Elm flooring offers exceptional durability and a unique open grain pattern ideal for high-traffic areas, while maple provides a hard, smooth surface with a consistent, light color perfect for modern interiors. Both woods are highly resistant to wear, but elm tends to absorb shock better, making it suitable for active households.
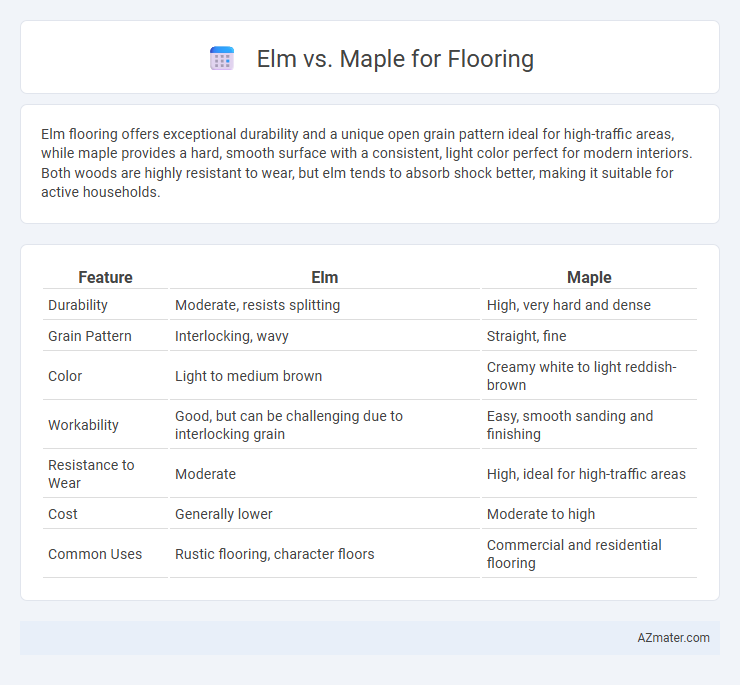
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elm | Maple |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, resists splitting | High, very hard and dense |
| Grain Pattern | Interlocking, wavy | Straight, fine |
| Color | Light to medium brown | Creamy white to light reddish-brown |
| Workability | Good, but can be challenging due to interlocking grain | Easy, smooth sanding and finishing |
| Resistance to Wear | Moderate | High, ideal for high-traffic areas |
| Cost | Generally lower | Moderate to high |
| Common Uses | Rustic flooring, character floors | Commercial and residential flooring |
Introduction to Elm vs Maple Flooring
Elm and maple flooring each offer unique characteristics suited to different design preferences and durability needs. Elm features a distinctive grain pattern with interlocking fibers that provide natural resistance to wear and moisture, ideal for high-traffic areas. Maple flooring boasts a smooth, light-toned surface with exceptional hardness and fine texture, making it a popular choice for modern, sleek interiors.
Key Characteristics of Elm Wood
Elm wood for flooring offers exceptional durability and resistance to splitting, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Its interlocking grain pattern provides unique visual texture and helps prevent warping or twisting over time. Compared to maple, elm has a warmer, more rustic appearance with natural dark streaks that add character to flooring designs.
Key Characteristics of Maple Wood
Maple wood stands out in flooring for its exceptional hardness and durability, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Its fine, uniform grain provides a smooth surface that enhances both aesthetic appeal and resistance to wear. Compared to Elm, Maple offers a lighter color palette and greater stability, reducing the likelihood of warping or cupping over time.
Visual Differences: Grain and Color
Elm flooring features a distinctive grain pattern characterized by interlocking and wavy lines that create a dynamic, textured appearance, often highlighted by variations in color intensity ranging from light tan to reddish-brown. Maple flooring offers a smoother, more uniform grain with subtle, consistent patterns and a lighter, creamy white to pale golden color that brightens interior spaces. The visual contrast between elm's bold, rustic grain and maple's clean, refined look makes each wood type ideal for different design aesthetics, with elm adding warmth and character while maple delivers a sleek, modern feel.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Elm flooring offers moderate durability and a Janka hardness rating of approximately 830, making it resistant to everyday wear and suitable for moderate traffic areas. Maple flooring is significantly harder, with a Janka hardness of about 1450, providing superior resistance to dents and scratches and ideal for high-traffic spaces. The increased hardness of maple makes it a more durable choice for flooring applications where longevity and resilience are priorities.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Elm flooring offers a durable surface with a moderately high resistance to wear, requiring regular sweeping and occasional refinishing to maintain its natural beauty. Maple flooring features a dense grain structure that resists scratches and stains, benefiting from routine cleaning with pH-neutral cleaners and periodic polishing to preserve its smooth finish. Both materials demand prompt spill cleanup and controlled humidity levels to prevent warping and ensure long-lasting performance.
Cost Comparison: Elm vs Maple Flooring
Elm flooring typically costs between $5 and $8 per square foot, making it a more affordable option compared to maple, which ranges from $7 to $10 per square foot. The price difference is influenced by the wood's availability, hardness, and demand in the flooring market. Homeowners seeking budget-friendly hardwood flooring often prefer elm for its distinctive grain and cost-effectiveness without sacrificing durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elm flooring offers strong durability with a moderate environmental footprint, as its wood is often sourced from sustainably managed forests and is biodegradable. Maple flooring, favored for its hardness and longevity, typically comes from faster-growing trees, which can lead to more efficient resource renewal and less ecological strain. Both woods support sustainability when certified by organizations like FSC, but maple's quicker growth cycle often translates to a lower overall environmental impact.
Best Use Cases for Each Wood Type
Elm flooring excels in high-traffic areas due to its exceptional toughness and natural resistance to splitting, making it ideal for family rooms and hallways. Maple offers a smooth, fine grain and superior hardness, providing durability and a clean, modern aesthetic suited for kitchens and contemporary living spaces. Both woods handle wear well, but elm's rustic charm complements traditional interiors, while maple's light, uniform appearance enhances minimalist designs.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Elm and Maple
Elm flooring offers exceptional durability with a rustic appearance and natural resistance to moisture, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and homes prone to humidity. Maple provides a smooth, consistent grain pattern and a lighter, contemporary look with impressive hardness that resists dents and scratches. Selecting between elm and maple flooring depends on whether you prioritize a warm, textured aesthetic with moisture resilience or a clean, modern finish with superior hardness for long-lasting wear.
Infographic: Elm vs Maple for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com