Ramin wood offers a lightweight, pale finish ideal for modern handrails, while Walnut provides a dense, durable hardwood with rich, dark tones suited for elegant, high-traffic installations. Walnut's superior strength and natural resistance to wear make it preferable for long-lasting handrail applications.
Table of Comparison
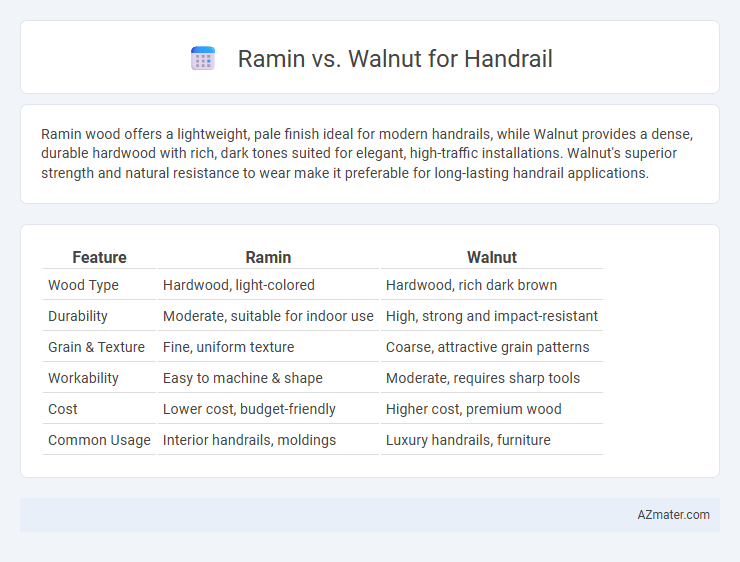
| Feature | Ramin | Walnut |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood, light-colored | Hardwood, rich dark brown |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for indoor use | High, strong and impact-resistant |
| Grain & Texture | Fine, uniform texture | Coarse, attractive grain patterns |
| Workability | Easy to machine & shape | Moderate, requires sharp tools |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium wood |
| Common Usage | Interior handrails, moldings | Luxury handrails, furniture |
Introduction to Ramin and Walnut Wood
Ramin wood, sourced primarily from Southeast Asia, is known for its pale yellow to light brown color and straight grain, making it a popular choice for handrails due to its smooth finish and durability. Walnut wood, prized for its rich, dark brown color and intricate grain patterns, offers superior strength and an elegant aesthetic for high-end handrails. Both woods provide distinct visual appeal and functional qualities; Ramin excels in affordability and workability, while Walnut is favored for its luxurious appearance and robust hardness.
Appearance and Grain Patterns Comparison
Ramin wood displays a uniform light yellow to pale cream color with a fine, straight grain that creates a smooth and consistent appearance ideal for minimalist handrails. Walnut features rich, deep chocolate brown tones with striking, irregular grain patterns and occasional swirls, offering a more dramatic and luxurious look. The subtle, even texture of ramin contrasts sharply with walnut's bold, varied grain, influencing the overall aesthetic and design style of handrails.
Durability and Strength Differences
Ramin wood offers moderate durability and strength, making it suitable for interior handrails with light to medium usage, while walnut provides superior strength and exceptional durability, ideal for high-traffic or outdoor handrail applications. Walnut's dense hardwood structure resists wear, impact, and moisture better than ramin, which can be more prone to denting and decay over time. Choosing walnut ensures a longer-lasting, sturdier handrail with enhanced resistance to structural stress compared to ramin.
Workability: Ramin vs Walnut
Ramin offers superior workability compared to Walnut due to its lightweight texture and straight grain, making it easier to cut, sand, and shape for handrail applications. Walnut's dense and hardwood nature requires more effort and specialized tools during woodworking but provides exceptional durability and a smooth finish. Both woods can be finished beautifully, but Ramin's ease of machining makes it a preferred choice for intricate handrail designs.
Maintenance and Longevity
Ramin wood offers moderate maintenance needs with occasional sealing to prevent moisture damage, while Walnut requires more frequent care due to its natural oils that can wear off over time. Both woods demonstrate good longevity, but Walnut is prized for its durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic handrails. Choosing between Ramin and Walnut depends on balancing maintenance commitment against the desired lifespan and aesthetic of the handrail.
Cost and Availability
Ramin wood, known for its affordability and wide availability, often serves as a cost-effective choice for handrails compared to walnut, which commands a higher price due to its premium quality and limited supply. Walnut's rich color and durability make it a preferred option for high-end projects, but its cost can be two to three times that of Ramin. Availability of Ramin is more consistent in regions with tropical forests, whereas walnut sourcing may require longer lead times depending on regional demand and import restrictions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ramin handrails, sourced primarily from Southeast Asia, often raise concerns due to deforestation and habitat loss linked to unsustainable logging practices. Walnut handrails, commonly harvested from North American forests, tend to have a lower environmental footprint when sourced from certified sustainable forests, such as those managed by the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC). Choosing walnut from sustainable forestry ensures reduced carbon emissions and promotes biodiversity conservation, making it a more eco-friendly option compared to ramin.
Suitability for Handrail Applications
Ramin wood offers a fine, uniform texture and good workability, making it suitable for smooth, intricately carved handrails that require a polished finish. Walnut stands out for its exceptional durability, rich color, and natural resistance to wear, ideal for high-traffic areas where long-lasting strength and aesthetic appeal are crucial. Both woods perform well in handrail applications, but Walnut provides superior robustness, while Ramin excels in detailed craftsmanship and affordability.
Pros and Cons of Ramin Handrails
Ramin handrails offer a smooth texture and light color, making them ideal for modern interior designs and easy customization through staining or painting. They are lightweight and affordable but tend to be softer and less durable compared to walnut, resulting in higher susceptibility to dents and scratches in high-traffic areas. Maintenance requires regular sealing to preserve their appearance, unlike walnut which offers natural hardness and rich color durability with less frequent upkeep.
Pros and Cons of Walnut Handrails
Walnut handrails offer exceptional durability and a rich, dark color that enhances the aesthetic appeal of staircases, making them a premium choice for high-end interior designs. Their natural resistance to wear and moderate hardness ensures longevity, but walnut can be more expensive and may require regular maintenance to prevent scratches and maintain its polished appearance. Compared to ramin, walnut provides superior visual warmth and uniqueness, though it may be less sustainable due to slower growth rates and higher cost.
Infographic: Ramin vs Walnut for Handrail
 azmater.com
azmater.com