Elm veneer offers a unique interlocking grain pattern with high durability and excellent resistance to splitting, making it ideal for furniture requiring strength and aesthetic appeal. Poplar veneer is lightweight, smooth, and easy to stain, often favored for painted finishes and cost-effective projects due to its uniform texture and affordability.
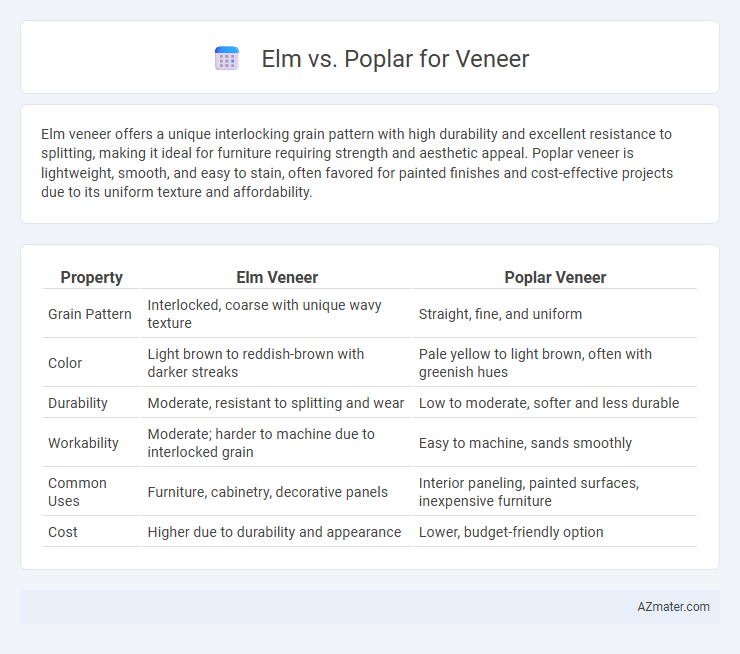
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elm Veneer | Poplar Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Interlocked, coarse with unique wavy texture | Straight, fine, and uniform |
| Color | Light brown to reddish-brown with darker streaks | Pale yellow to light brown, often with greenish hues |
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to splitting and wear | Low to moderate, softer and less durable |
| Workability | Moderate; harder to machine due to interlocked grain | Easy to machine, sands smoothly |
| Common Uses | Furniture, cabinetry, decorative panels | Interior paneling, painted surfaces, inexpensive furniture |
| Cost | Higher due to durability and appearance | Lower, budget-friendly option |
Introduction to Elm and Poplar Veneer
Elm veneer is prized for its intricate grain patterns and durability, making it ideal for decorative woodwork and furniture. Poplar veneer offers a lighter, uniform texture with excellent workability, often used in painted finishes and interior applications. Both woods provide versatile options, with elm delivering rich aesthetics and poplar favored for smooth, stable surfaces.
Botanical Profile: Elm vs Poplar
Elm trees, belonging to the Ulmaceae family, feature serrated leaves and a distinctive net-like grain pattern in their veneer, offering durability and an attractive texture. Poplar, from the Salicaceae family, presents a lighter color with a straighter, more uniform grain, making it easier to work with and ideal for smooth, consistent decorative finishes. Elm's open pores and interlocking grain contrast with Poplar's fine, closed texture, influencing both the aesthetic and functional properties in veneer applications.
Grain Patterns and Aesthetic Appeal
Elm veneer showcases an intricate interlocking grain pattern with prominent swirling and cathedrals that add dynamic visual interest, making it a favored choice for rustic and traditional interiors. Poplar veneer, by contrast, features a straighter, more uniform grain with subtle, muted patterns that provide a smoother, cleaner aesthetic ideal for modern and minimalist designs. The warm, varied coloration of Elm enhances its unique appeal, while Poplar's consistent pale tones offer versatility in staining and finishing options.
Color Variations and Finishes
Elm veneer features rich color variations ranging from pale honey to deep reddish-brown, offering a warm, natural aesthetic that enhances rustic and traditional designs. Poplar veneer exhibits more consistent pale yellow to light greenish hues, providing a smoother, more neutral base ideal for painted or stained finishes. Elm's open grain pattern accepts stains well, creating striking depth, while Poplar's fine, uniform texture delivers a smooth finish preferred for modern, clean looks.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Elm veneer exhibits superior strength and durability due to its interlocking grain pattern, which resists splitting and warping over time. Poplar veneer, while less dense, offers moderate strength and is more prone to dents and scratches, making it less durable under heavy use. For applications requiring long-lasting resilience, elm is generally the preferred choice over poplar.
Workability and Machining Properties
Elm veneer excels in workability due to its interlocked grain, which enhances strength but can cause occasional difficulty in machining, requiring sharp tools to prevent tear-out. Poplar veneer offers superior machining properties with its fine, straight grain, allowing for smooth cuts and easy processing, making it ideal for detailed work and intricate designs. While Elm provides durability and resistance to splitting, Poplar stands out for its consistent finish and ease of sanding, optimizing production efficiency.
Cost and Availability of Veneers
Elm veneer generally commands a higher price due to its limited availability and distinctive grain patterns, making it a premium choice for furniture and decorative applications. Poplar veneer is more cost-effective and widely available, favored for its consistent color and ease of workability in mass production. The choice between elm and poplar veneers often depends on budget constraints and the desired aesthetic impact within project requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elm veneer is prized for its durability and natural grain but typically has a higher environmental impact due to slower growth rates and less widespread availability compared to poplar. Poplar veneer offers a more sustainable choice, characterized by rapid growth, efficient carbon sequestration, and frequent cultivation in managed plantations that reduce deforestation risks. Selecting poplar over elm can significantly lower the carbon footprint of veneer products while supporting sustainable forestry practices and ecosystem conservation.
Common Applications in Woodworking
Elm veneer is favored for furniture making and cabinetry due to its interlocking grain, which provides both strength and distinctive wavy patterns enhancing visual appeal. Poplar veneer is commonly used in interior paneling, moldings, and painted furniture because of its smooth texture and uniform grain that accepts finishes well. Both woods serve niche roles in woodworking, with elm preferred for decorative strength and poplar chosen for its workability and paint compatibility.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Elm and Poplar for Veneer
Elm veneer offers a distinctive grain pattern and durability, making it ideal for decorative furniture and intricate woodworking projects, while poplar veneer provides a smooth, uniform texture that is easier to stain and paint for a versatile finish. Selecting between elm and poplar veneer depends on whether the priority is aesthetic uniqueness and strength or cost-effectiveness and ease of customization. For high-end applications requiring character and resilience, elm is preferred, whereas poplar suits budget-conscious projects needing a consistent surface.
Infographic: Elm vs Poplar for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com