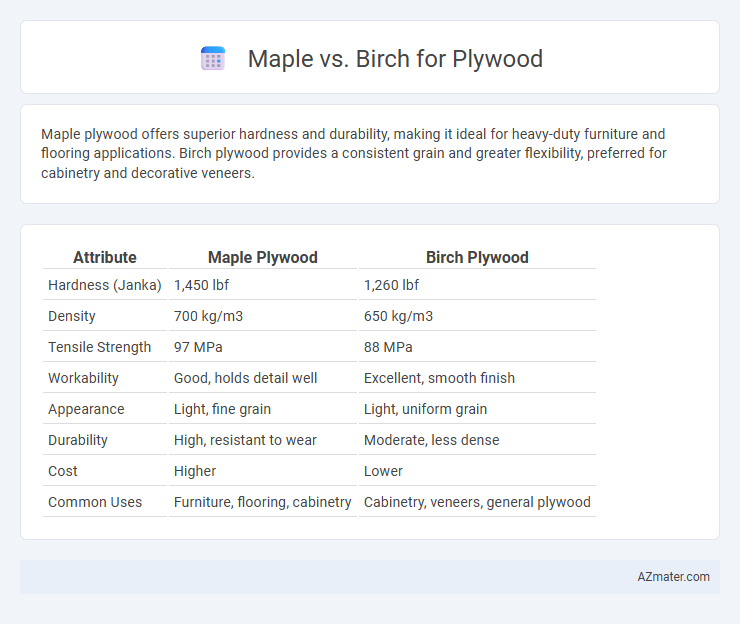
Maple plywood offers superior hardness and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty furniture and flooring applications. Birch plywood provides a consistent grain and greater flexibility, preferred for cabinetry and decorative veneers.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Maple Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Janka) | 1,450 lbf | 1,260 lbf |
| Density | 700 kg/m3 | 650 kg/m3 |
| Tensile Strength | 97 MPa | 88 MPa |
| Workability | Good, holds detail well | Excellent, smooth finish |
| Appearance | Light, fine grain | Light, uniform grain |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear | Moderate, less dense |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry | Cabinetry, veneers, general plywood |
Introduction to Maple and Birch Plywood
Maple plywood, prized for its fine, uniform grain and exceptional durability, offers a smooth surface ideal for cabinetry and furniture making. Birch plywood features a tighter grain with a slightly lighter color and is known for its strength and resistance to warping, making it suitable for structural and decorative applications. Both types provide reliable stability and workability, with maple favored for its aesthetic appeal and birch chosen for cost-effectiveness and versatility.
Botanical Differences: Maple vs Birch Trees
Maple (Acer spp.) and birch (Betula spp.) trees differ significantly in their botanical characteristics, influencing plywood quality and properties. Maple trees belong to the Sapindaceae family and typically feature dense, fine-grained wood with a uniform texture, while birch, from the Betulaceae family, has a lighter color and slightly coarser grain pattern. These inherent botanical differences affect the plywood's strength, appearance, and suitability for various applications such as cabinetry and furniture.
Physical Properties Comparison
Maple plywood offers higher density and superior hardness compared to birch plywood, making it more resistant to dents and wear. Birch plywood features a fine, uniform grain with excellent strength-to-weight ratio, providing good stiffness and durability. Both woods exhibit strong dimensional stability, but birch plywood tends to have better resistance to moisture-induced warping.
Grain Patterns and Aesthetics
Maple plywood exhibits a fine, consistent grain pattern with a smooth, light-colored surface ideal for modern and minimalist aesthetics. Birch plywood features a more pronounced, straight grain with a slightly warmer tone, offering a natural, rustic appearance favored in traditional cabinetry and furniture. Both woods provide durable surfaces, but maple enhances brightness and uniformity, while birch highlights texture and warmth.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Maple plywood exhibits superior strength and durability compared to birch due to its denser grain structure and higher Janka hardness rating, typically around 1450, which enhances resistance to wear and impact. Birch plywood, while still offering good hardness with a Janka rating near 1260, is more prone to dents and scratches under heavy use. For applications requiring robust load-bearing capacity and extended lifespan, maple plywood is the preferred choice given its increased stiffness, resistance to delamination, and overall toughness.
Workability and Machining Ease
Maple plywood is highly regarded for its excellent workability, offering smooth machining with minimal tear-out due to its fine and uniform grain structure. Birch plywood also exhibits good workability but tends to be slightly harder and denser, making machining marginally more challenging without sharp tools. Both species respond well to sanding and finishing, though maple's consistent grain pattern allows for more precise cutting and shaping in detailed woodworking projects.
Cost Differences and Availability
Birch plywood typically commands a higher price than maple plywood due to its denser grain and superior durability, which increases manufacturing costs. Maple plywood is more widely available in North American markets, providing a cost-effective option for large-scale projects requiring consistent supply. Birch's limited regional availability can lead to higher shipping costs and longer lead times, influencing overall project budgets.
Common Applications in Woodworking
Maple plywood is widely used in furniture making and cabinetry due to its fine grain, strength, and smooth finish that permits detailed painting or staining. Birch plywood offers superior durability and resistance to warping, making it ideal for shelving, flooring, and structural components in construction projects. Both maple and birch plywood are favored in woodworking for their stability, but maple excels in aesthetic applications while birch is preferred for heavy-duty uses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Maple plywood generally has a lower environmental impact due to the tree's faster growth rate and higher availability, promoting sustainable forestry practices. Birch plywood, while valued for its durability and strength, often comes from slower-growing trees, which can contribute to longer carbon sequestration but may increase resource depletion risks if not sourced responsibly. Both types of plywood benefit from certifications like FSC and PEFC, ensuring responsible forestry and reduced environmental footprint.
Choosing the Right Wood for Your Project
Maple plywood offers superior hardness and durability, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry that require a smooth, fine finish and resistance to wear. Birch plywood provides excellent strength and a consistent grain pattern, favored for structural applications and projects needing a balance between cost and performance. Selecting between maple and birch plywood depends on the project's demands for hardness, appearance, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Maple vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com