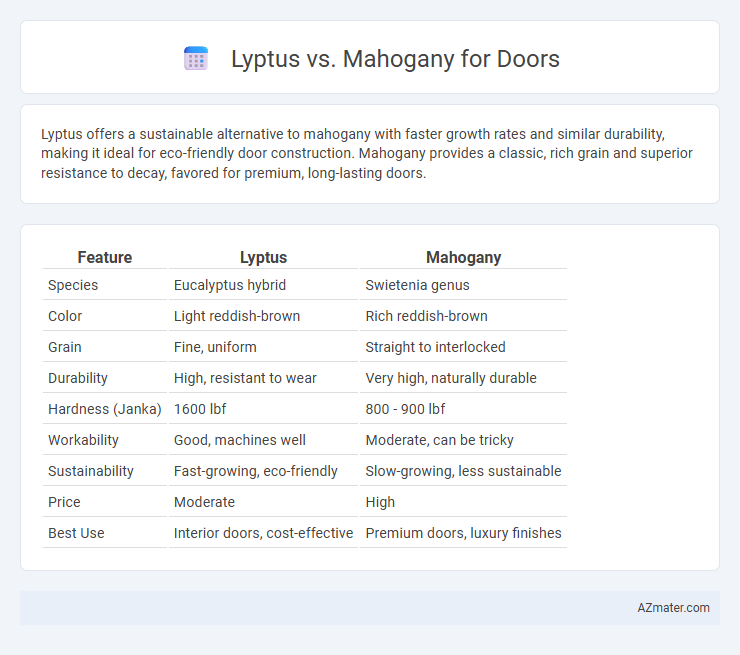
Lyptus offers a sustainable alternative to mahogany with faster growth rates and similar durability, making it ideal for eco-friendly door construction. Mahogany provides a classic, rich grain and superior resistance to decay, favored for premium, long-lasting doors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lyptus | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Species | Eucalyptus hybrid | Swietenia genus |
| Color | Light reddish-brown | Rich reddish-brown |
| Grain | Fine, uniform | Straight to interlocked |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear | Very high, naturally durable |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1600 lbf | 800 - 900 lbf |
| Workability | Good, machines well | Moderate, can be tricky |
| Sustainability | Fast-growing, eco-friendly | Slow-growing, less sustainable |
| Price | Moderate | High |
| Best Use | Interior doors, cost-effective | Premium doors, luxury finishes |
Introduction to Lyptus and Mahogany
Lyptus is a fast-growing hybrid eucalyptus tree known for its dense, durable wood, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional hardwoods like mahogany. Mahogany, prized for its rich reddish-brown color and fine grain, has long been a classic choice for high-end doors due to its strength and natural resistance to decay. Both woods offer excellent durability and aesthetic appeal, but Lyptus provides a more sustainable option with a faster harvest cycle compared to the slower-growing, more expensive mahogany.
Origin and Sustainability
Lyptus wood, sourced from Eucalyptus trees grown in managed plantations primarily in Brazil, offers a fast-growing and renewable option, reducing deforestation impact compared to traditional hardwoods. Mahogany, traditionally harvested from tropical forests in Central America, faces sustainability challenges due to overharvesting and slower growth rates. Certified Lyptus provides a more environmentally responsible choice for door construction while maintaining durability and aesthetics similar to mahogany.
Appearance and Color Variations
Lyptus offers a consistent, light reddish-brown hue with subtle grain patterns that create a smooth, modern appearance ideal for contemporary doors. Mahogany presents a richer color spectrum, ranging from deep reddish-brown to darker, more dramatic tones with pronounced, intricate grain patterns that add classic elegance and warmth. The color stability of Lyptus provides uniformity over large projects, while Mahogany's natural variations deliver unique, artisan character to each door.
Grain Patterns and Texture
Lyptus features a consistent, fine grain pattern with a smooth texture, making it ideal for contemporary door designs that require a uniform appearance. Mahogany exhibits a more pronounced, interlocking grain with a rich, natural texture that adds depth and character to traditional or classic doors. Both woods offer durability, but the choice depends on whether a sleek or textured aesthetic is preferred for the door's visual impact.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Lyptus offers exceptional hardness and resistance to wear, making it highly durable for doors exposed to heavy use. Mahogany, prized for its dense, fine grain, provides superior strength and stability, ensuring long-lasting structural integrity. While both hardwoods deliver excellent durability, mahogany's natural resistance to moisture and pests often surpasses Lyptus in demanding environments.
Workability and Finishing
Lyptus offers excellent workability due to its fine, uniform grain and consistent density, allowing for smooth cutting, sanding, and shaping with minimal effort. Mahogany's workability is also praised, characterized by its straight grain and ease of machining, which reduces the risk of splintering or tearing. Both woods accept finishes well, but mahogany tends to achieve a richer, deeper color and smoother, more lustrous finish, making it a preferred choice for high-end door applications.
Resistance to Moisture and Weather
Lyptus offers superior resistance to moisture and weather due to its dense, eucalyptus-based composition, making it less prone to warping and swelling compared to traditional hardwoods. Mahogany, while naturally durable and resistant to rot, can be more susceptible to moisture damage if not properly sealed and maintained. For exterior doors, Lyptus provides enhanced longevity in humid or variable climates, whereas mahogany requires more frequent upkeep to preserve its structural integrity against weather effects.
Cost and Availability
Lyptus wood offers a more cost-effective option compared to mahogany, often priced 20-30% lower, making it attractive for budget-conscious door projects. While mahogany is highly valued for its rich color and grain, its availability is limited due to stricter logging regulations and higher demand, leading to longer lead times and increased prices. Lyptus, a fast-growing hybrid eucalyptus, is more sustainably harvested and widely available, ensuring consistent supply and shorter delivery schedules for door manufacturing.
Environmental Impact
Lyptus, a fast-growing Eucalyptus hybrid, offers a more sustainable alternative to Mahogany due to its plantation-based cultivation and rapid maturity, reducing deforestation pressure on natural forests. Mahogany, often sourced from slow-growing tropical hardwood forests, faces significant environmental concerns related to illegal logging and habitat destruction. Choosing Lyptus doors supports better forest management and lowers carbon footprint compared to traditional Mahogany, promoting eco-friendly construction practices.
Which Wood is Best for Your Door?
Lyptus is a sustainable hardwood known for its fast growth and durability, making it an eco-friendly option for doors with a smooth, consistent grain that resists warping and cracking. Mahogany offers a rich, deep reddish-brown color, exceptional stability, and natural resistance to rot, ideal for high-end doors with classic aesthetics. Choosing between Lyptus and Mahogany depends on your priorities for environmental impact, budget, and desired door appearance.
Infographic: Lyptus vs Mahogany for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com