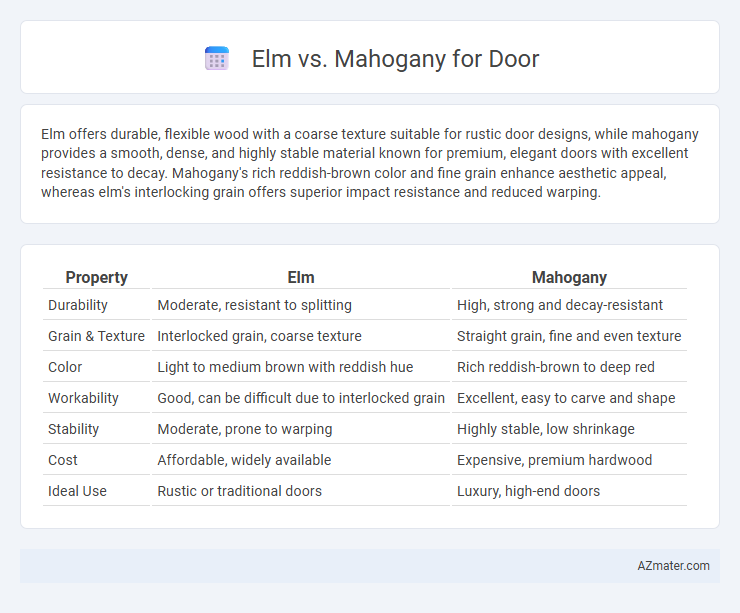
Elm offers durable, flexible wood with a coarse texture suitable for rustic door designs, while mahogany provides a smooth, dense, and highly stable material known for premium, elegant doors with excellent resistance to decay. Mahogany's rich reddish-brown color and fine grain enhance aesthetic appeal, whereas elm's interlocking grain offers superior impact resistance and reduced warping.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elm | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to splitting | High, strong and decay-resistant |
| Grain & Texture | Interlocked grain, coarse texture | Straight grain, fine and even texture |
| Color | Light to medium brown with reddish hue | Rich reddish-brown to deep red |
| Workability | Good, can be difficult due to interlocked grain | Excellent, easy to carve and shape |
| Stability | Moderate, prone to warping | Highly stable, low shrinkage |
| Cost | Affordable, widely available | Expensive, premium hardwood |
| Ideal Use | Rustic or traditional doors | Luxury, high-end doors |
Introduction to Elm and Mahogany as Door Materials
Elm offers a durable, flexible hardwood with natural resistance to splitting and shock, making it ideal for doors requiring strength and longevity. Mahogany, prized for its deep reddish-brown color and fine grain, provides exceptional stability and resistance to moisture, enhancing door aesthetics and durability. Both woods deliver unique qualities suited for high-quality doors, with elm excelling in toughness and mahogany favored for elegance and weather resistance.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability Comparison
Elm wood boasts exceptional strength and natural resistance to splitting due to its interlocking grain, making it highly durable for door construction. Mahogany features a dense, tight grain pattern that offers excellent stability, decay resistance, and long-lasting durability under various environmental conditions. Both woods provide robust performance, but mahogany typically exhibits superior moisture resistance and longevity in outdoor applications compared to elm.
Aesthetic Appeal: Grain Patterns and Color Variations
Elm wood features distinctive interlocking grain patterns with a coarse texture, providing a rustic and natural aesthetic ideal for doors that emphasize organic charm. Mahogany offers a smooth, straight grain with rich reddish-brown hues that deepen over time, delivering a luxurious and elegant appearance favored for high-end door designs. Both woods exhibit unique color variations and grain characteristics, with elm showcasing more dramatic contrast and mahogany presenting consistent warmth, influencing the overall visual impact of door projects.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Mahogany offers superior weather resistance due to its dense grain and natural oils that repel moisture, making it ideal for exterior doors exposed to harsh climates. Elm, while moderately durable, tends to absorb moisture more readily, which can lead to warping and reduced longevity in wet conditions. Choosing mahogany ensures longer-lasting door performance with minimal maintenance in variable weather environments.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Elm wood offers excellent workability due to its interlocking grain, allowing for precise shaping and smooth finishing, making it easier to handle during installation. Mahogany is prized for its uniform grain and softness, which enables clean cuts and effortless sanding, reducing labor time in door fitting. Both woods provide reliable ease of installation, with mahogany typically favored for intricate details and elm for robust structural components.
Cost Analysis: Elm vs Mahogany Doors
Elm doors generally offer a more budget-friendly option compared to mahogany, with elm wood costing approximately $5 to $7 per board foot, whereas mahogany ranges from $10 to $15 per board foot. The higher price of mahogany is due to its superior durability, rich color, and resistance to decay, making it a premium choice for long-lasting doors. Considering installation and maintenance, elm doors may incur slightly higher upkeep costs over time due to their softer nature, while mahogany's hardness and natural oils reduce long-term expenses despite the initial higher investment.
Maintenance Requirements and Upkeep
Elm doors require moderate maintenance due to their open grain structure, which benefits from regular sealing and periodic sanding to prevent moisture damage and warping. Mahogany doors offer superior durability and are naturally resistant to rot and insects, demanding less frequent upkeep but still benefiting from occasional refinishing to maintain their rich color and smooth surface. Both woods require proper sealing and protection from prolonged exposure to harsh weather to ensure long-term performance and aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elm doors offer higher sustainability due to the tree's rapid growth and natural resistance to pests, resulting in less chemical treatment and lower deforestation rates. Mahogany, often sourced from slow-growing tropical hardwoods, has a greater environmental impact due to habitat loss and unsustainable logging practices despite its durability. Choosing certified sustainable sources and responsible forestry practices is essential for minimizing the ecological footprint of both elm and mahogany doors.
Common Applications in Door Design
Elm wood offers exceptional flexibility and strength, making it ideal for curved or intricate door designs often found in traditional and rustic interiors. Mahogany's dense grain and rich reddish-brown color provide durability and luxurious aesthetics, commonly used in high-end, classic-style entry and interior doors. Both woods are prized for their resistance to warping and ability to take finishes well, ensuring longevity and beauty in door applications.
Choosing the Right Wood: Elm or Mahogany for Your Door
Elm wood offers exceptional durability and resistance to splitting, making it ideal for doors exposed to variable weather conditions, while its interlocking grain provides a unique, attractive texture. Mahogany delivers superior strength, a fine, straight grain, and rich reddish-brown color that enhances door aesthetics and longevity, especially in upscale settings. Selecting between elm and mahogany depends on your priority of weather resistance or premium appearance, with mahogany favored for luxury and elm for robust outdoor performance.
Infographic: Elm vs Mahogany for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com