Poplar siding offers lightweight, fine-grain wood with excellent paint adhesion but lower natural durability. Larch siding provides superior rot resistance and strength with a coarse grain, making it ideal for exterior applications in harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
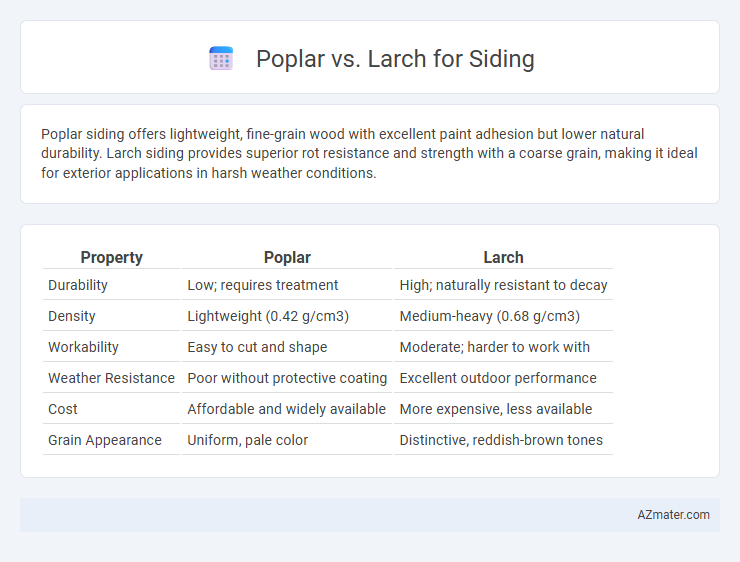
| Property | Poplar | Larch |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Low; requires treatment | High; naturally resistant to decay |
| Density | Lightweight (0.42 g/cm3) | Medium-heavy (0.68 g/cm3) |
| Workability | Easy to cut and shape | Moderate; harder to work with |
| Weather Resistance | Poor without protective coating | Excellent outdoor performance |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available | More expensive, less available |
| Grain Appearance | Uniform, pale color | Distinctive, reddish-brown tones |
Introduction to Poplar and Larch for Siding
Poplar siding offers a lightweight, affordable option with a smooth grain ideal for painting and interior use, but it lacks the durability needed for harsh exterior conditions. Larch siding, characterized by its dense, resinous composition, provides superior weather resistance and natural decay protection, making it a favored choice for exterior cladding. Both woods present unique benefits, where poplar excels in cost-efficiency and larch in longevity and exterior performance.
Physical Characteristics: Poplar vs Larch
Poplar wood features a light, creamy color with a fine, even texture and relatively soft hardness, making it easy to cut and shape for siding applications. Larch, by contrast, offers a distinct reddish hue with a coarse texture and higher density, providing superior durability and natural resistance to moisture and decay. The dimensional stability of larch makes it more suitable for exterior siding exposed to varying weather conditions compared to poplar's tendency to warp and dent.
Durability and Longevity
Poplar siding offers moderate durability with good resistance to wear but is more susceptible to dents and moisture damage compared to larch. Larch siding stands out for its exceptional hardness and natural resistance to rot, decay, and insect infestation, contributing to superior longevity in exterior applications. Choosing larch over poplar enhances siding lifespan and reduces maintenance costs due to its robust durability and weather-resistant properties.
Weather Resistance and Maintenance
Poplar siding offers moderate weather resistance but requires regular sealing and painting to protect against moisture and rot, making maintenance more frequent. Larch siding excels in weather resistance due to its dense grain and natural resin content, providing superior durability against rain, snow, and UV rays with less frequent upkeep. Choosing larch siding reduces long-term maintenance costs and extends the siding's lifespan compared to poplar.
Cost Comparison: Poplar vs Larch Siding
Poplar siding is generally more affordable than larch siding due to its faster growth rate and wider availability, making it a cost-effective option for budget-conscious homeowners. Larch siding, while typically more expensive, offers superior durability and natural resistance to rot and insects, which can reduce long-term maintenance costs. Choosing between poplar and larch siding depends on balancing upfront installation expenses with potential savings in maintenance and longevity.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Poplar siding offers a smooth, fine-grained texture with subtle, consistent color variations ranging from pale yellow to light brown, making it ideal for a clean, modern aesthetic. Larch siding displays a more pronounced grain pattern with natural reddish-brown hues that deepen over time, providing a rustic, warm appearance. Both woods enhance curb appeal, but poplar suits contemporary designs while larch complements traditional or rustic architecture.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Poplar siding offers a renewable and fast-growing resource with low environmental impact due to its efficient carbon sequestration and minimal chemical treatment requirements. Larch, known for its natural durability and rot resistance, reduces the need for preservatives, enhancing sustainability through longer lifespan and lower maintenance. Both woods contribute to eco-friendly siding options, but Poplar's rapid growth makes it a more sustainable choice in terms of resource renewal rate.
Ease of Installation
Poplar siding is known for its lightweight and consistent grain, making it easier to cut and install with basic tools, which reduces labor time and effort. Larch siding offers natural durability and resistance to decay, but its denser, harder texture can make it more challenging to work with, requiring sharper blades and more precision during installation. Choosing poplar can streamline the installation process, especially for DIY projects, while larch demands more expertise but provides long-term resilience.
Common Applications and Popular Uses
Poplar siding is favored for interior applications such as trim and paneling due to its smooth texture and ease of painting, making it ideal for residential projects. Larch siding is commonly used for exterior cladding because of its natural durability and resistance to weather, often seen in rustic or coastal homes. Both woods serve well in siding, but poplar suits painted finishes, while larch excels in natural stain or untreated outdoor environments.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Siding Project
Poplar offers a smooth, consistent grain and is easier to paint or stain, making it ideal for homeowners seeking a cost-effective and easily customizable siding option. Larch provides superior durability and natural resistance to decay and insects due to its dense, resin-rich composition, making it suitable for exterior applications in harsh climates. When choosing the right wood for your siding project, consider factors such as climate exposure, maintenance preferences, and aesthetic goals to balance poplar's affordability against larch's long-term resilience.
Infographic: Poplar vs Larch for Siding
 azmater.com
azmater.com