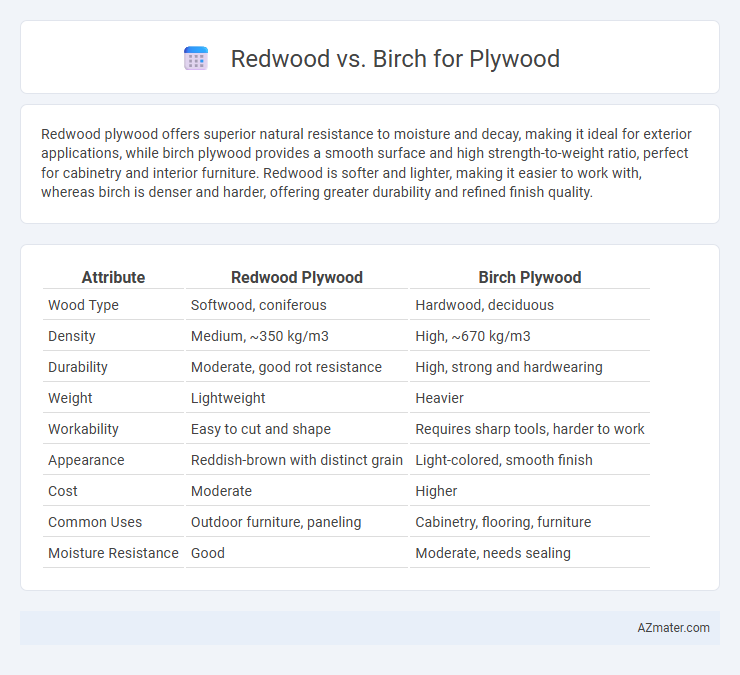
Redwood plywood offers superior natural resistance to moisture and decay, making it ideal for exterior applications, while birch plywood provides a smooth surface and high strength-to-weight ratio, perfect for cabinetry and interior furniture. Redwood is softer and lighter, making it easier to work with, whereas birch is denser and harder, offering greater durability and refined finish quality.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Redwood Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Softwood, coniferous | Hardwood, deciduous |
| Density | Medium, ~350 kg/m3 | High, ~670 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Moderate, good rot resistance | High, strong and hardwearing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Requires sharp tools, harder to work |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown with distinct grain | Light-colored, smooth finish |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Common Uses | Outdoor furniture, paneling | Cabinetry, flooring, furniture |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Moderate, needs sealing |
Introduction to Redwood and Birch Plywood
Redwood plywood is prized for its natural resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications. Birch plywood features a dense, fine grain and offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio, often used in furniture and cabinetry for its smooth finish and durability. Both woods provide unique advantages: redwood for environmental resilience, birch for structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Origin and Growth Habits of Redwood vs Birch
Redwood, primarily found along the western coast of North America, thrives in the temperate rainforests of California and Oregon, exhibiting rapid vertical growth and extensive root systems that enhance its stability. Birch, native to the cooler climates of the Northern Hemisphere including North America, Europe, and Asia, grows as a deciduous hardwood with moderate height, known for its adaptability to various soil types and fast regeneration after disturbance. The contrasting growth habits influence plywood characteristics, with redwood offering durability and resistance to decay, while birch provides strength and a fine grain suitable for smooth finishes.
Appearance and Grain Characteristics
Redwood plywood features a rich reddish hue and a straight, fine grain pattern, creating an elegant and warm aesthetic ideal for decorative applications. Birch plywood exhibits a light cream color with a smooth, uniform grain, offering a clean and modern look suitable for cabinetry and furniture. The natural grain of birch is generally finer and more consistent, while redwood's grain can display more character and variation, enhancing visual interest in finished projects.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Redwood plywood offers moderate strength and excellent resistance to moisture and decay, making it suitable for outdoor applications where durability is crucial. Birch plywood is renowned for its superior strength, stiffness, and uniform grain structure, providing exceptional load-bearing capacity and resistance to impact. While birch plywood excels in structural uses requiring high strength, redwood plywood is preferred for environments demanding enhanced weather resistance and longevity.
Moisture Resistance and Weather Performance
Redwood plywood offers superior moisture resistance due to its natural oils and tight grain structure, making it highly durable in damp environments. Birch plywood, while strong and dense, is less resistant to moisture and prone to warping or swelling if exposed to sustained wet conditions. For outdoor or high-humidity applications, redwood plywood provides better weather performance and longevity compared to birch.
Workability: Cutting, Sanding, and Finishing
Redwood plywood is easier to cut and sands smoothly due to its softer grain structure, making it ideal for precision woodworking and detailed projects. Birch plywood offers a harder surface, requiring sharper tools for clean cuts, but provides an excellent finish with a fine, even texture that accepts stains and paints uniformly. Both woods work well for finishing, yet Redwood's natural resistance to splintering enhances its appeal for intricate designs, while Birch's durability supports long-lasting, high-quality surfaces.
Common Applications in Construction and Design
Redwood plywood is favored in exterior construction and outdoor furniture due to its natural resistance to decay and insect damage, making it ideal for decks, siding, and garden structures. Birch plywood offers superior strength and a smooth, fine grain, commonly used in interior applications such as cabinetry, flooring, and furniture where a premium finish is desired. Both materials provide unique advantages, with redwood excelling in durability for weather-exposed projects and birch preferred for its aesthetic appeal and machinability in detailed interior design.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Redwood plywood is sourced from naturally rot-resistant trees that grow slower, resulting in stronger carbon sequestration but potentially higher environmental costs due to limited regional availability and longer growth cycles. Birch plywood, often harvested from fast-growing plantations primarily in Northern Europe and Russia, offers a renewable resource with efficient production processes and less habitat disruption. Sustainable forestry certifications, such as FSC or PEFC, are critical in determining the true eco-friendliness of both redwood and birch plywood products, ensuring responsible harvesting and minimal carbon footprint.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Redwood plywood tends to be more expensive than birch plywood due to its limited availability and slower growth rate, making it a premium choice in the market. Birch plywood is widely available and cost-effective, sourced from fast-growing birch trees predominantly found in Northern Europe and North America. The price difference between the two materials reflects the balance of durability and aesthetic appeal versus widespread supply.
Choosing the Best Wood for Your Plywood Project
Redwood plywood offers superior durability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor projects and areas with high humidity. Birch plywood provides a smooth finish with excellent strength and stability, perfect for furniture and cabinetry where appearance and structural integrity are crucial. Choosing between redwood and birch depends on the specific project requirements, balancing environmental exposure and aesthetic preferences.
Infographic: Redwood vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com