Rubberwood panels offer durability and resistance to warping, making them suitable for furniture and cabinetry. Bamboo panels provide superior sustainability and flexibility, ideal for eco-friendly construction and decorative applications.
Table of Comparison
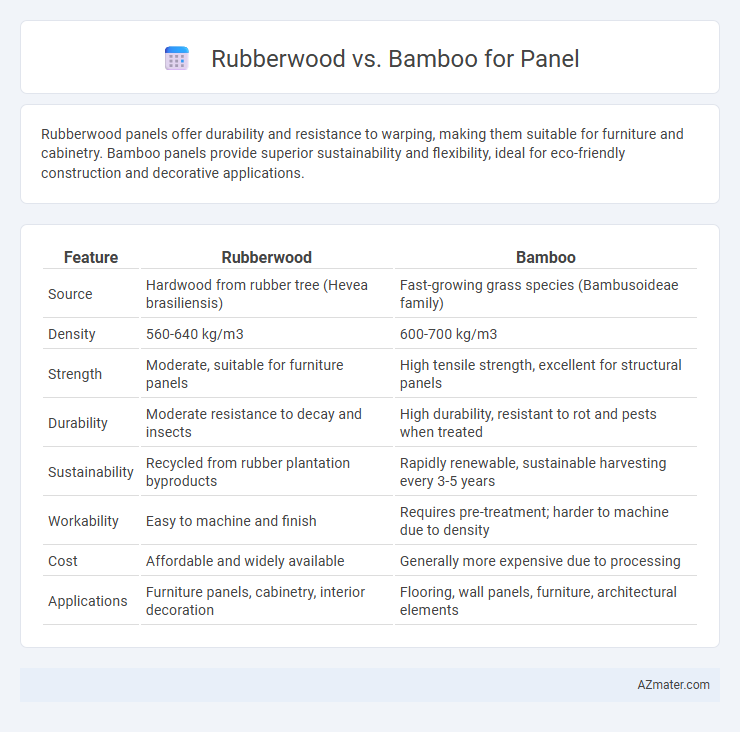
| Feature | Rubberwood | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hardwood from rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) | Fast-growing grass species (Bambusoideae family) |
| Density | 560-640 kg/m3 | 600-700 kg/m3 |
| Strength | Moderate, suitable for furniture panels | High tensile strength, excellent for structural panels |
| Durability | Moderate resistance to decay and insects | High durability, resistant to rot and pests when treated |
| Sustainability | Recycled from rubber plantation byproducts | Rapidly renewable, sustainable harvesting every 3-5 years |
| Workability | Easy to machine and finish | Requires pre-treatment; harder to machine due to density |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available | Generally more expensive due to processing |
| Applications | Furniture panels, cabinetry, interior decoration | Flooring, wall panels, furniture, architectural elements |
Introduction to Rubberwood and Bamboo Panels
Rubberwood panels, derived from the Hevea brasiliensis tree, offer a dense, durable surface ideal for furniture and flooring due to their smooth finish and resistance to warping. Bamboo panels, crafted from fast-growing bamboo grass, provide exceptional strength and sustainability, making them popular for eco-friendly construction and design projects. Both materials feature natural grain patterns and are valued for their renewable sourcing and environmental benefits in panel manufacturing.
Material Source and Sustainability
Rubberwood is derived from the Para rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis), harvested primarily after the latex-producing phase, maximizing the tree's lifecycle and reducing waste. Bamboo, a fast-growing grass native to Asia, regenerates quickly without the need for replanting, making it a highly renewable resource. Both materials offer sustainable alternatives to traditional hardwoods, with rubberwood utilizing plantation byproducts and bamboo offering rapid biomass replenishment.
Physical Properties and Strength Comparison
Rubberwood exhibits a density of approximately 560-640 kg/m3, offering moderate hardness and good dimensional stability, making it suitable for durable panel applications. Bamboo, with its higher tensile strength ranging from 140-230 MPa and density around 600-900 kg/m3, provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent impact resistance. The cellular structure of bamboo delivers enhanced flexibility and resilience compared to rubberwood, influencing panel performance in load-bearing and impact scenarios.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Rubberwood panels have a lower environmental impact due to utilizing plantation byproducts, reducing deforestation and promoting sustainable forestry practices. Bamboo panels demonstrate rapid renewability with fast growth rates, carbon sequestration, and minimal pesticide use but may involve energy-intensive processing. Evaluating lifecycle emissions, resource usage, and ecological footprint reveals bamboo's potential for lower carbon emissions, whereas rubberwood supports circular economy models through forestry waste valorization.
Durability and Longevity
Rubberwood offers moderate durability with resistance to insect damage but is prone to moisture absorption, which can reduce its lifespan in humid conditions. Bamboo panels exhibit superior longevity due to their high density and natural resistance to wear, moisture, and pests, making them ideal for heavy-use environments. Choosing bamboo over rubberwood enhances panel durability significantly, particularly in applications demanding long-term structural integrity.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Options
Rubberwood panels offer a warm, light to medium brown tone with a straight grain pattern, providing a classic and versatile aesthetic suitable for traditional and modern interiors. Bamboo panels, characterized by their smooth texture and distinctive node patterns, present a contemporary and eco-friendly appearance with options ranging from natural light hues to carbonized darker shades. Both materials support diverse design options, but rubberwood allows for easier staining and finishing, while bamboo excels in innovative, sustainable designs with its unique, linear visual appeal.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Rubberwood offers excellent workability with its fine grain and consistent texture, making it easy to cut, sand, and finish, ideal for panel manufacturing. Bamboo panels, known for their hardness and density, require specialized tools and techniques for cutting and joining, which can complicate installation. Rubberwood's moderate density also contributes to easier fastening and attachment during panel installation, compared to the more fibrous structure of bamboo.
Cost and Market Availability
Rubberwood panels generally offer lower costs compared to bamboo due to the abundant supply of rubber trees primarily in Southeast Asia, making them widely available in global markets. Bamboo panels, while often more expensive, benefit from rapid growth rates and increasing demand in sustainable construction, influencing niche availability and premium pricing. Market availability favors rubberwood with established supply chains, whereas bamboo panels remain more specialized but are expanding in eco-friendly product segments.
Common Applications in Panels
Rubberwood panels are commonly used in furniture manufacturing, cabinetry, and interior paneling due to their durability and smooth finish. Bamboo panels are favored for flooring, wall cladding, and decorative partitions because of their sustainability and natural resistance to moisture. Both materials offer eco-friendly solutions but cater to different aesthetic and functional panel applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Rubberwood offers durability and a stable grain, making it ideal for heavy-use panel applications, while bamboo provides exceptional sustainability and natural resistance to moisture. Bamboo's rapid growth and eco-friendly properties favor environmentally conscious projects, whereas rubberwood's strength and ease of finishing suit traditional designs. Selecting the right material depends on balancing durability requirements with environmental impact and aesthetic preferences.
Infographic: Rubberwood vs Bamboo for Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com