Elm offers exceptional durability and a rich, interlocking grain ideal for high-end millwork, while poplar provides a softer, more uniform texture that is easier to paint and cost-effective for detailed trim. Choosing between elm and poplar hinges on prioritizing strength and natural beauty versus finish versatility and budget.
Table of Comparison
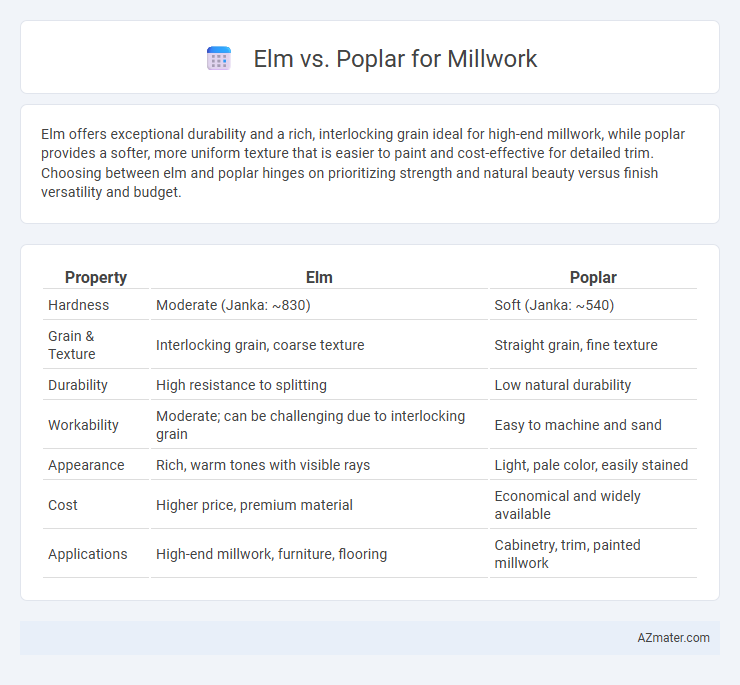
| Property | Elm | Poplar |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Moderate (Janka: ~830) | Soft (Janka: ~540) |
| Grain & Texture | Interlocking grain, coarse texture | Straight grain, fine texture |
| Durability | High resistance to splitting | Low natural durability |
| Workability | Moderate; can be challenging due to interlocking grain | Easy to machine and sand |
| Appearance | Rich, warm tones with visible rays | Light, pale color, easily stained |
| Cost | Higher price, premium material | Economical and widely available |
| Applications | High-end millwork, furniture, flooring | Cabinetry, trim, painted millwork |
Introduction to Elm and Poplar for Millwork
Elm offers exceptional strength and interlocking grain patterns, making it ideal for millwork requiring durability and unique textures. Poplar features a fine, uniform grain and is easy to machine, providing a smooth surface for painting or staining in millwork applications. Both woods balance performance and aesthetics, with elm favored for structural integrity and poplar preferred for versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Botanical Overview: Elm vs Poplar
Elm trees, belonging to the genus Ulmus, are hardwood species characterized by interlocking grain and a coarse texture, making their wood durable and resistant to splitting, ideal for millwork requiring strength and longevity. Poplar, from the genus Liriodendron, is a softer hardwood with a fine, even texture and straight grain, offering ease of machining and a smooth finish commonly favored for painted millwork and cabinetry. Botanical differences influence wood properties: elm's fibrous structure contributes to its toughness, while poplar's faster growth results in a lighter, more uniform material suitable for intricate shaping.
Grain Patterns and Aesthetic Appeal
Elm exhibits interlocking grain patterns with a coarse texture that offers a unique, rustic aesthetic ideal for traditional millwork designs. Poplar features a straight, fine grain with a smooth texture, providing a uniform appearance well-suited for painted finishes and contemporary millwork projects. The choice between Elm's distinctive, natural character and Poplar's clean, versatile look depends on the desired visual impact and style preference.
Workability and Machining Characteristics
Elm offers excellent workability with moderate hardness that allows for smooth machining, making it suitable for detailed millwork and intricate joinery. Poplar is softer and more uniform in texture, providing superior ease of cutting, shaping, and sanding, which reduces wear on tools and enables faster production. Both woods respond well to hand and machine tools, but Poplar's consistent grain minimizes tear-out, enhancing precision in machining tasks.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Elm offers superior strength and flexibility due to its interlocking grain, making it highly resistant to splitting and ideal for millwork requiring durability under stress. Poplar, while easier to work with and more stable in low-moisture conditions, is softer and less durable, often susceptible to dents and wear over time. For millwork projects demanding long-term structural integrity and resistance to impact, elm stands out as the more robust and durable choice.
Stability and Resistance to Warping
Elm wood offers excellent stability and natural resistance to warping due to its interlocking grain structure, making it ideal for millwork in environments with fluctuating humidity. Poplar, while softer and more affordable, tends to be less stable and more prone to warping under moisture changes, requiring careful sealing and finishing. For millwork projects prioritizing long-term durability and minimal deformation, elm provides superior performance compared to poplar.
Finishing Qualities: Staining and Painting
Elm offers excellent finishing qualities with a smooth grain that readily accepts stains for a rich, warm appearance, making it ideal for millwork requiring a natural wood look. Poplar, favored for its uniform texture, holds paint exceptionally well, providing a smooth, even surface that minimizes brush marks and enhances color vibrancy. Both woods are versatile, but Poplar's consistent absorption makes it preferable for painted millwork, while Elm's natural grain shines under stain finishes.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Elm offers moderate cost efficiency with good durability, but its availability can be limited due to slower growth rates and regional supply constraints. Poplar is widely available and tends to be more cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious millwork projects without compromising ease of machining and finishing. Both woods provide stable performance, but Poplar's broader availability often results in quicker turnaround times and lower overall material costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elm wood offers moderate sustainability with its fast growth rate and natural resistance to pests, contributing to reduced chemical use in millwork production. Poplar is highly favored for eco-friendly millwork due to its rapid growth, ability to thrive in diverse soils, and efficient carbon sequestration, minimizing its environmental footprint. Choosing Poplar over Elm supports sustainable forestry practices and lowers the overall ecological impact in woodcraft manufacturing.
Best Applications for Elm and Poplar in Millwork
Elm is ideal for millwork requiring durability and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for window frames, doors, and furniture with intricate detailing. Poplar is favored for interior millwork, including moldings, trim, and cabinetry, due to its smooth grain, ease of painting, and affordability. Both woods offer versatility, but elm's interlocking grain provides strength for structural millwork, while poplar excels in applications demanding a uniform finish.
Infographic: Elm vs Poplar for Millwork
 azmater.com
azmater.com