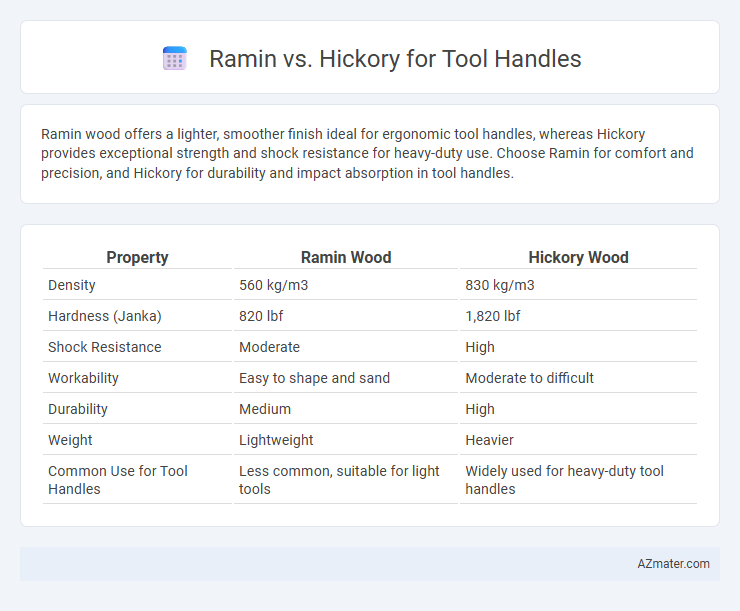
Ramin wood offers a lighter, smoother finish ideal for ergonomic tool handles, whereas Hickory provides exceptional strength and shock resistance for heavy-duty use. Choose Ramin for comfort and precision, and Hickory for durability and impact absorption in tool handles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ramin Wood | Hickory Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 560 kg/m3 | 830 kg/m3 |
| Hardness (Janka) | 820 lbf | 1,820 lbf |
| Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Workability | Easy to shape and sand | Moderate to difficult |
| Durability | Medium | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Common Use for Tool Handles | Less common, suitable for light tools | Widely used for heavy-duty tool handles |
Introduction to Ramin and Hickory Wood
Ramin wood, sourced primarily from Southeast Asian rainforests, is known for its lightweight, smooth texture, and pale yellow to light reddish-brown color, making it suitable for delicate tool handles that require fine detail and moderate strength. Hickory, native to North America, is renowned for its exceptional density, toughness, and shock resistance, ideal for heavy-duty tool handles needing durability and impact absorption. Both woods offer distinct benefits: Ramin excels in ease of shaping and fine finish, while Hickory provides superior strength and long-lasting performance.
Origin and Availability of Ramin and Hickory
Ramin wood originates from Southeast Asia, primarily found in Malaysia and Indonesia, where it grows in tropical rainforests, making it a sustainable option with increasing plantation availability. Hickory, native to the eastern United States, is widely accessible due to extensive hardwood forests and long-standing commercial harvesting practices. The availability of ramin is more regional and regulated due to conservation efforts, while hickory benefits from abundant natural growth and established supply chains in North America.
Physical Properties: Strength and Density
Ramin wood displays moderate strength with a density ranging from 560 to 640 kg/m3, making it suitable for lightweight tool handles. Hickory, known for its exceptional toughness and impact resistance, has a higher density between 770 and 900 kg/m3, providing superior durability under heavy use. The greater density and mechanical strength of Hickory make it the preferred choice for tool handles requiring resilience and longevity.
Durability and Longevity as Tool Handles
Ramin wood is softer and less dense, resulting in moderate durability and shorter lifespan as a tool handle compared to Hickory. Hickory, known for its exceptional hardness, shock resistance, and tensile strength, offers superior durability and longevity, making it the preferred choice for heavy-use tool handles. Its dense grain structure helps withstand repeated impact and reduce wear, ensuring extended service life under demanding conditions.
Workability and Ease of Shaping
Ramin wood offers superior workability and ease of shaping compared to Hickory, making it a preferred choice for tool handles that require detailed carving and smooth finishing. Its fine, even texture and low density allow for quicker cutting and less effort during sanding, while Hickory's dense, coarse grain provides exceptional strength but demands more time and skill to shape effectively. Choosing Ramin enhances precision and reduces crafting fatigue, especially for users prioritizing intricate handle designs and ergonomic comfort.
Shock Absorption and Comfort in Use
Ramin wood offers excellent shock absorption due to its fine, dense grain, making it ideal for tool handles that require comfortable grip and reduced vibration impact. Hickory, known for its toughness and resilience, provides superior shock absorption by flexing under stress without breaking, enhancing user comfort during extended use. When comparing both, Ramin is favored for smoother handling and lighter weight, while Hickory excels in durability and resistance to repeated impact.
Resistance to Moisture and Decay
Ramin wood exhibits moderate resistance to moisture but is more prone to decay under prolonged exposure, making it less ideal for tool handles in humid or wet conditions. Hickory offers superior moisture resistance and exceptional durability, maintaining structural integrity and reducing the risk of rot and fungal decay over time. Choosing hickory for tool handles ensures enhanced longevity and reliable performance in environments with high moisture levels.
Cost Comparison: Ramin vs Hickory
Ramin wood typically costs less than hickory, making it a more budget-friendly option for tool handles. Hickory is known for its superior strength and shock resistance, which can justify its higher price in applications requiring durability. The cost difference reflects hickory's enhanced performance qualities versus the more economical but less robust ramin wood.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ramin wood, sourced primarily from Southeast Asia, often raises sustainability concerns due to over-harvesting and slow growth rates, leading to deforestation and habitat loss. Hickory, commonly found in North America, is generally considered more sustainable for tool handles because it is abundant, fast-growing, and frequently harvested from managed forests. Choosing Hickory over Ramin reduces environmental impact by supporting responsible forestry practices and promoting renewable resource use in tool manufacturing.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Wood for Your Tool Handle
Ramin wood offers a lightweight and smooth surface, making it ideal for tool handles that require precision and comfort, such as carving knives and small woodworking tools. Hickory, known for its exceptional strength, shock resistance, and durability, is best suited for heavy-duty tool handles like hammers, axes, and sledgehammers, where impact absorption is critical. Selecting between Ramin and Hickory depends on the tool's intended use: Ramin excels in fine detail work, while Hickory withstands rigorous force and heavy impact.
Infographic: Ramin vs Hickory for Tool Handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com