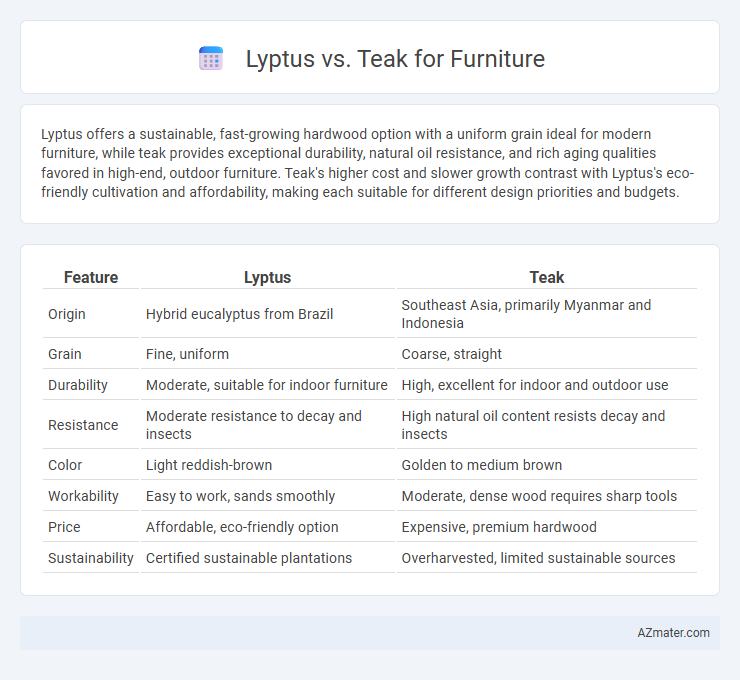
Lyptus offers a sustainable, fast-growing hardwood option with a uniform grain ideal for modern furniture, while teak provides exceptional durability, natural oil resistance, and rich aging qualities favored in high-end, outdoor furniture. Teak's higher cost and slower growth contrast with Lyptus's eco-friendly cultivation and affordability, making each suitable for different design priorities and budgets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lyptus | Teak |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Hybrid eucalyptus from Brazil | Southeast Asia, primarily Myanmar and Indonesia |
| Grain | Fine, uniform | Coarse, straight |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for indoor furniture | High, excellent for indoor and outdoor use |
| Resistance | Moderate resistance to decay and insects | High natural oil content resists decay and insects |
| Color | Light reddish-brown | Golden to medium brown |
| Workability | Easy to work, sands smoothly | Moderate, dense wood requires sharp tools |
| Price | Affordable, eco-friendly option | Expensive, premium hardwood |
| Sustainability | Certified sustainable plantations | Overharvested, limited sustainable sources |
Introduction to Lyptus and Teak
Lyptus is a fast-growing hybrid hardwood derived from the Eucalyptus species, prized for its sustainability and consistent grain pattern, making it an eco-friendly alternative for furniture manufacturing. Teak, native to Southeast Asia, is renowned for its exceptional durability, natural oils, and resistance to water and insects, often used in high-end outdoor furniture. Both woods offer unique benefits, with Lyptus valued for its rapid renewability and teak for its long-lasting strength and luxurious appearance.
Botanical Origins and Growth Regions
Lyptus is a hybrid eucalyptus species primarily grown in fast-growing plantations in Brazil, combining Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla, while teak (Tectona grandis) is native to south and southeast Asia, especially India, Myanmar, and Thailand. Lyptus thrives in tropical and subtropical climates with rapid growth cycles of around 15 years, whereas teak requires a longer maturation period, often 40 to 50 years. Both woods have distinct botanical origins and growth regions shaping their availability and environmental impact in furniture making.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Lyptus, a hybrid eucalyptus, offers a highly sustainable option due to its rapid growth rate and plantation sourcing, minimizing deforestation and habitat disruption compared to teak, which grows slower and is often harvested from natural forests. The carbon footprint of lyptus is lower, with plantations efficiently absorbing CO2, whereas teak extraction can contribute to biodiversity loss and soil degradation in tropical regions. Choosing lyptus supports renewable forestry practices and reduces environmental impact, making it a greener alternative to traditional teak for eco-conscious furniture production.
Appearance and Aesthetic Qualities
Lyptus wood features a consistent, fine grain with a reddish-brown hue that deepens over time, offering a modern and uniform aesthetic ideal for sleek, contemporary furniture designs. Teak boasts a rich golden-brown color with natural grain variations and oily texture, providing a warm, luxurious appearance that enhances both traditional and rustic furniture styles. The natural oils in teak contribute to its smooth finish and resistance to moisture, making it visually appealing and durable for both indoor and outdoor furniture applications.
Hardness and Durability Comparison
Lyptus wood exhibits a Janka hardness rating of approximately 2,300 lbf, making it harder than many common hardwoods, while teak registers around 1,155 lbf, indicating Lyptus offers superior resistance to dents and scratches. In terms of durability, teak contains natural oils that provide excellent resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage, ideal for outdoor furniture; Lyptus, being a hybrid eucalyptus, offers good durability but requires proper sealing to withstand environmental elements. Both woods are suitable for furniture, but Lyptus excels in hardness, whereas teak is preferred for long-lasting outdoor performance.
Workability and Ease of Use
Lyptus offers excellent workability with a consistent grain and medium density that allows for easy cutting, sanding, and finishing, making it ideal for detailed cabinetry and furniture projects. Teak, known for its high oil content and natural resistance to decay, requires sharp tools and some experience to handle effectively, as its density can dull blades quickly but results in durable, long-lasting furniture. Both woods provide good workability, but Lyptus is generally preferred for novice woodworkers due to its smoother processing characteristics and predictable behavior.
Resistance to Pests and Decay
Lyptus wood exhibits strong resistance to pests and decay due to its dense grain and natural oils, making it a durable choice for furniture in humid or insect-prone environments. Teak is highly prized for its exceptional resistance to termites, fungi, and moisture, attributed to its high oil content and tight grain structure, ensuring longevity even in outdoor or harsh conditions. Both woods offer excellent durability, but teak's superior natural oils provide a higher level of protection against decay and pests compared to Lyptus.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Lyptus wood demands regular dusting and occasional polishing to maintain its smooth, reddish surface, benefiting from a humid environment to prevent cracking. Teak, renowned for its natural oils, requires less frequent maintenance, often only periodic cleaning with mild soap and water to preserve its durability and resistance to moisture. Both woods benefit from protective finishes to extend lifespan, but teak's inherent oily properties offer superior resilience against pests and weathering compared to Lyptus.
Cost and Availability
Lyptus wood is generally more affordable and readily available due to its fast growth and sustainable plantation sources, making it a cost-effective choice for furniture manufacturers. Teak, known for its natural oils and durability, tends to be significantly more expensive and less accessible because of slower growth rates and limited supply from natural forests. Availability of Lyptus is higher in areas with tropical plantations, while teak's premium pricing reflects its global demand and restricted harvesting regulations.
Best Applications: Which Wood to Choose?
Lyptus offers a sustainable, fast-growing hardwood ideal for indoor furniture such as cabinets and flooring due to its durability and smooth grain. Teak, known for its natural oils and high resistance to moisture and pests, excels in outdoor furniture and high-end indoor pieces requiring longevity and weather resistance. Choosing between Lyptus and Teak depends on application needs: opt for Lyptus for eco-friendly, indoor use and Teak for robust, outdoor or luxury furniture projects.
Infographic: Lyptus vs Teak for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com