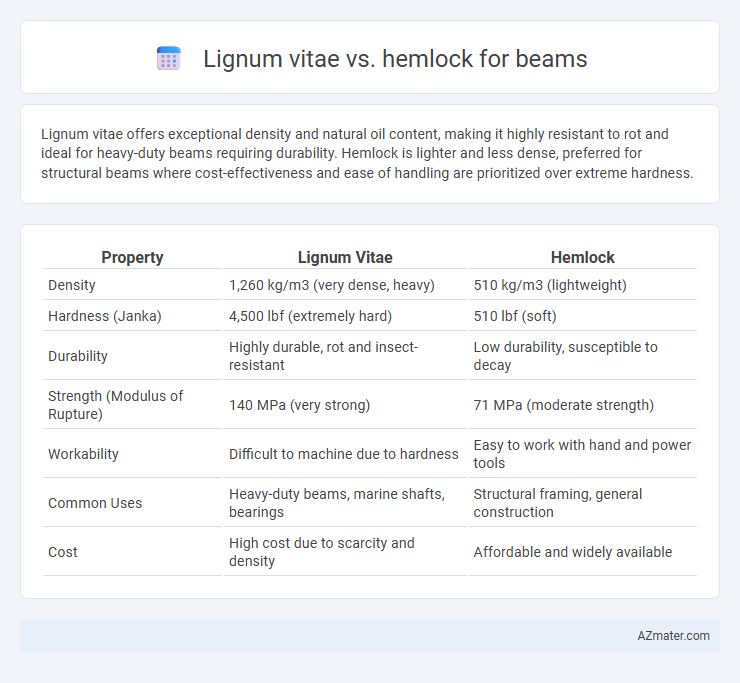
Lignum vitae offers exceptional density and natural oil content, making it highly resistant to rot and ideal for heavy-duty beams requiring durability. Hemlock is lighter and less dense, preferred for structural beams where cost-effectiveness and ease of handling are prioritized over extreme hardness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lignum Vitae | Hemlock |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1,260 kg/m3 (very dense, heavy) | 510 kg/m3 (lightweight) |
| Hardness (Janka) | 4,500 lbf (extremely hard) | 510 lbf (soft) |
| Durability | Highly durable, rot and insect-resistant | Low durability, susceptible to decay |
| Strength (Modulus of Rupture) | 140 MPa (very strong) | 71 MPa (moderate strength) |
| Workability | Difficult to machine due to hardness | Easy to work with hand and power tools |
| Common Uses | Heavy-duty beams, marine shafts, bearings | Structural framing, general construction |
| Cost | High cost due to scarcity and density | Affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Lignum Vitae and Hemlock
Lignum vitae, known for its exceptional density and natural oils, offers unmatched durability and resistance to decay, making it ideal for heavy-load beams in marine and construction applications. Hemlock, a softer softwood species native to North America, provides a lightweight and cost-effective option with moderate strength but less resistance to moisture and insect damage. When choosing between Lignum vitae and Hemlock for beams, considerations include load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Botanical Origins and Growth Habits
Lignum vitae originates from the genus Guaiacum, native to the Caribbean and northern parts of South America, known for its slow growth and dense hardwood characteristics. Hemlock comes from the Tsuga genus, predominantly found in North America and parts of Asia, characterized by fast growth and softer, lighter wood. The contrasting botanical origins and growth rates of Lignum vitae and Hemlock significantly influence their suitability and durability as beam materials in construction.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Lignum vitae exhibits exceptional density, hardness, and natural oil content, providing outstanding compressive strength and durability for beam applications. Hemlock, on the other hand, is lighter with lower density and tensile strength but offers moderate stiffness and ease of machining. The superior wear resistance and high modulus of rupture of Lignum vitae make it ideal for heavy-load beams, while Hemlock serves well in lighter structural elements where flexibility is prioritized.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacities
Lignum vitae exhibits exceptional strength and load-bearing capacity with a Janka hardness of around 4,500 lbf and a density of approximately 76 lbs/ft3, making it one of the hardest and densest woods ideal for heavy structural beams. Hemlock, with a lower Janka hardness of about 490 lbf and a density near 31 lbs/ft3, provides moderate strength and is more suitable for light to medium load-bearing applications. The superior compressive strength of Lignum vitae, roughly 12,000 psi compared to Hemlock's 4,700 psi, ensures greater durability and resistance under heavy loads in beam construction.
Durability and Rot Resistance
Lignum vitae is renowned for its exceptional durability and natural rot resistance, making it one of the hardest and densest woods ideal for beams exposed to harsh conditions. Hemlock, while moderately durable, is more susceptible to decay and insect damage unless properly treated, resulting in shorter service life for structural applications. For beam construction requiring longevity and minimal maintenance, lignum vitae outperforms hemlock due to its superior natural oils and dense grain structure.
Workability and Ease of Construction
Lignum vitae offers exceptional workability due to its dense, oily grain that resists wear and reduces friction during machining, making it suitable for precise beam construction. Hemlock is much easier to cut and shape because of its softer texture and straight grain, facilitating quicker assembly but potentially requiring extra treatment for durability. The choice between the two depends on project demands for strength versus speed and ease of workmanship in beam fabrication.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Lignum vitae, known for its exceptional density and durability, is significantly more expensive and less readily available than hemlock, which is more abundant and budget-friendly for beam construction. Hemlock offers lower upfront costs and widespread availability in North America, making it a cost-effective choice despite its lower hardness and longevity compared to lignum vitae. Project requirements and long-term performance expectations influence the selection, with lignum vitae favored for high-stress applications where cost is less restrictive.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lignum vitae offers exceptional durability and natural resistance to decay, reducing the need for chemical treatments, which enhances its environmental sustainability compared to many wood species. Hemlock, while more abundant and faster growing, tends to require more frequent replacement and chemical preservation, leading to higher environmental impacts over its lifecycle. Choosing Lignum vitae for beams supports longer-lasting structures and minimizes resource consumption, whereas Hemlock's sustainability depends heavily on responsible forest management and treatment practices.
Typical Applications in Beam Construction
Lignum vitae is prized in beam construction for its exceptional density and natural oil content, which provide superior durability and resistance to water, making it ideal for heavy-load structural beams in marine or outdoor environments. Hemlock, valued for its lightweight and ease of handling, is commonly used in interior framing and non-load-bearing beams where moderate strength is sufficient. Choosing between Lignum vitae and Hemlock depends on specific requirements such as load capacity, exposure to moisture, and longevity expectations in beam applications.
Choosing the Right Wood: Lignum Vitae vs Hemlock
Lignum vitae offers exceptional density, natural oils, and durability, making it ideal for heavy-load beams requiring high strength and resistance to decay. Hemlock, being lighter and more affordable, suits interior beams where structural demands are moderate and ease of handling is prioritized. Selecting between Lignum vitae and Hemlock depends on balancing factors like load capacity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints for optimal beam performance.
Infographic: Lignum vitae vs Hemlock for Beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com