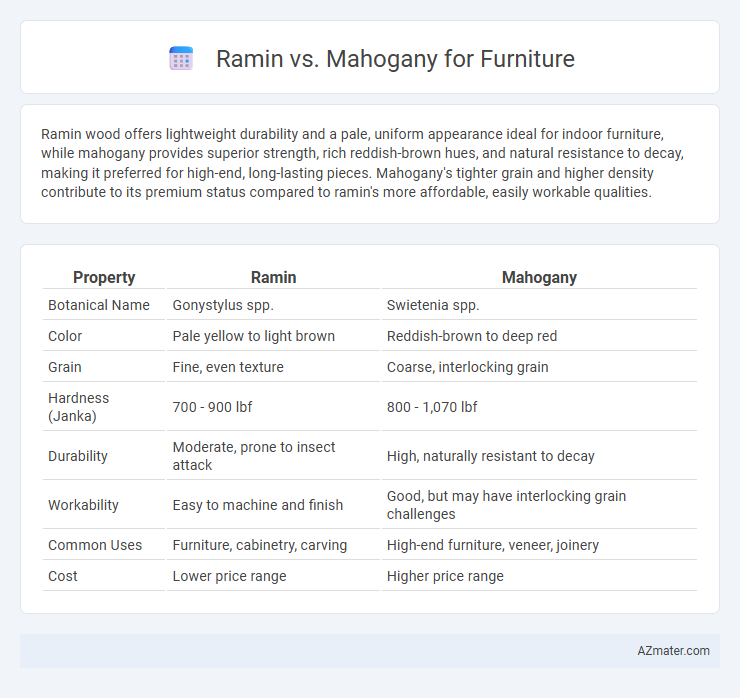
Ramin wood offers lightweight durability and a pale, uniform appearance ideal for indoor furniture, while mahogany provides superior strength, rich reddish-brown hues, and natural resistance to decay, making it preferred for high-end, long-lasting pieces. Mahogany's tighter grain and higher density contribute to its premium status compared to ramin's more affordable, easily workable qualities.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ramin | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Botanical Name | Gonystylus spp. | Swietenia spp. |
| Color | Pale yellow to light brown | Reddish-brown to deep red |
| Grain | Fine, even texture | Coarse, interlocking grain |
| Hardness (Janka) | 700 - 900 lbf | 800 - 1,070 lbf |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to insect attack | High, naturally resistant to decay |
| Workability | Easy to machine and finish | Good, but may have interlocking grain challenges |
| Common Uses | Furniture, cabinetry, carving | High-end furniture, veneer, joinery |
| Cost | Lower price range | Higher price range |
Introduction to Ramin and Mahogany Woods
Ramin is a lightweight, pale-yellow tropical hardwood from Southeast Asia, known for its fine texture and smooth grain, making it ideal for furniture requiring detailed carving and a polished finish. Mahogany, a rich reddish-brown hardwood native to Central and South America, is highly prized for its durability, natural luster, and deep, warm hues, lending itself to high-end furniture and cabinetry. Both woods are valued in the furniture industry, with Ramin favored for intricate designs and Mahogany chosen for its strength and classic elegance.
Origin and Availability of Ramin vs Mahogany
Ramin wood originates primarily from Southeast Asia, specifically Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand, making it widely available in tropical rainforests. Mahogany, sourced predominantly from Central and South America as well as West Africa, is less abundant due to stricter logging regulations and its slower growth rate. The availability of ramin is generally higher and more cost-effective, while mahogany is often considered a premium wood with more limited supply.
Physical Characteristics: Grain, Color, and Texture
Ramin wood features a fine, straight grain with a creamy white to pale yellow color, offering a smooth texture that enhances its workability for furniture making. In contrast, mahogany presents a more pronounced, interlocking grain with rich reddish-brown hues and a slightly coarse texture, contributing to its luxurious appearance and durability. The distinct grain patterns and color depths of mahogany make it ideal for high-end furniture, while ramin's lighter tone and fine texture suit more contemporary, lightweight designs.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Ramin wood offers moderate durability with a Janka hardness rating around 1,210, making it suitable for indoor furniture but less resistant to heavy wear compared to mahogany. Mahogany is renowned for its exceptional strength and durability, featuring a Janka hardness ranging from 800 to 900 in some species but often outperforming Ramin in resistance to rot and insect damage. For long-lasting furniture that withstands both physical stress and environmental factors, mahogany is generally the superior choice over Ramin.
Workability and Ease of Crafting
Ramin wood offers excellent workability due to its uniform texture and fine grain, making it easy to cut, shape, and sand with minimal effort. Mahogany, while also prized for its smooth grain, can be slightly harder to work with because of its density and tendency to chip if not handled carefully. Both woods finish beautifully, but Ramin typically requires less specialized tools, making it a preferred choice for intricate or detailed furniture crafting.
Aesthetic Appeal in Furniture Design
Ramin wood offers a light, creamy yellow tone with a fine, uniform grain that enhances modern furniture designs with a sleek and clean aesthetic. Mahogany features a richer, reddish-brown hue and pronounced grain patterns, lending a warm, classic, and luxurious appeal to high-end furniture pieces. The choice between Ramin and Mahogany greatly influences the overall ambiance of a room, with Ramin favoring minimalist styles and Mahogany suiting traditional or formal interiors.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ramin wood, sourced primarily from Southeast Asia, faces sustainability challenges due to overharvesting and habitat destruction, leading to its listing under CITES Appendix II to regulate trade. Mahogany, especially from responsibly managed plantations or FSC-certified sources, offers a more sustainable alternative with slower growth rates but better forest management practices. Choosing FSC-certified mahogany supports reduced environmental impact through biodiversity preservation and responsible forestry, making it a preferable option for eco-conscious furniture buyers.
Cost and Market Value Analysis
Ramin wood is generally more affordable than mahogany, offering cost-effective solutions for furniture manufacturing without compromising durability. Mahogany commands a higher market value due to its rich color, fine grain, and superior resistance to decay, making it a preferred choice for premium furniture. Market trends indicate that mahogany furniture consistently retains higher resale values compared to ramin, reflecting consumer preference for luxury and long-term investment quality.
Common Uses in Furniture Making
Ramin wood is commonly used for intricate furniture pieces such as carvings, turned objects, and moldings due to its fine grain and smooth texture. Mahogany is favored in high-end furniture making for its rich color, durability, and resistance to rot, often used in cabinetry, tables, and classic style chairs. Both woods offer versatility, but Ramin excels in detailed craftsmanship while Mahogany is preferred for structural and aesthetic luxury components.
Choosing Between Ramin and Mahogany: Which is Best?
Ramin wood offers a lightweight, smooth finish with excellent workability, making it ideal for detailed furniture pieces and indoor use where a pale, uniform appearance is desired. Mahogany, known for its deep reddish-brown color and exceptional durability, provides superior resistance to rot and insect damage, making it the preferred choice for high-end, long-lasting furniture in varying environments. Choosing between Ramin and Mahogany depends on the balance of budget, aesthetic preference, and intended furniture use, with Mahogany favored for luxury and outdoor resilience and Ramin for cost-effective, intricate indoor designs.
Infographic: Ramin vs Mahogany for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com