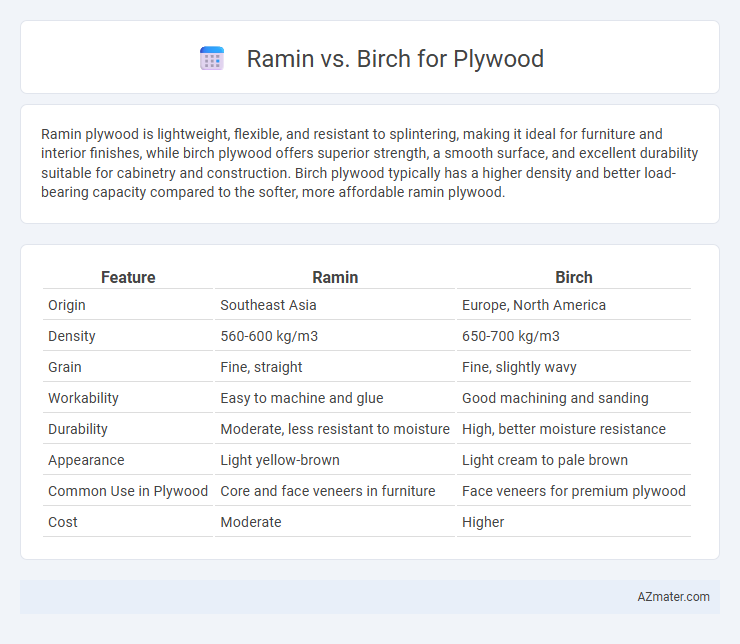
Ramin plywood is lightweight, flexible, and resistant to splintering, making it ideal for furniture and interior finishes, while birch plywood offers superior strength, a smooth surface, and excellent durability suitable for cabinetry and construction. Birch plywood typically has a higher density and better load-bearing capacity compared to the softer, more affordable ramin plywood.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ramin | Birch |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Southeast Asia | Europe, North America |
| Density | 560-600 kg/m3 | 650-700 kg/m3 |
| Grain | Fine, straight | Fine, slightly wavy |
| Workability | Easy to machine and glue | Good machining and sanding |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to moisture | High, better moisture resistance |
| Appearance | Light yellow-brown | Light cream to pale brown |
| Common Use in Plywood | Core and face veneers in furniture | Face veneers for premium plywood |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction: Comparing Ramin and Birch for Plywood
Ramin and Birch are two popular wood species used in plywood manufacturing, each offering unique properties that influence performance and aesthetics. Ramin plywood is known for its lightweight, fine grain, and smooth surface, making it ideal for detailed woodworking and indoor applications. Birch plywood stands out due to its strength, durability, and uniform grain, making it suitable for structural uses and furniture requiring robust support.
Botanical Overview: Ramin vs Birch
Ramin (Gonystylus spp.) is a tropical hardwood tree native to Southeast Asia, known for its light yellow to pale brown wood with a fine, uniform texture and moderate density, making it ideal for plywood production. Birch (Betula spp.), predominantly found in the Northern Hemisphere, exhibits a pale, creamy-white to light brown color with a smooth grain and higher density, offering greater strength and durability in plywood applications. Both species provide excellent workability and dimensional stability, but Ramin's softer texture contrasts with Birch's harder, more resilient fibers, influencing their suitability depending on plywood performance requirements.
Physical Properties and Appearance
Ramin plywood is known for its fine, pale yellow to light brown color with a smooth texture, offering good workability and a uniform grain pattern, making it suitable for intricate woodworking and interior applications. Birch plywood features a creamy white to light reddish-brown hue with a tight, even grain that provides superior strength, stiffness, and a smooth, paint-friendly surface ideal for cabinetry and furniture. Both types exhibit strong durability, but birch generally outperforms ramin in load-bearing capacity and resistance to warping due to its higher density and hardness.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ramin plywood is renowned for its lightweight yet strong characteristics, making it ideal for applications requiring moderate strength and smooth finishes. Birch plywood offers superior durability and high strength due to its dense hardwood composition, making it preferable for heavy-duty structural uses. While Ramin provides good strength for its weight, Birch plywood outperforms in terms of resistance to impact, wear, and long-term durability.
Workability and Machining Qualities
Ramin plywood is known for its excellent workability, featuring a fine, uniform texture that allows for smooth cutting, shaping, and sanding, making it ideal for detailed woodworking tasks. Birch plywood offers superior machining qualities due to its densely grained hardwood structure, resulting in clean edges and minimal splintering during routing, drilling, and finishing processes. The combination of Ramin's ease of handling and Birch's strength ensures both types are favored in applications demanding precision and durability.
Finishing and Aesthetic Appeal
Ramin plywood features a smooth, fine-grained surface ideal for high-quality finishing, offering excellent paint adhesion and a uniform look. Birch plywood provides a tight, even grain with a pale color, enabling a natural wood finish that enhances its aesthetic appeal in furniture and cabinetry. Both types deliver superior visual quality, but Ramin's consistent texture makes it preferable for intricate staining and coatings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ramin plywood, sourced from endangered tropical trees primarily in Southeast Asia, faces significant environmental concerns due to illegal logging and habitat destruction, resulting in poor sustainability ratings. Birch plywood, harvested from fast-growing temperate forests often managed under sustainable forestry certifications such as FSC, offers a more eco-friendly alternative with lower carbon footprints and higher regeneration rates. Choosing birch plywood supports sustainable forest management practices and reduces biodiversity loss compared to the ecological risks associated with ramin wood extraction.
Cost and Market Availability
Ramin plywood tends to be more expensive than Birch plywood due to its limited regional availability and slower growth rates affecting supply. Birch plywood offers a more cost-effective option with widespread market availability, supported by sustainable harvesting practices and established supply chains. Buyers often choose Birch plywood for budget-conscious projects without compromising on quality or durability.
Best Applications for Ramin and Birch Plywood
Ramin plywood is highly valued for its smooth finish and lightweight properties, making it ideal for indoor furniture, cabinetry, and decorative paneling where fine detailing and ease of handling are crucial. Birch plywood offers exceptional strength and durability, suitable for structural applications, flooring, and heavy-use furniture requiring a robust material with a consistent grain. Both types provide excellent workability, but Ramin excels in aesthetic indoor projects, while Birch is preferred for functional, load-bearing purposes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Ramin plywood offers a smooth finish and is lightweight, making it ideal for indoor furniture and cabinetry, while birch plywood provides superior strength and durability, perfect for structural applications and high-stress environments. Birch's fine grain and resistance to warping ensure long-lasting performance, whereas Ramin's affordability suits budget-conscious projects with less load-bearing requirements. Selecting the right wood depends on balancing budget, desired aesthetic, and structural needs for a successful project outcome.
Infographic: Ramin vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com