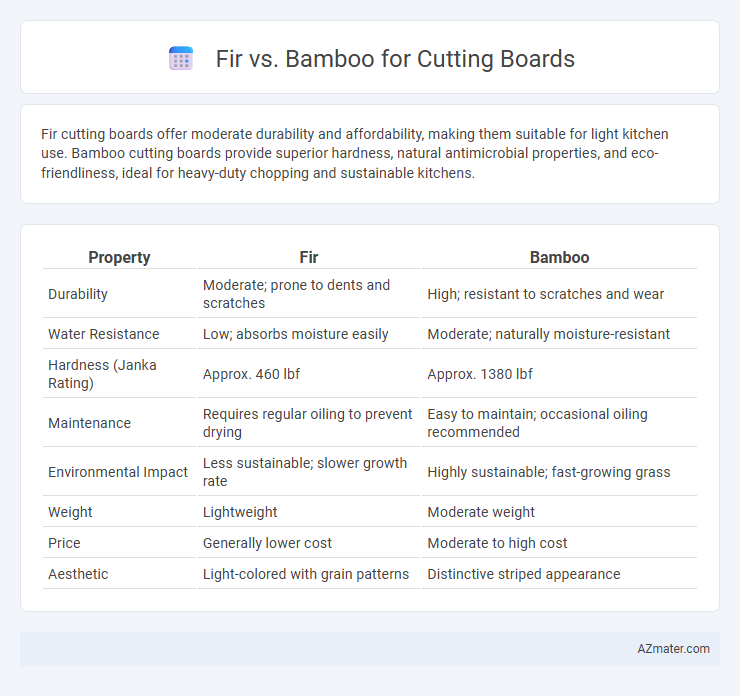
Fir cutting boards offer moderate durability and affordability, making them suitable for light kitchen use. Bamboo cutting boards provide superior hardness, natural antimicrobial properties, and eco-friendliness, ideal for heavy-duty chopping and sustainable kitchens.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fir | Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate; prone to dents and scratches | High; resistant to scratches and wear |
| Water Resistance | Low; absorbs moisture easily | Moderate; naturally moisture-resistant |
| Hardness (Janka Rating) | Approx. 460 lbf | Approx. 1380 lbf |
| Maintenance | Requires regular oiling to prevent drying | Easy to maintain; occasional oiling recommended |
| Environmental Impact | Less sustainable; slower growth rate | Highly sustainable; fast-growing grass |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Moderate to high cost |
| Aesthetic | Light-colored with grain patterns | Distinctive striped appearance |
Introduction: Fir vs Bamboo Cutting Boards
Fir and bamboo cutting boards each offer unique advantages for kitchen use. Fir boards are known for their softness and lightweight nature, which makes them gentle on knives but less durable for heavy chopping tasks. Bamboo cutting boards provide a harder, eco-friendly surface that resists moisture and bacteria, offering long-lasting performance ideal for frequent food preparation.
Material Composition and Sustainability
Fir cutting boards consist primarily of softwood with a lower density, making them lighter but more prone to dents and scratches compared to bamboo. Bamboo cutting boards are composed of rapidly renewable grass fibers tightly laminated, providing superior hardness and durability while resisting moisture and bacteria better. Bamboo's fast growth cycle and minimal need for pesticides enhance its sustainability profile, contrasting with fir, which requires longer growth periods and more intensive forestry management.
Durability and Longevity
Fir cutting boards are generally less durable and prone to dents and scratches due to their softwood nature, resulting in shorter longevity compared to bamboo. Bamboo cutting boards offer superior hardness and resistance to wear, making them more durable and capable of withstanding heavy, consistent use over time. The natural antibacterial properties of bamboo also contribute to maintaining its integrity and extending the board's lifespan.
Knife Friendliness and Surface Hardness
Fir cutting boards offer moderate surface hardness, providing a balance between durability and gentle knife impact, which helps preserve blade sharpness. Bamboo cutting boards are harder and more resistant to wear, but their dense fibers can dull knives faster compared to softer woods like fir. Choosing between fir and bamboo depends on prioritizing either knife friendliness, where fir excels, or long-lasting surface hardness, where bamboo stands out.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Fir cutting boards require regular oiling due to their porous softwood nature, which helps prevent moisture absorption and bacterial growth, while they are more prone to knife marks and stains. Bamboo cutting boards, made from dense, hard grass fibers, are naturally more resistant to moisture and bacteria, demanding less frequent oiling and easier cleaning with mild soap and warm water. Both materials should be thoroughly dried after washing to maintain durability and hygiene, but bamboo offers superior resistance to warping and cracking under regular maintenance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Fir cutting boards showcase a warm, reddish-brown hue with distinct grain patterns that add rustic charm to kitchen aesthetics. Bamboo boards offer a modern, sleek appearance with their fine, uniform texture and natural light color variations, enhancing minimalist and contemporary designs. Both materials provide versatile design options, but bamboo's eco-friendly profile and smooth finish often appeal to those seeking stylish, sustainable kitchenware.
Resistance to Bacteria and Odors
Bamboo cutting boards exhibit higher resistance to bacteria and odors due to their natural antimicrobial properties and dense fiber structure, which inhibits microbial growth and absorption of strong smells. Fir cutting boards, composed of softer wood with more porous surfaces, tend to retain moisture and odors more easily, creating a favorable environment for bacteria. Choosing bamboo enhances hygiene and durability for prolonged kitchen use.
Cost Comparison: Fir vs Bamboo
Fir cutting boards are generally more affordable due to the wide availability of fir wood, making them a budget-friendly option for kitchen use. Bamboo cutting boards, while slightly more expensive, offer enhanced durability and resistance to moisture, which can justify the higher initial cost over time. Consumers seeking cost efficiency often weigh fir's lower price against bamboo's long-term value and sustainability benefits.
Environmental Impact and Eco-Friendliness
Fir cutting boards have a lower environmental impact due to their rapid growth and sustainable harvesting practices, making them a renewable resource with minimal deforestation effects. Bamboo cutting boards outperform many hardwoods in eco-friendliness because bamboo grows incredibly fast, requires no pesticides, and helps reduce soil erosion, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Both materials offer sustainable options, but bamboo's regenerative properties and durability often position it as the greener choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Which Cutting Board Material is Right for You?
Fir cutting boards offer a lightweight, durable option with natural antibacterial properties, making them ideal for everyday kitchen use. Bamboo cutting boards are highly eco-friendly, resistant to knife scars, and require less maintenance, appealing to environmentally-conscious cooks seeking longevity. Choosing between fir and bamboo depends on your preferences for weight, sustainability, and ease of upkeep in your culinary workspace.
Infographic: Fir vs Bamboo for Cutting Board
 azmater.com
azmater.com