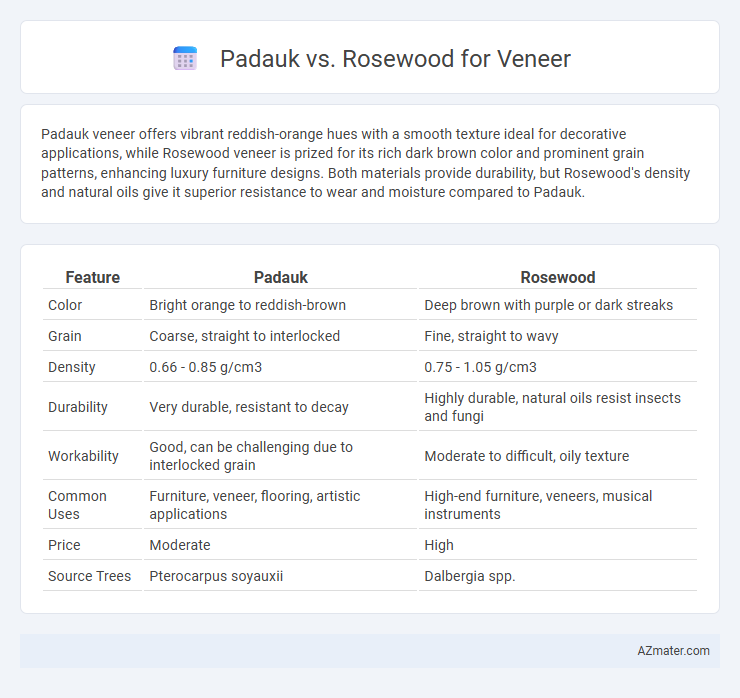
Padauk veneer offers vibrant reddish-orange hues with a smooth texture ideal for decorative applications, while Rosewood veneer is prized for its rich dark brown color and prominent grain patterns, enhancing luxury furniture designs. Both materials provide durability, but Rosewood's density and natural oils give it superior resistance to wear and moisture compared to Padauk.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Padauk | Rosewood |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Bright orange to reddish-brown | Deep brown with purple or dark streaks |
| Grain | Coarse, straight to interlocked | Fine, straight to wavy |
| Density | 0.66 - 0.85 g/cm3 | 0.75 - 1.05 g/cm3 |
| Durability | Very durable, resistant to decay | Highly durable, natural oils resist insects and fungi |
| Workability | Good, can be challenging due to interlocked grain | Moderate to difficult, oily texture |
| Common Uses | Furniture, veneer, flooring, artistic applications | High-end furniture, veneers, musical instruments |
| Price | Moderate | High |
| Source Trees | Pterocarpus soyauxii | Dalbergia spp. |
Introduction to Padauk and Rosewood Veneer
Padauk veneer is prized for its vibrant reddish-orange hues and fine grain pattern, making it a popular choice for striking furniture and cabinetry. Rosewood veneer features rich, dark brown tones with dramatic black streaks, offering a luxurious and classic appearance often favored in high-end wood finishes. Both veneers provide excellent durability and workability, with Padauk noted for its color stability and Rosewood for its deep, complex grain variations.
Origin and Botanical Differences
Padauk veneers primarily come from the Pterocarpus genus, native to tropical regions in Africa and Asia, particularly India and Myanmar, while rosewood veneers are derived from several species in the Dalbergia genus, predominantly found in Brazil, India, and Madagascar. Botanically, padauk trees belong to the Fabaceae family, known for their dense, oily heartwood with a bright reddish-orange hue that darkens over time, whereas rosewood exhibits a more varied grain pattern and richer, darker brown to purple tones due to its complex lignin composition. The distinct geographic origins and botanical lineages influence not only the aesthetic qualities but also the durability and workability of these veneers in fine woodworking and furniture making.
Visual Appearance and Color Variations
Padauk veneer is prized for its vibrant orange to reddish-brown hues that deepen to a rich, dark red over time, often showcasing a straight to interlocked grain pattern with moderate luster. Rosewood veneer exhibits a wide range of color variations, typically featuring deep brown to purplish-black tones with distinctive dark streaks and a natural sheen, providing a dramatic and exotic look. Both veneers offer unique visual appeal for high-end furniture and decorative applications, with Padauk delivering a brighter, warmer aesthetic, while Rosewood provides a more muted, sophisticated elegance.
Grain Patterns and Texture
Padauk veneer displays a distinctive grain pattern characterized by straight to interlocked grains with occasional wavy figures, yielding a dramatic visual effect. Its texture is coarse yet smooth to the touch, offering a striking contrast to Rosewood veneers, which feature more pronounced, swirling, and often darker grain patterns with fine texture. Rosewood's dense grain structure creates a luxurious, polished look, whereas Padauk provides vibrant, bold aesthetics suitable for accent pieces.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Padauk veneer offers high durability with a Janka hardness rating around 1,750, making it resistant to dents and wear in high-traffic applications. Rosewood veneer, particularly Brazilian rosewood, often exhibits a Janka hardness between 1,600 and 2,200, depending on the species, providing excellent hardness and long-lasting protection. Both woods are prized for strength; however, Rosewood tends to have a more consistent hardness range, while Padauk's durability is complemented by its exceptional stability and resistance to decay.
Workability and Application
Padauk veneer exhibits excellent workability due to its fine, even texture and moderate density, making it easy to cut, sand, and glue. Rosewood veneer, while harder and denser, offers superior durability and a smoother finish but requires more skill and sharper tools to handle without chipping. Padauk is preferred for vibrant, decorative applications such as inlay and furniture accents, while Rosewood's rich color and grain pattern make it ideal for high-end cabinetry and musical instruments.
Cost Differences and Availability
Padauk veneer generally costs less than rosewood due to its more abundant availability and faster growth rate in tropical regions. Rosewood veneer commands a higher price resulting from its limited supply, stricter trade regulations, and high demand in luxury furniture markets. Availability of padauk is more consistent, while rosewood faces restrictions under CITES, impacting its market presence and cost.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Padauk veneer is prized for its rapid growth and renewability, making it a more sustainable choice compared to slower-growing rosewood species, which often face overharvesting pressures and are listed under CITES regulations to prevent illegal trade. Rosewood's extraction contributes to deforestation and habitat loss, while Padauk plantations typically require less chemical intervention and support better soil conservation practices. Choosing Padauk over rosewood for veneer reduces ecological footprint and promotes responsible forestry management.
Common Uses in Furniture and Design
Padauk veneer is frequently used in furniture making for its striking reddish-orange hue and durability, making it ideal for decorative accents and high-end cabinetry. Rosewood veneer is prized for its rich, deep brown tones with darker veining, commonly utilized in luxury furniture, musical instruments, and intricate inlays. Both woods offer exceptional workability and are favored in fine woodworking and designer interiors for their unique aesthetic appeal and strength.
Conclusion: Choosing Padauk or Rosewood for Veneer
Padauk veneer offers vibrant reddish-orange hues and exceptional hardness, making it ideal for bold, durable furniture designs. Rosewood veneer, prized for its deep brown tones with intricate grain patterns, provides a luxurious and classic aesthetic suited for high-end cabinetry and musical instruments. Selecting between Padauk and Rosewood hinges on whether the project prioritizes striking color intensity and toughness or elegant grain complexity and traditional luxury.
Infographic: Padauk vs Rosewood for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com