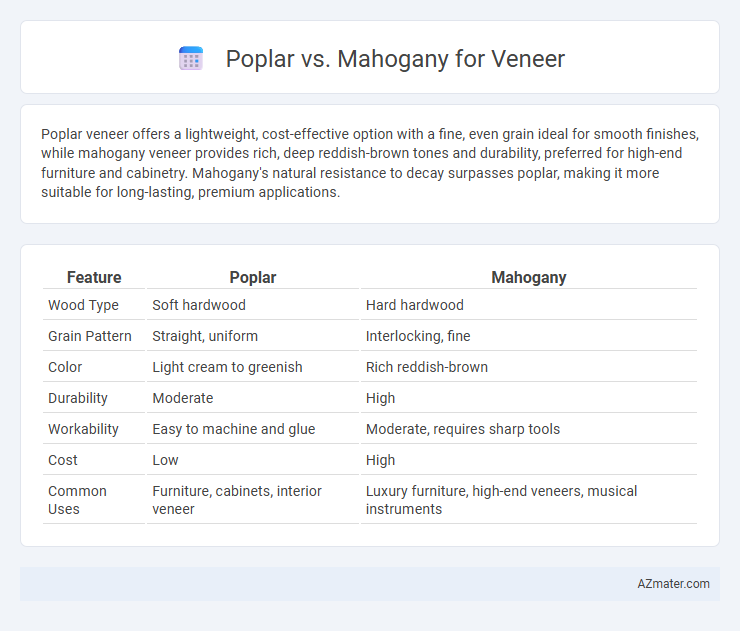
Poplar veneer offers a lightweight, cost-effective option with a fine, even grain ideal for smooth finishes, while mahogany veneer provides rich, deep reddish-brown tones and durability, preferred for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Mahogany's natural resistance to decay surpasses poplar, making it more suitable for long-lasting, premium applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Poplar | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Soft hardwood | Hard hardwood |
| Grain Pattern | Straight, uniform | Interlocking, fine |
| Color | Light cream to greenish | Rich reddish-brown |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Workability | Easy to machine and glue | Moderate, requires sharp tools |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Common Uses | Furniture, cabinets, interior veneer | Luxury furniture, high-end veneers, musical instruments |
Introduction to Poplar and Mahogany Veneer
Poplar veneer is lightweight and cost-effective, often used for its smooth texture and pale, consistent grain that is easy to stain for various finishes. Mahogany veneer is prized for its rich reddish-brown color, fine grain, and durability, making it a premium choice for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Both veneers offer distinct aesthetics and functional benefits, with poplar providing affordability and versatility, while mahogany delivers luxury and longevity.
Botanical Origins and Distribution
Poplar veneer originates from the Populus genus, predominantly found across North America, Europe, and Asia, thriving in temperate regions with moist soils. Mahogany veneer is derived from the Swietenia genus, native to tropical regions of Central and South America, valued for its rich reddish-brown color and durability. The botanical differences reflect their distinct growth environments, with Poplar offering a lighter, softer wood, while Mahogany provides a harder, denser texture ideal for high-quality furniture veneers.
Color and Grain Characteristics
Poplar veneer features a light cream to yellowish-brown color with subtle greenish or grayish undertones, offering a smooth, straight grain that sometimes exhibits occasional knots or streaks, ideal for painted finishes. Mahogany veneer presents a rich, reddish-brown hue that deepens over time, characterized by a fine, even grain with a natural luster and occasional interlocking patterns, lending itself to elegant, polished appearances. The color stability and distinctive grain pattern of mahogany make it preferable for high-end furniture, whereas poplar's lighter tone and uniform grain suit more versatile applications.
Workability and Machinability
Poplar veneer is highly favored for its exceptional workability due to its soft texture, allowing easy cutting, shaping, and sanding without significant wear on tools. Mahogany veneer, while harder and denser, offers excellent machinability with precise cutting and smooth finishes but requires sharper tools and slower processing to avoid burning or tearing. Both materials present advantages in veneer applications, with poplar suited for intricate, detailed work and mahogany preferred for durable, fine furniture surfaces.
Durability and Lifespan
Poplar veneer offers moderate durability with a lifespan of about 5 to 10 years under typical indoor conditions, making it suitable for light-use furniture and cabinetry. Mahogany veneer is significantly more durable, providing a lifespan that can exceed 20 years due to its dense hardwood structure and natural resistance to wear and decay. Choosing mahogany for veneer applications ensures enhanced longevity and superior performance in high-traffic or frequently handled surfaces.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Poplar veneer is significantly more affordable than mahogany, making it a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious projects. Poplar is widely available in North America, ensuring a steady supply and shorter lead times, whereas mahogany, being a premium hardwood sourced from tropical regions like Central and South America, often faces supply constraints and higher import costs. The price disparity and availability differences make poplar veneer ideal for large-scale or cost-sensitive applications, while mahogany veneer is preferred for luxury finishes despite its premium price and less consistent availability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Poplar veneer is generally considered more sustainable due to its rapid growth rate, widespread availability, and lower environmental footprint compared to mahogany, which is often sourced from slower-growing tropical hardwood trees facing deforestation concerns. Mahogany veneer, prized for its durability and rich color, typically has a higher environmental impact because it is harvested in sensitive rainforest ecosystems and is frequently listed on CITES or other restricted trade lists. Choosing poplar veneer supports more sustainable forestry practices and reduces the risk of contributing to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
Common Applications in Veneer
Poplar veneer is commonly used for budget-friendly furniture, cabinetry, and decorative paneling due to its light color and smooth grain, which readily accepts stains and finishes. Mahogany veneer is preferred in high-end furniture, musical instruments, and luxury interiors for its rich reddish-brown hue and durability that add elegance and warmth. Both veneers are utilized in architectural millwork, but mahogany suits projects requiring a premium aesthetic and long-lasting appeal.
Pros and Cons of Poplar Veneer
Poplar veneer is valued for its affordability and light, uniform appearance, making it an excellent choice for budget-friendly projects and easy staining to mimic more expensive woods. However, poplar's softness can result in dents and scratches, limiting its durability compared to harder veneers like mahogany, which offers superior strength and rich color. While poplar veneer is versatile and smooth, it may require careful handling and finishing to achieve the desired aesthetic and performance.
Pros and Cons of Mahogany Veneer
Mahogany veneer offers a rich, deep reddish-brown color and a fine, straight grain that enhances the aesthetic appeal of furniture and cabinetry, making it highly prized for luxury interior finishes. Its durability and resistance to warping and cracking provide long-lasting performance, but mahogany veneer can be more expensive and harder to source sustainably compared to poplar. While mahogany's natural oils contribute to its resilience against pests and moisture, it requires careful maintenance to prevent discoloration and preserve its polished appearance.
Infographic: Poplar vs Mahogany for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com