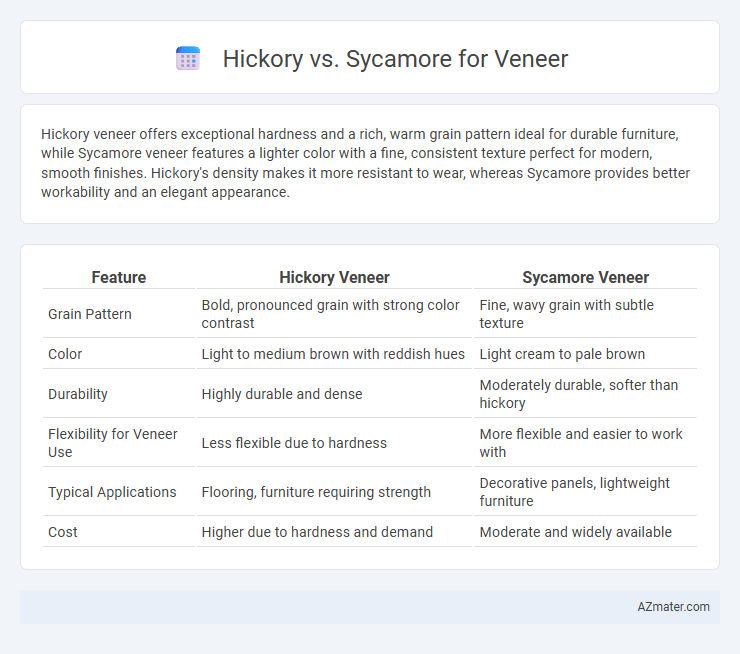
Hickory veneer offers exceptional hardness and a rich, warm grain pattern ideal for durable furniture, while Sycamore veneer features a lighter color with a fine, consistent texture perfect for modern, smooth finishes. Hickory's density makes it more resistant to wear, whereas Sycamore provides better workability and an elegant appearance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hickory Veneer | Sycamore Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Bold, pronounced grain with strong color contrast | Fine, wavy grain with subtle texture |
| Color | Light to medium brown with reddish hues | Light cream to pale brown |
| Durability | Highly durable and dense | Moderately durable, softer than hickory |
| Flexibility for Veneer Use | Less flexible due to hardness | More flexible and easier to work with |
| Typical Applications | Flooring, furniture requiring strength | Decorative panels, lightweight furniture |
| Cost | Higher due to hardness and demand | Moderate and widely available |
Introduction to Hickory and Sycamore Veneer
Hickory veneer is prized for its exceptional hardness, distinct grain patterns, and rich color variations, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry that require durability and visual appeal. Sycamore veneer offers a lighter, more uniform texture with subtle grain, providing an elegant and refined appearance often favored for interior paneling and decorative accents. Both veneers deliver unique aesthetic qualities and performance attributes, with hickory emphasizing strength and boldness, while sycamore highlights smoothness and light coloration.
Botanical Overview: Hickory vs Sycamore
Hickory, belonging to the genus Carya, is renowned for its dense hardwood and distinctive grain patterns, featuring strong shock resistance and durability ideal for veneer applications. Sycamore, from the genus Platanus, exhibits a lighter, more uniform texture with pale coloration and subtle figuring, offering a softer and more consistent veneer surface. Both species present unique botanical characteristics influencing veneer appearance, with hickory's complex grain contrasting Sycamore's smooth, fine texture.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Hickory veneer exhibits a rich, warm appearance with pronounced color variation ranging from creamy white to reddish-brown and features bold, irregular grain patterns that create a dynamic, rustic look. Sycamore veneer offers a lighter, more uniform cream to pale brown color with subtle grain patterns that appear straight or slightly wavy, lending a smooth and elegant aesthetic. The contrasting boldness of Hickory grains suits designs desiring strong visual impact, while Sycamore's softer, consistent grain pattern enhances understated sophistication in veneer applications.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Hickory veneer exhibits exceptional durability and hardness, ranking around 1820 on the Janka hardness scale, making it one of the toughest domestic hardwoods ideal for high-traffic areas. Sycamore veneer, with a Janka hardness around 950, is significantly softer and less resistant to dents and wear compared to Hickory. Choosing Hickory veneer ensures superior longevity and scratch resistance, while Sycamore offers aesthetic appeal but requires more careful maintenance due to its lower hardness rating.
Workability in Veneer Application
Hickory offers excellent workability for veneer applications due to its dense grain and strength, allowing for smooth slicing without excessive splintering. Sycamore, while also popular for veneer, features a more uniform texture and moderate hardness that supports easy cutting and consistent adhesion. Both species provide reliable bonding surfaces, but hickory's resilience makes it preferable for high-traffic furniture veneers requiring durability.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Hickory veneer generally costs more due to its dense grain and durability, making it a popular choice for high-end furniture and cabinetry. Sycamore veneer is more affordable and widely available because of its faster growth rate and abundance in North American forests. Availability fluctuations for Hickory depend on regional harvesting restrictions, while Sycamore maintains consistent market supply.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Hickory veneer is harvested from slower-growing trees, making it a more sustainable choice due to its durability and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacement. Sycamore veneer comes from faster-growing species, which can be more rapidly replenished, yet its softer wood may require more maintenance and replacement over time. Both options support sustainable forestry practices when sourced from certified suppliers adhering to responsible harvesting and reforestation guidelines.
Common Uses in Interior Design
Hickory veneer is prized for its strength and distinctive grain, making it ideal for rustic cabinetry, flooring, and furniture that require durability and a warm, natural aesthetic. Sycamore veneer, with its fine, consistent texture and light color, is commonly used in modern interior design elements such as wall panels, decorative inlays, and contemporary furniture for a clean, elegant look. Both veneers enhance interior spaces by providing unique visual appeal while supporting functional design needs.
Pros and Cons of Hickory Veneer
Hickory veneer offers exceptional durability and a rich, varied grain pattern that adds warmth and character to furniture and cabinetry, making it a popular choice for rustic and traditional designs. Its hardness ensures excellent resistance to dents and scratches, though this can also make it more challenging to work with compared to softer veneers like sycamore. Hickory's darker tones may overshadow subtle finishes, whereas sycamore veneer features lighter, more uniform coloring that better suits contemporary aesthetics but lacks hickory's robustness.
Pros and Cons of Sycamore Veneer
Sycamore veneer offers a fine, uniform texture with a light, creamy color that brightens interior spaces and provides excellent versatility for furniture and paneling. Its stability and resistance to warping make it a durable choice for veneers, while its subtle grain pattern can sometimes lack the character found in Hickory's more pronounced, rustic appearance. The main drawbacks of Sycamore veneer include its lower hardness compared to Hickory, which makes it more susceptible to dents and scratches, and its lighter color, which may require staining to match darker design schemes.
Infographic: Hickory vs Sycamore for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com