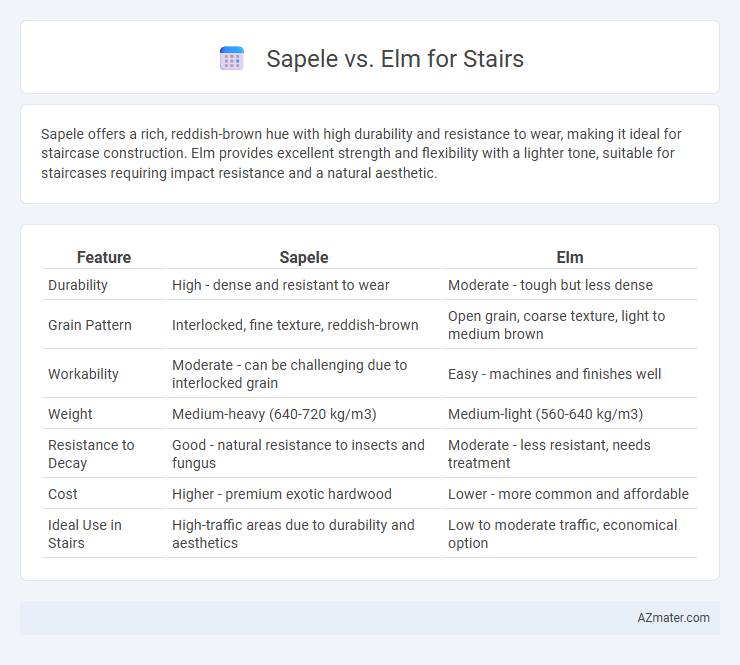
Sapele offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with high durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for staircase construction. Elm provides excellent strength and flexibility with a lighter tone, suitable for staircases requiring impact resistance and a natural aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sapele | Elm |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High - dense and resistant to wear | Moderate - tough but less dense |
| Grain Pattern | Interlocked, fine texture, reddish-brown | Open grain, coarse texture, light to medium brown |
| Workability | Moderate - can be challenging due to interlocked grain | Easy - machines and finishes well |
| Weight | Medium-heavy (640-720 kg/m3) | Medium-light (560-640 kg/m3) |
| Resistance to Decay | Good - natural resistance to insects and fungus | Moderate - less resistant, needs treatment |
| Cost | Higher - premium exotic hardwood | Lower - more common and affordable |
| Ideal Use in Stairs | High-traffic areas due to durability and aesthetics | Low to moderate traffic, economical option |
Introduction to Sapele and Elm for Stairs
Sapele, a tropical hardwood from West Africa, is prized for its rich reddish-brown color, durability, and fine grain, making it an excellent choice for staircases that require both strength and aesthetic appeal. Elm, known for its interlocking grain and natural resistance to splitting, offers a lighter, warm tone with flexibility that enhances the structural integrity of stair components. Both woods provide unique qualities for stairs, with Sapele excelling in hardness and visual elegance, while Elm delivers resilience and distinctive grain patterns ideal for traditional and rustic stair designs.
Wood Characteristics: Sapele vs Elm
Sapele wood is dense and durable with a fine, interlocked grain that offers excellent resistance to wear, making it ideal for stairs requiring long-lasting strength and a polished appearance. Elm features a distinctive interlocking grain as well, with moderate hardness and good shock resistance, providing natural flexibility and durability suitable for staircases exposed to frequent use. Both woods present rich textures and warm hues, but Sapele's higher density and natural luster often result in a more refined and resilient stair surface compared to Elm.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Sapele wood offers high durability and resistance to wear, making it an excellent choice for staircases subject to heavy foot traffic, with a Janka hardness rating of approximately 1,410 lbf. Elm wood, while also durable and tough, has a slightly lower Janka hardness around 830-1,150 lbf depending on the species, and tends to be more flexible, providing better shock resistance but less overall hardness than Sapele. For stair strength and longevity, Sapele outperforms Elm due to its denser grain structure and superior resistance to dents and scratches.
Aesthetic Appeal and Grain Patterns
Sapele wood offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with a fine, interlocking grain that creates a lustrous, ribbon-like pattern, enhancing the stair's visual depth and warmth. Elm displays a lighter, golden tone with a distinctive, wavy grain that provides a more rustic yet elegant appearance, showcasing prominent medullary rays and natural texture. Both woods deliver unique aesthetic appeals, with Sapele favored for its luxurious sheen and Elm prized for its organic, textured grain patterns.
Cost and Availability
Sapele offers a rich, reddish-brown tone with moderate cost and high availability, making it a popular choice for staircases in regions like West Africa. Elm, known for its durability and attractive grain pattern, tends to be less expensive but has variable availability depending on the region, primarily sourced from North America and Europe. When comparing cost and availability, Sapele is generally more accessible and consistent in price, while Elm may require sourcing efforts and fluctuates in price due to supply constraints.
Workability for Stair Construction
Sapele offers excellent workability for stair construction due to its moderate density and fine, interlocked grain, allowing for smooth cutting, shaping, and sanding without significant splintering. Elm, while also workable, has a more open grain structure and can be prone to interlocking fibers that cause some difficulty during detailed carving or shaping, requiring sharper tools and more careful handling. For stair components needing precise joinery and a smooth finish, Sapele generally provides more consistent workability compared to Elm.
Finishing and Maintenance Requirements
Sapele offers a rich, reddish-brown hue with a natural luster that deepens over time, requiring regular polishing and occasional oiling to maintain its vibrant finish and resist wear. Elm features a lighter, more textured appearance with prominent grain patterns, typically finished with clear varnish or polyurethane to protect against moisture and scratches while needing less frequent upkeep. Both woods demand periodic cleaning and moisture control to prevent warping, but Sapele's denser composition may provide slightly enhanced durability for high-traffic stair areas.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sapele wood, sourced from West African tropical forests, offers moderate sustainability but often faces scrutiny due to deforestation concerns and slow regrowth rates compared to Elm, which is native to temperate regions with generally better-managed and sustainable forestry practices. Elm trees have a lower environmental impact as they grow relatively quickly and are often harvested from certified sustainable forests, promoting biodiversity and reducing carbon footprints. Choosing Elm for stairs supports eco-friendly construction through responsible sourcing and enhanced durability, while Sapele's exotic status may contribute to higher transportation emissions and habitat disruption.
Best Applications: Where Each Wood Excels
Sapele excels in stair applications requiring rich, reddish-brown color with interlocked grain patterns that resist wear and provide excellent durability for high-traffic areas. Elm is best suited for stairs needing flexibility and shock resistance, thanks to its interlocking grain and natural resilience, making it ideal for curved stair parts and steps prone to heavy impact. Both woods offer stability, but Sapele is preferred for a polished, exotic look, while Elm is favored for its toughness and ability to absorb stress.
Final Recommendation: Sapele or Elm for Stairs?
Sapele offers superior durability and a rich, reddish-brown color that enhances staircase aesthetics and withstands heavy foot traffic. Elm provides excellent stability and flexibility with a lighter tone, ideal for traditional or rustic designs but may require more maintenance over time. For a long-lasting, visually striking staircase, Sapele is generally the preferred choice due to its hardness and resistance to wear.
Infographic: Sapele vs Elm for Stair
 azmater.com
azmater.com