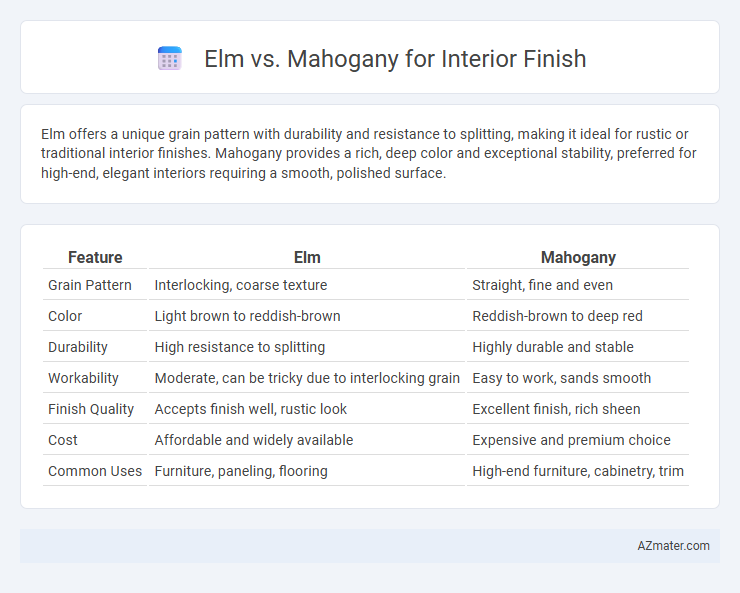
Elm offers a unique grain pattern with durability and resistance to splitting, making it ideal for rustic or traditional interior finishes. Mahogany provides a rich, deep color and exceptional stability, preferred for high-end, elegant interiors requiring a smooth, polished surface.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elm | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Interlocking, coarse texture | Straight, fine and even |
| Color | Light brown to reddish-brown | Reddish-brown to deep red |
| Durability | High resistance to splitting | Highly durable and stable |
| Workability | Moderate, can be tricky due to interlocking grain | Easy to work, sands smooth |
| Finish Quality | Accepts finish well, rustic look | Excellent finish, rich sheen |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available | Expensive and premium choice |
| Common Uses | Furniture, paneling, flooring | High-end furniture, cabinetry, trim |
Introduction to Elm and Mahogany in Interior Design
Elm wood features a distinctive interlocking grain, offering exceptional strength and resistance to splitting, making it ideal for durable interior finishes. Mahogany is prized for its rich, reddish-brown hue and smooth texture, providing a luxurious and timeless appeal in interior design. Both woods offer unique characteristics that enhance cabinetry, furniture, and paneling, balancing durability with aesthetic elegance.
Appearance and Grain Patterns Comparison
Elm wood features a distinctive interlocking grain with dramatic wavy and cathedral patterns, offering a rustic yet elegant appearance ideal for unique interior finishes. Mahogany presents a smoother, more uniform grain with rich reddish-brown hues and a fine, straight texture that exudes classic luxury and warmth. The contrasting grain patterns make elm suitable for striking, dynamic designs, while mahogany provides a consistently refined and polished look for sophisticated interior spaces.
Durability and Hardness: Elm vs Mahogany
Elm wood offers moderate durability and hardness, making it resistant to splitting and suitable for interior finishes exposed to wear. Mahogany, known for its exceptional hardness and durability, withstands scratches and dents better, providing a long-lasting, premium finish for interiors. When comparing Elm vs Mahogany, mahogany's superior density and resistance to decay make it ideal for high-traffic areas, while elm suits moderately used spaces with its balanced toughness.
Cost Differences
Elm wood generally costs less than mahogany, making it a more budget-friendly option for interior finishes. Mahogany, known for its rich color and durability, commands a higher price due to its premium quality and slower growth rate. The cost difference can significantly impact overall project expenses, with mahogany often priced two to three times higher than elm.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Elm offers excellent workability due to its interlocking grain, making it easy to plane and shape without significant splintering, which simplifies installation for interior finishes. Mahogany, known for its smooth texture and consistent grain, allows for precise cutting and sanding, enhancing ease of fitting and achieving a polished final look. Both woods provide excellent machinability, but elm's toughness slightly increases effort during installation compared to the more manageable mahogany.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Elm offers a highly sustainable choice for interior finishes due to its rapid growth rate and natural resistance to pests, reducing the need for chemical treatments. Mahogany, while prized for its rich color and durability, often faces criticism for deforestation and slower replenishment rates in tropical hardwood forests. Choosing elm supports eco-friendly practices and a lower environmental impact, aligning with sustainable forestry certifications such as FSC and PEFC.
Maintenance and Longevity
Elm wood offers moderate maintenance requirements due to its open grain, which may need periodic sealing to prevent moisture damage, while mahogany features a naturally dense and oily composition that resists decay and requires less frequent upkeep. Mahogany's superior durability provides a longer lifespan for interior finishes, maintaining its rich color and structural integrity over decades with minimal effort. Elm, although visually appealing and strong, generally has a shorter lifespan and greater vulnerability to scratches and dents compared to the more resilient mahogany.
Popular Uses in Interior Finishes
Elm wood is highly favored for interior finishes due to its attractive grain patterns and natural resistance to splitting, making it ideal for flooring, paneling, and furniture that require durability and aesthetic appeal. Mahogany is prized for its rich, deep reddish-brown color and smooth texture, commonly used in high-end cabinetry, moldings, and luxury furniture, offering a timeless, elegant look. Both woods provide excellent workability, but mahogany's superior resistance to moisture and decay makes it especially popular in humid interior environments.
Design Styles Best Suited for Each Wood
Elm's distinctive grain patterns and warm tones complement rustic, farmhouse, and traditional interior design styles by adding natural texture and character. Mahogany's deep reddish-brown hue and smooth finish suit classic, colonial, and luxurious interiors, enhancing elegance and refinement. Both woods provide versatile aesthetics, but elm excels in creating cozy and organic atmospheres, while mahogany elevates formal and sophisticated spaces.
Choosing Between Elm and Mahogany for Your Project
Elm offers a striking grain pattern and excellent durability, making it ideal for rustic or traditional interior finishes where texture and warmth are desired. Mahogany provides a rich, deep red-brown hue with fine grain, preferred for elegant, high-end furniture and cabinetry requiring superior stability and resistance to warping. Choosing between elm and mahogany depends on the project's aesthetic goals, budget constraints, and the need for hardness and workability in the interior finish.
Infographic: Elm vs Mahogany for Interior Finish
 azmater.com
azmater.com