and reddish-brown hue favored for rustic and durable pieces. Sycamore's hardness and resistance to warping enhance the longevity of tables, chairs, and cabinetry, contrasting with hemlock's workability and natural resistance to decay suit structural furniture components. Selecting between sycamore and hemlock depends on the desired aesthetic, durability, and application in furniture making.
Botanical Overview: Sycamore and Hemlock Trees
Sycamore trees (Platanus occidentalis) are large deciduous hardwoods known for their distinctive mottled bark and broad, palmate leaves, commonly found in eastern North America. Hemlock trees (Tsuga canadensis) are evergreen conifers characterized by their fine, flat needles and slender, pliable branches, native to the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. The wood of sycamore is dense and resistant to splitting, ideal for furniture requiring smooth finishes, while hemlock's softer, lighter wood is favored for structural framing rather than fine woodworking.
Wood Appearance and Grain Patterns
Sycamore wood features a light, creamy appearance with subtle wavy grain patterns that create a smooth, refined texture ideal for contemporary furniture designs. Hemlock presents a more uniform, straight grain with a reddish-brown hue, offering a classic and rustic aesthetic suited for traditional or cabin-style furnishings. The contrasting grain structures and color tones of Sycamore and Hemlock significantly influence the visual impact and style of crafted furniture pieces.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Sycamore wood offers moderate durability with a fine, consistent grain that is resistant to warping, making it suitable for furniture that demands smooth finishes and light structural use. Hemlock exhibits greater strength and hardness, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity and resistance to dents, which makes it ideal for heavier furniture pieces requiring long-term durability. While Sycamore excels in aesthetic appeal, Hemlock's superior mechanical properties ensure better performance under stress and wear.
Workability and Machinability
Sycamore wood exhibits excellent workability due to its fine, even texture and moderate hardness, making it easy to shape, carve, and finish with minimal splintering. Hemlock, while moderately hard, tends to have lower machinability because of its coarse grain and occasional resin pockets, which can blunt cutting tools faster. For furniture requiring precision and smooth surfaces, sycamore outperforms hemlock in both ease of machining and the quality of the finished product.
Resistance to Decay and Insect Damage
Sycamore wood exhibits moderate resistance to decay and insect damage, making it less durable in outdoor or high-moisture environments compared to Hemlock. Hemlock wood has a higher natural resistance to decay and insects, which enhances its longevity in furniture exposed to variable conditions. Choosing Hemlock for furniture ensures better durability and reduced maintenance over time.
Finishing Qualities: Staining and Polishing
Sycamore wood exhibits excellent finishing qualities, absorbing stains evenly to reveal its fine, uniform grain, making it ideal for achieving smooth, polished surfaces in furniture. Hemlock, while less porous, accepts stains moderately well but may require a wood conditioner to avoid blotchy finishes, resulting in a more rustic, matte appearance after polishing. Both woods respond effectively to polishing, with Sycamore producing a glassy sheen and Hemlock offering a softer luster, influencing the final aesthetic based on the furniture style.
Cost and Availability
Sycamore wood generally offers a moderate cost with good availability in North American markets, making it a practical choice for furniture projects requiring durability and a fine, even grain. Hemlock, often more affordable due to its faster growth and widespread presence, is readily accessible but is softer and less durable, which can impact furniture longevity. Choosing between sycamore and hemlock hinges on balancing budget constraints with the desired quality and availability in local lumber suppliers.
Recommended Furniture Applications
Sycamore's fine grain and light color make it ideal for cabinetry, tabletops, and decorative furniture pieces requiring smooth finishes and intricate detailing. Hemlock's strength and straight grain pattern suit structural furniture elements, framing, and rustic-style furniture where durability and resistance to warping are essential. Both woods are favored for indoor applications but sycamore is preferred for visible surfaces while hemlock excels in supportive components.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sycamore wood is a fast-growing hardwood that offers a renewable option for furniture production, with lower carbon footprints due to its rapid growth cycle. Hemlock, a softwood, is abundant in North American forests and is often sourced from sustainably managed plantations, contributing to reduced environmental impact. Both woods support eco-friendly furniture making, but Sycamore's quicker regeneration rate may offer greater long-term sustainability benefits.
Infographic: Sycamore vs Hemlock for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com