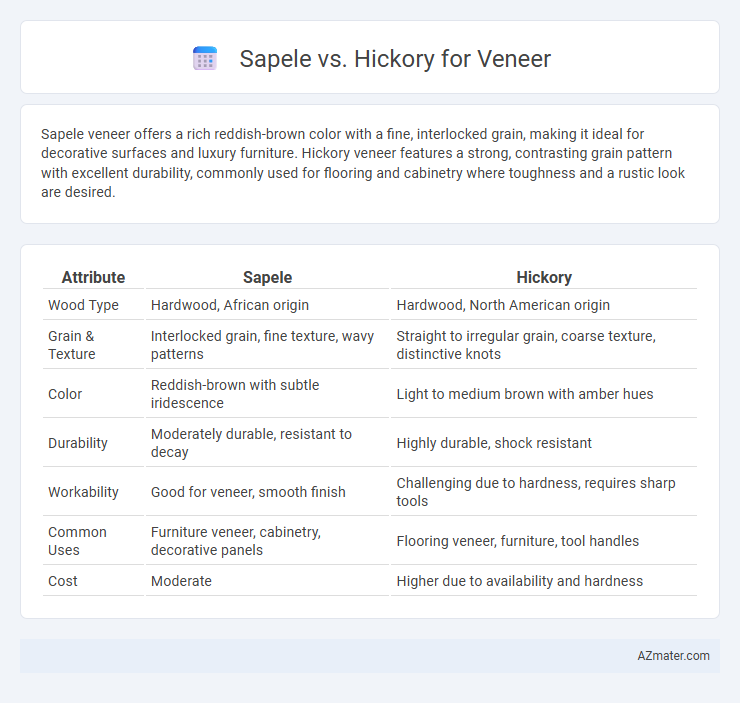
Sapele veneer offers a rich reddish-brown color with a fine, interlocked grain, making it ideal for decorative surfaces and luxury furniture. Hickory veneer features a strong, contrasting grain pattern with excellent durability, commonly used for flooring and cabinetry where toughness and a rustic look are desired.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Sapele | Hickory |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood, African origin | Hardwood, North American origin |
| Grain & Texture | Interlocked grain, fine texture, wavy patterns | Straight to irregular grain, coarse texture, distinctive knots |
| Color | Reddish-brown with subtle iridescence | Light to medium brown with amber hues |
| Durability | Moderately durable, resistant to decay | Highly durable, shock resistant |
| Workability | Good for veneer, smooth finish | Challenging due to hardness, requires sharp tools |
| Common Uses | Furniture veneer, cabinetry, decorative panels | Flooring veneer, furniture, tool handles |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to availability and hardness |
Introduction to Sapele and Hickory Veneers
Sapele veneer, derived from the African Sapele tree, features a rich reddish-brown hue with a pronounced interlocking grain pattern, offering exceptional durability and a smooth finish ideal for fine furniture and cabinetry. Hickory veneer, sourced from American hickory trees, displays a lighter cream to brown color with a highly distinctive, contrasting grain pattern known for robustness and shock resistance, making it suitable for flooring and high-impact surfaces. Both veneers present unique aesthetic and structural qualities, with Sapele favored for elegance and warmth, while Hickory is prized for strength and rustic appeal.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Sapele (Entandrophragma cylindricum) is a hardwood native to West Africa, primarily found in countries like Nigeria, Ghana, and the Democratic Republic of Congo, thriving in tropical rainforests. Hickory (Carya spp.), belonging to the Juglandaceae family, grows predominantly in North America, especially in the eastern United States and parts of Canada, favoring temperate forest regions. The distinct botanical origins and growth climates of Sapele and Hickory influence their grain patterns, density, and suitability for veneer applications.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Sapele veneer exhibits a rich, reddish-brown hue with a distinctive interlocked grain pattern that creates a shimmering effect under light, ideal for luxurious cabinetry and furniture. Hickory veneer displays a lighter color palette ranging from creamy white to medium brown, featuring bold and varied grain patterns with prominent knots and streaks that enhance rustic and dynamic designs. Both woods offer unique aesthetics, with Sapele prized for elegance and uniformity, while Hickory attracts those seeking a rugged and natural appearance.
Color Variations and Consistency
Sapele veneer features a rich, reddish-brown color with subtle interlocking grain patterns that create a shimmering effect, offering moderate color variation across sheets. Hickory veneer displays a wide range of color from pale cream to dark brown with prominent streaks, resulting in more pronounced color variation and a rustic appearance. Consistency in Sapele veneer is higher due to its uniform grain and coloration, while Hickory's natural color differences provide a distinctive, varied aesthetic ideal for dynamic design projects.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Sapele veneer exhibits moderate hardness with a Janka rating around 1,410 lbf, offering good resistance to wear and denting, making it suitable for decorative interiors. Hickory veneer is significantly harder, boasting a Janka rating of approximately 1,820 lbf, which ensures superior durability and impact resistance for high-traffic areas or furniture subjected to frequent use. The increased hardness of Hickory makes it more resistant to scratches and dents, while Sapele provides a balance of hardness and stability with a rich, reddish-brown appearance.
Workability and Machining Properties
Sapele veneer offers excellent workability due to its fine, even texture and moderate hardness, allowing for smooth slicing and minimal blade wear during machining processes. Hickory veneer, known for its exceptional toughness and density, can be more challenging to machine, causing increased tool dulling and requiring sharper blades. Both woods respond well to sanding and finishing, but Sapele's consistent grain pattern makes it preferable for detailed veneer applications where precision is critical.
Cost and Availability
Sapele veneer is generally more affordable and widely available due to its abundant supply and popularity in furniture and cabinetry, making it a cost-effective choice. Hickory veneer tends to be pricier and less readily available because it is harvested in smaller quantities and prized for its distinctive grain and durability. Choosing between Sapele and Hickory for veneer depends on budget constraints and the desired aesthetic impact.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sapele veneer is sourced from West African mahogany species that are generally harvested under regulated forestry practices aimed at reducing deforestation impact. Hickory veneer, derived primarily from North American hardwoods, benefits from sustainable forest management with faster growing cycles and widespread reforestation efforts. Both veneers offer eco-friendly options, but Hickory's regional sourcing and renewable harvesting methods often result in a lower carbon footprint compared to imported Sapele.
Best Uses in Interior Design
Sapele veneer offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with a fine grain, making it ideal for elegant cabinetry, wall paneling, and furniture that demands a sophisticated African hardwood aesthetic. Hickory veneer features a varied grain pattern and lighter color palette, best suited for rustic or country-style interiors where durability and a bold wood texture enhance flooring, cabinetry, and decorative accents. Both veneers provide excellent dimensional stability, but Sapele is preferred for high-end, refined designs while Hickory supports more casual, robust interior elements.
Sapele vs Hickory Veneer: Which to Choose?
Sapele veneer offers a rich, reddish-brown color with fine, interlocked grain patterns, ideal for elegant furniture and cabinetry, whereas Hickory veneer features a lighter, creamy to reddish-brown hue with prominent grain variations, providing a rustic and durable aesthetic. Sapele's density and natural luster make it more resistant to wear and suitable for high-end interior applications, while Hickory's toughness and striking contrast in wood grain are preferred for durable, country-style designs. Choosing between Sapele and Hickory veneer depends on the desired visual appeal and functional requirements, with Sapele delivering a smooth, sophisticated finish and Hickory emphasizing ruggedness and dynamic texture.
Infographic: Sapele vs Hickory for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com