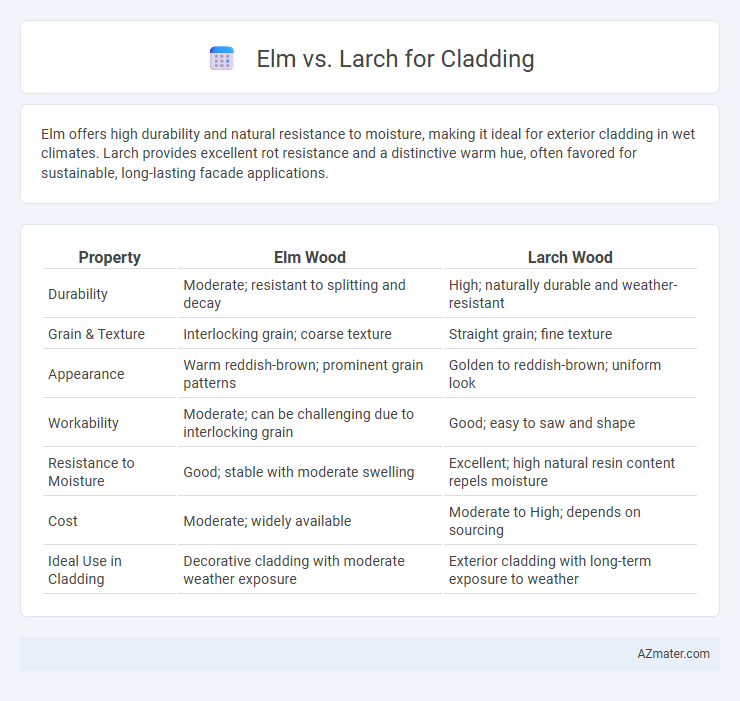
Elm offers high durability and natural resistance to moisture, making it ideal for exterior cladding in wet climates. Larch provides excellent rot resistance and a distinctive warm hue, often favored for sustainable, long-lasting facade applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elm Wood | Larch Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate; resistant to splitting and decay | High; naturally durable and weather-resistant |
| Grain & Texture | Interlocking grain; coarse texture | Straight grain; fine texture |
| Appearance | Warm reddish-brown; prominent grain patterns | Golden to reddish-brown; uniform look |
| Workability | Moderate; can be challenging due to interlocking grain | Good; easy to saw and shape |
| Resistance to Moisture | Good; stable with moderate swelling | Excellent; high natural resin content repels moisture |
| Cost | Moderate; widely available | Moderate to High; depends on sourcing |
| Ideal Use in Cladding | Decorative cladding with moderate weather exposure | Exterior cladding with long-term exposure to weather |
Introduction to Elm and Larch as Cladding Materials
Elm and Larch are popular timber choices for cladding due to their durability and aesthetic appeal. Elm wood features interlocking grain that provides resistance to splitting and natural decay, making it suitable for exterior applications. Larch offers a high resin content that enhances weather resistance and stability, ensuring long-lasting performance in cladding installations.
Appearance and Aesthetic Differences
Elm offers a rich, warm tone with intricate grain patterns and subtle color variations, creating a classic and rustic aesthetic ideal for traditional or craftsman-style cladding. Larch features a straighter grain with a lighter, golden hue that weathers to a silvery-gray, providing a more modern and natural look suited for contemporary and Scandinavian design. The dense texture of Elm emphasizes depth and character, while Larch's smoother and more uniform appearance enhances clean lines and minimalist cladding applications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Elm wood offers moderate durability and good resistance to weather, making it suitable for cladding in temperate climates with proper treatment to prevent decay. Larch stands out with high natural durability and exceptional weather resistance due to its dense resin content, enabling it to withstand harsh outdoor conditions with minimal maintenance. In comparison, larch cladding provides longer-lasting protection against moisture and insect damage than elm, making it a preferred choice for exterior applications in more demanding environments.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Elm wood offers high durability and natural resistance to pests, reducing the need for chemical treatments and lowering environmental impact in cladding applications. Larch is highly valued for its rapid growth and carbon sequestration abilities, making it a sustainable choice with a smaller ecological footprint. Both woods provide renewable resources with low embodied energy, but Larch's faster renewability typically gives it an edge in sustainable cladding solutions.
Workability and Installation
Elm offers excellent workability due to its interlocked grain, making it easier to cut, shape, and install for cladding projects. Larch, known for its natural durability and resistance to decay, can be more challenging to work with because of its dense, resinous nature which may require specialized tools during installation. Both woods provide strong cladding options, but elm's smoother handling often results in faster, more precise fitting on site.
Maintenance Requirements
Elm cladding requires regular maintenance due to its susceptibility to moisture and fungal decay, necessitating periodic sealing or treatment to preserve durability and appearance. Larch offers superior natural resistance to rot and insects, reducing the frequency of treatments and making it a low-maintenance option for exterior cladding. Both woods benefit from UV protection coatings to maintain color and structural integrity over time.
Cost Comparison
Elm cladding generally incurs higher costs due to its density and durability, making it more resistant to weather and wear. Larch offers a more budget-friendly option with moderate durability, often favored for its natural resistance to decay and insect damage. Installation expenses tend to be similar, but Elm's long-term maintenance costs may be lower, balancing the initial investment.
Insulation and Thermal Efficiency
Elm wood offers moderate insulation properties and natural thermal efficiency due to its dense grain structure, making it suitable for cladding in temperate climates. Larch, with its higher resin content and tighter growth rings, provides enhanced thermal insulation and better resistance to moisture infiltration, improving overall energy efficiency in building envelopes. Both woods contribute to sustainable construction, but Larch generally delivers superior thermal performance for cladding applications.
Common Applications in Cladding Projects
Elm cladding is favored for its durability and rich grain, making it ideal for exterior applications such as residential facades, garden structures, and decking where weather resistance is essential. Larch cladding offers superior rot resistance and dimensional stability, commonly used in commercial buildings, timber-framed houses, and public spaces exposed to harsh climates. Both woods enhance aesthetic appeal and protect structures, but Larch's natural oils provide better longevity in high-moisture environments.
Choosing the Right Timber: Elm vs Larch
Elm cladding offers exceptional durability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for areas prone to damp conditions, while its unique grain provides a distinctive aesthetic appeal. Larch, known for its high resin content and natural decay resistance, excels in outdoor environments with excellent dimensional stability and a warm, golden hue that enhances architectural designs. Choosing between elm and larch for cladding requires assessing the specific climate exposure, desired visual impact, and maintenance preferences to ensure long-lasting performance and beauty.
Infographic: Elm vs Larch for Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com