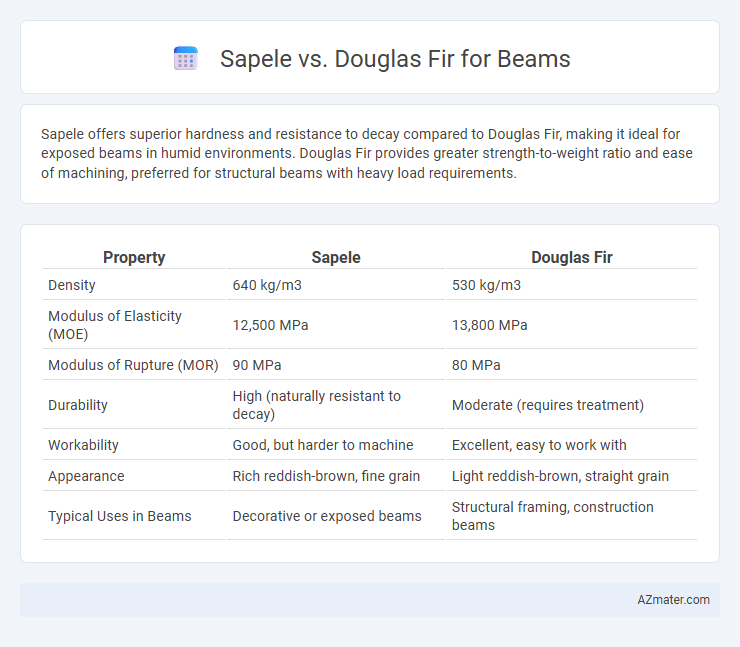
Sapele offers superior hardness and resistance to decay compared to Douglas Fir, making it ideal for exposed beams in humid environments. Douglas Fir provides greater strength-to-weight ratio and ease of machining, preferred for structural beams with heavy load requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sapele | Douglas Fir |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 640 kg/m3 | 530 kg/m3 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (MOE) | 12,500 MPa | 13,800 MPa |
| Modulus of Rupture (MOR) | 90 MPa | 80 MPa |
| Durability | High (naturally resistant to decay) | Moderate (requires treatment) |
| Workability | Good, but harder to machine | Excellent, easy to work with |
| Appearance | Rich reddish-brown, fine grain | Light reddish-brown, straight grain |
| Typical Uses in Beams | Decorative or exposed beams | Structural framing, construction beams |
Introduction to Sapele and Douglas Fir
Sapele is an African hardwood prized for its rich reddish-brown color, high durability, and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for structural beams in both indoor and outdoor applications. Douglas Fir, a softwood native to North America, offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and dimensional stability, commonly used in construction for its reliable load-bearing capacity and ease of machining. Selecting between Sapele and Douglas Fir for beams depends on factors such as aesthetic preference, environmental exposure, and structural requirements.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Sapele, scientifically classified as Entandrophragma cylindricum, is native to West Africa, predominantly thriving in tropical rainforests across countries like Nigeria, Ghana, and Cameroon. Douglas Fir, or Pseudotsuga menziesii, originates from the temperate forests of western North America, spanning regions from British Columbia in Canada to California in the United States. The distinct climatic and ecological conditions of these growth regions influence the wood density and grain patterns, making Sapele denser and more uniform compared to the generally stronger but more variable Douglas Fir.
Physical Appearance and Grain Patterns
Sapele features a rich reddish-brown color with a subtle interlocking grain pattern that creates a ribbon-like effect, making it visually striking for beams. Douglas Fir exhibits a pale yellow to light brown hue with a straight, even grain and prominent growth rings, giving beams a classic, rustic appearance. The distinct grain texture of Sapele offers a more decorative look, while Douglas Fir provides a cleaner, more uniform aesthetic ideal for structural beams.
Density and Structural Strength
Sapele has a density of approximately 640 kg/m3, providing good strength and durability for beam applications, while Douglas Fir is slightly lighter with a density around 530 kg/m3 but is renowned for its superior structural strength and stiffness. Douglas Fir's high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for load-bearing beams in construction, whereas Sapele offers better resistance to wear and moisture due to its denser hardwood properties. Choosing between the two depends on the specific structural load requirements and environmental exposure of the beam installation.
Durability and Resistance to Decay
Sapele wood offers excellent durability and moderate resistance to decay, making it suitable for indoor beams where moisture exposure is limited. Douglas Fir, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, exhibits lower natural decay resistance but performs well when treated for outdoor use. Choosing between Sapele and Douglas Fir depends on environmental conditions and the necessity for natural durability versus engineered protection.
Workability and Ease of Machining
Sapele wood offers excellent workability with its fine grain and stability, making it easy to plane, sand, and shape for beams. Douglas Fir, known for its straight grain and medium hardness, machines efficiently with minimal dulling of tools, allowing for smooth cuts and consistent shaping. Both woods are well-suited for beam construction, but Douglas Fir's lighter weight often translates to easier handling during machining processes.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Sapele offers a mid-range cost option for beams, typically priced higher than Douglas Fir but lower than exotic hardwoods, making it a cost-effective choice for projects prioritizing durability and aesthetic appeal. Douglas Fir is widely available in North America, resulting in lower prices and greater accessibility, which benefits large-scale construction requiring consistent supply. Availability of Sapele may be limited outside West Africa, potentially increasing shipping costs and lead times compared to the abundant supply and competitive pricing of Douglas Fir in local markets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sapele wood is a hardwood harvested primarily from West African tropical forests, raising concerns about deforestation and habitat loss due to inconsistent logging regulations. Douglas Fir, sourced mainly from sustainably managed forests in North America, offers a more environmentally responsible option with certifications like FSC supporting its renewable use. Choosing Douglas Fir for beams typically results in lower carbon footprints and better long-term sustainability compared to Sapele, which faces challenges from overexploitation and slower regrowth rates.
Best Applications in Beam Construction
Sapele, known for its high durability and rich reddish-brown color, is ideal for exposed beam construction where aesthetic appeal and resistance to decay are crucial, such as in outdoor pergolas and decorative interiors. Douglas Fir offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stability, making it the preferred choice for structural beams in heavy load-bearing applications like residential framing and large roof trusses. Both woods excel in beam construction, with Sapele favored for finish and durability in visible settings, while Douglas Fir is chosen for its strength and reliability in core structural components.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Beam Material
Sapele offers exceptional durability and rich aesthetics, making it ideal for high-end architectural beams requiring strength and visual appeal. Douglas Fir provides a cost-effective, lightweight option with reliable structural performance, suitable for general construction and load-bearing applications. Selecting between Sapele and Douglas Fir depends on project budget, desired appearance, and specific strength requirements for optimal beam material choice.
Infographic: Sapele vs Douglas Fir for Beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com