Hickory offers superior strength and durability for drawers, making it ideal for heavy use and long-lasting performance. Alder provides a softer, smoother finish with natural grain patterns, perfect for aesthetic appeal in furniture drawers.
Table of Comparison
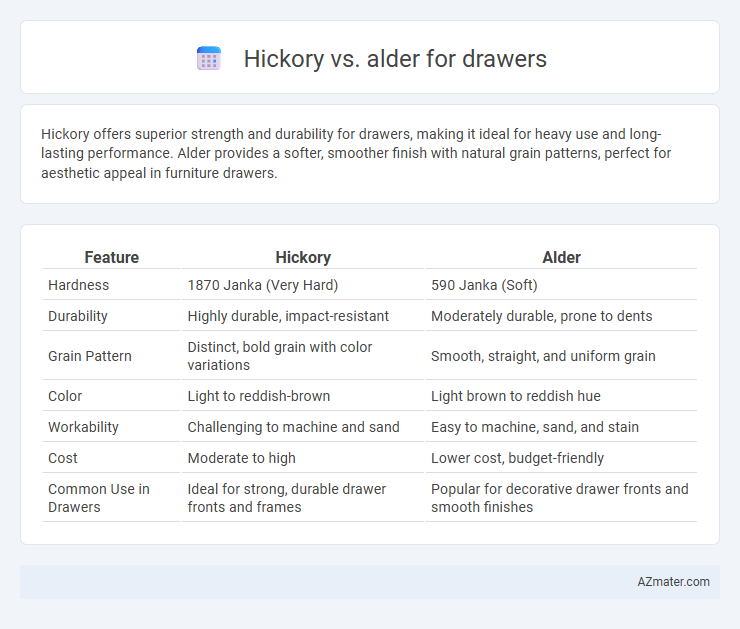
| Feature | Hickory | Alder |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | 1870 Janka (Very Hard) | 590 Janka (Soft) |
| Durability | Highly durable, impact-resistant | Moderately durable, prone to dents |
| Grain Pattern | Distinct, bold grain with color variations | Smooth, straight, and uniform grain |
| Color | Light to reddish-brown | Light brown to reddish hue |
| Workability | Challenging to machine and sand | Easy to machine, sand, and stain |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Common Use in Drawers | Ideal for strong, durable drawer fronts and frames | Popular for decorative drawer fronts and smooth finishes |
Introduction: Hickory vs Alder for Drawer Construction
Hickory and alder are two popular wood choices for drawer construction, each offering unique characteristics. Hickory is known for its exceptional hardness and durability, making it ideal for drawers that require long-lasting strength and resistance to wear. Alder provides a softer, fine-grained texture with a warm, uniform color suitable for smooth finishes and a more flexible design approach.
Wood Characteristics: Hickory vs Alder
Hickory is renowned for its exceptional hardness and durability, with a Janka hardness rating of 1,820, making it highly resistant to dents and scratches, ideal for heavy-use drawers. Alder, softer with a Janka rating of around 590, offers a smoother, more uniform grain and takes stains evenly, providing a warm, consistent appearance. Hickory's pronounced grain and color variation contrast with Alder's subtle, fine grain, influencing both aesthetics and maintenance in drawer construction.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Hickory offers superior durability and strength for drawers due to its dense, hard grain structure, making it highly resistant to dents and wear over time. Alder, while softer and easier to work with, is less durable and more prone to dents and scratches, requiring more maintenance in high-use areas. For long-lasting drawer construction, hickory is the preferred choice, especially in environments demanding heavy use and impact resistance.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Hickory features a bold, varied grain pattern with dark streaks and contrasting tones that create a rustic, dynamic appearance ideal for statement drawer fronts. Alder offers a more uniform, smooth grain with subtle knots and a warm, reddish-brown color that suits a softer, classic aesthetic in cabinetry. Both woods provide distinct visual textures, with Hickory emphasizing rugged character and Alder highlighting gentle elegance.
Workability: Ease of Crafting Drawers
Hickory is a dense hardwood known for its strength and durability, which can make crafting drawers more challenging due to its hardness and resistance to cutting and sanding. Alder, being a softer hardwood, offers superior workability with easier cutting, shaping, and sanding, making it a preferred choice for intricate drawer designs and fine joinery. Woodworkers often select alder for projects requiring seamless finishes and detailed craftsmanship, while hickory is chosen where robustness and long-term wear resistance are prioritized.
Cost and Availability
Hickory cabinets typically cost more than alder due to their denser grain and greater durability, commanding higher prices in both raw lumber and finished drawer components. Alder is more readily available and budget-friendly, often sourced from sustainable plantations, making it a popular choice for cost-conscious projects. Availability fluctuations of hickory can also lead to longer lead times, whereas alder's widespread supply ensures quicker procurement for cabinetry needs.
Weight and Density Differences
Hickory is significantly denser and heavier than alder, with a density of approximately 830 kg/m3 compared to alder's 560 kg/m3, making hickory a more durable option for drawers subjected to frequent use. The weight difference affects ease of handling during installation and contributes to the overall sturdiness of drawer construction. Choosing hickory results in a solid, long-lasting drawer, while alder offers a lighter, more manageable alternative with moderate strength.
Best Uses: Hickory and Alder in Drawer Applications
Hickory is ideal for drawers requiring exceptional durability and resistance to wear, making it perfect for heavy-use furniture like kitchen cabinets and tool chests. Alder offers a smooth, uniform grain and is well-suited for decorative drawers in bedroom dressers and living room furniture, where aesthetic appeal is prioritized over extreme hardness. Both woods provide excellent workability, but Hickory's hardness supports structural integrity, while Alder's softer texture allows for intricate carvings and finishes.
Finishing and Maintenance
Hickory drawer fronts offer a dense grain structure that accepts stains and finishes uniformly, resulting in a durable surface resistant to wear and scratches. Alder wood features a softer texture, making it more prone to dents and requiring gentler sanding before applying finishes, which typically enhances its natural reddish tone. Both woods benefit from regular sealing and maintenance, but hickory demands less frequent touch-ups due to its hardness and resilience against moisture and temperature changes.
Which Wood Should You Choose for Drawers?
Hickory offers superior hardness and durability, making it an excellent choice for drawers that require long-lasting wear resistance and strength. Alder provides a softer, smoother texture with rich, warm tones, ideal for drawers where aesthetic appeal and ease of staining are priorities. Choose hickory for heavy-use drawers and alder for decorative or lightly used drawer surfaces to balance functionality and design.
Infographic: Hickory vs Alder for Drawer
 azmater.com
azmater.com