Sapele timber offers superior durability, rich reddish-brown color, and fine grain, making it ideal for high-quality furniture and flooring. Pine is softer, lighter, and more affordable, preferred for construction and lightweight applications but less resistant to wear and moisture.
Table of Comparison
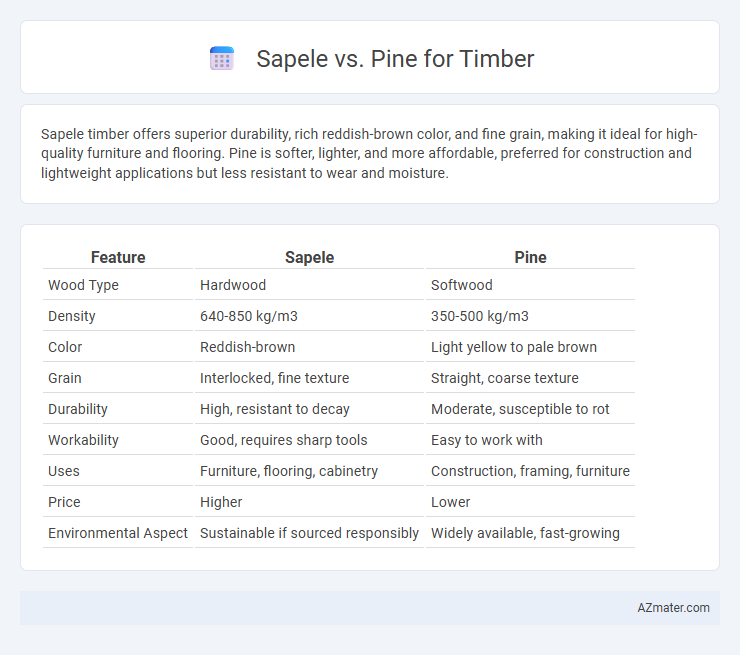
| Feature | Sapele | Pine |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Softwood |
| Density | 640-850 kg/m3 | 350-500 kg/m3 |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Light yellow to pale brown |
| Grain | Interlocked, fine texture | Straight, coarse texture |
| Durability | High, resistant to decay | Moderate, susceptible to rot |
| Workability | Good, requires sharp tools | Easy to work with |
| Uses | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry | Construction, framing, furniture |
| Price | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Aspect | Sustainable if sourced responsibly | Widely available, fast-growing |
Introduction to Sapele and Pine Timber
Sapele timber, derived from the Entandrophragma cylindricum tree native to West Africa, is renowned for its rich reddish-brown color and interlocking grain, making it highly valued in high-end furniture and cabinetry. Pine timber, primarily from species like Pinus sylvestris and Pinus strobus, is widely harvested across Europe and North America for its light color, straight grain, and versatility in construction and woodworking projects. Both timbers differ significantly in durability, workability, and aesthetic properties, influencing their applications in the timber industry.
Botanical Differences: Sapele vs Pine
Sapele (Entandrophragma cylindricum) is a tropical hardwood native to West Africa, characterized by dense, interlocked grain and rich reddish-brown coloration, while Pine (genus Pinus) is a softwood commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere with a lighter color and distinct growth rings. The botanical cell structure of Sapele features parenchyma cells arranged in bands, contributing to its durability and fine finish, whereas Pine exhibits resin canals within its tracheids, influencing its knotty texture and susceptibility to sap exudation. These botanical differences impact the wood's physical properties, making Sapele suitable for high-end furniture and flooring, while Pine is preferred for construction and paneling due to its ease of workability and faster growth rate.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Sapele timber features a rich reddish-brown color with a lustrous, interlocked grain that creates a striking ribbon-like pattern, making it highly desirable for decorative woodworking and high-end furniture. Pine timber displays a lighter, pale yellow to creamy white hue with a straight, uniform grain and distinctive knots, offering a rustic and natural aesthetic ideal for casual and country-style interiors. The deep, complex grain of Sapele contrasts with Pine's simpler, softer grain, influencing choice based on visual appeal and design requirements.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Sapele wood offers superior durability with high resistance to rot, fungi, and insects, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-use applications compared to Pine, which is more prone to decay and damage. In terms of strength, Sapele has a higher Janka hardness rating around 1,410 lbf, whereas Pine typically ranges between 350 to 870 lbf, indicating that Sapele is significantly harder and more impact-resistant. The dense grain structure of Sapele enhances its load-bearing capacity and structural integrity, outperforming the softer and lighter Pine species in demanding environments.
Workability and Machining Properties
Sapele timber offers superior workability due to its fine, interlocking grain, which produces smooth finishes without excessive splintering, making it ideal for detailed joinery and fine furniture. Pine is easier to machine overall because of its softer texture but can be prone to tear-out and requires careful handling to avoid dents and deformities. Both woods respond well to common woodworking tools, but Sapele's higher density demands sharper blades and slower feed rates for optimal machining results.
Resistance to Decay and Insects
Sapele timber exhibits superior resistance to decay and insect attack compared to Pine, making it a preferred choice for outdoor and high-moisture applications. The natural oils and dense grain structure in Sapele enhance its durability against fungal decay and termites, whereas Pine, particularly untreated varieties, is more susceptible to rot and insect damage. Proper treatment can improve Pine's resistance, but Sapele remains inherently more resistant for long-term structural use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sapele timber is often considered more sustainable than pine due to its slower growth rate and status as a tropical hardwood, which requires responsible forest management to prevent deforestation. Pine, being a fast-growing softwood, is typically sourced from managed plantations that support carbon sequestration and reduce pressure on natural forests. Both materials' environmental impacts heavily depend on certification standards such as FSC or PEFC that ensure sustainable harvesting practices and forest regeneration.
Price and Availability Considerations
Sapele timber generally commands a higher price due to its premium quality and rich, reddish-brown appearance, making it less widely available compared to pine. Pine is more commonly found and is significantly more affordable, benefiting from faster growth rates and abundant supply in many regions. Price sensitivity and project scale often drive the choice between Sapele's luxury cost and Pine's economical availability.
Best Applications for Sapele vs Pine
Sapele timber is highly valued for its durability and rich reddish-brown color, making it ideal for high-end furniture, cabinetry, and flooring where aesthetic appeal and strength are critical. Pine, being softer and lighter, excels in construction, framing, and interior trim where affordability and ease of workability are prioritized. For applications requiring weather resistance and fine finishing, Sapele outperforms Pine, which is better suited to less demanding environments.
Choosing Between Sapele and Pine: Key Takeaways
Sapele, a hardwood native to West Africa, offers exceptional durability, rich reddish-brown hues, and fine grain, making it ideal for high-end furniture and flooring. Pine, a softwood commonly grown in temperate regions, provides affordability, ease of workability, and a light, natural color suitable for construction and paneling. When choosing between Sapele and Pine, consider project requirements for strength, aesthetic appeal, and budget constraints to select the most appropriate timber.
Infographic: Sapele vs Pine for Timber
 azmater.com
azmater.com