Douglas fir offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for durable exterior doors. Ash provides superior hardness and a distinct grain pattern, preferred for aesthetic interior doors requiring high impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
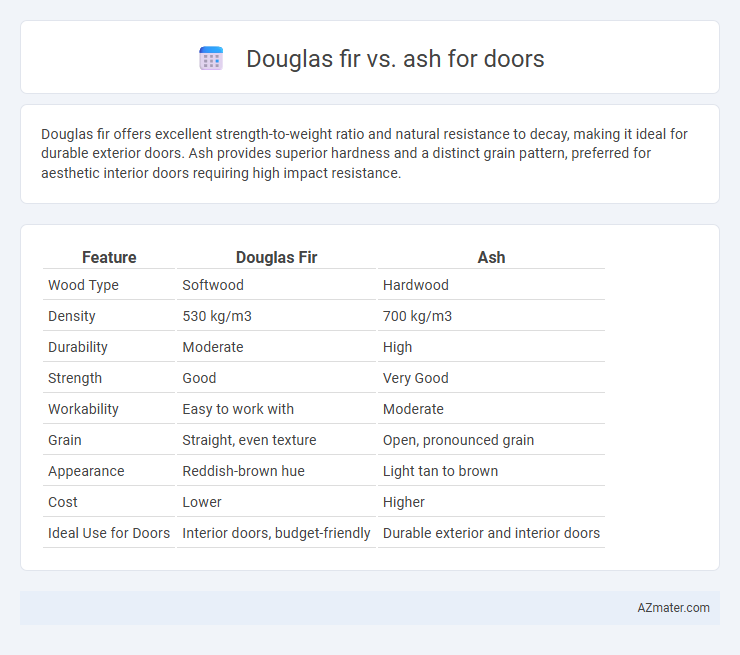
| Feature | Douglas Fir | Ash |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Softwood | Hardwood |
| Density | 530 kg/m3 | 700 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Strength | Good | Very Good |
| Workability | Easy to work with | Moderate |
| Grain | Straight, even texture | Open, pronounced grain |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown hue | Light tan to brown |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal Use for Doors | Interior doors, budget-friendly | Durable exterior and interior doors |
Introduction to Douglas Fir and Ash Wood
Douglas fir features a straight grain with a reddish-brown hue, prized for its strength and durability in door construction. Ash wood stands out with its pale color and pronounced grain patterns, offering excellent shock resistance and workability. Both woods provide distinct aesthetic and structural benefits suited to different door design preferences.
Key Characteristics of Douglas Fir
Douglas fir is prized for its exceptional strength, stability, and tight, straight grain, making it a durable and reliable choice for doors subject to heavy use and weather exposure. Its natural resistance to decay and moderate hardness enhances longevity, while the warm, reddish-brown hue provides an attractive finish that complements various architectural styles. Compared to ash, Douglas fir offers superior dimensional stability and resistance to warping, ensuring doors maintain their shape and function over time.
Key Characteristics of Ash Wood
Ash wood offers exceptional hardness and durability, making it highly resistant to dents and wear for heavily used doors. It features a straight grain with a light, creamy color that can be easily stained or finished to enhance its natural appearance. Its excellent shock resistance and stability under varying humidity levels make ash an ideal choice for both interior and exterior door applications.
Durability Comparison: Douglas Fir vs Ash
Douglas fir offers moderate durability with good resistance to decay and insects, making it suitable for interior doors but requiring protective finishes for exterior use. Ash wood is harder and denser, providing higher resistance to wear and impact, which enhances its longevity in both interior and exterior door applications. Overall, ash outperforms Douglas fir in durability, especially in high-traffic areas or environments exposed to moisture.
Grain and Aesthetic Differences
Douglas fir features a tight, straight grain with a warm reddish-brown hue that deepens over time, offering a classic, rustic aesthetic ideal for traditional and modern door designs. Ash displays a more pronounced, open grain pattern with lighter, creamy tones and occasional dark streaks, providing a bold, textured appearance that enhances contemporary and natural styles. The grain structure of Douglas fir gives a smoother finish, while ash's distinctive grain emphasizes its natural character and visual contrast.
Workability and Ease of Fabrication
Douglas fir offers excellent workability due to its straight grain and moderate hardness, making it easier to cut, shape, and sand for door fabrication. Ash, known for its toughness and elasticity, machines well but can be harder to carve or rout precisely compared to Douglas fir. Both woods respond well to finishing, but Douglas fir's consistent texture generally provides a smoother surface for detailed door designs.
Door Strength and Structural Integrity
Douglas fir offers superior door strength and structural integrity due to its dense grain pattern and high resistance to warping, making it ideal for heavy-use exterior doors. Ash, while also strong and durable, has a slightly lower hardness and may be more prone to dents and wear over time compared to Douglas fir. For applications requiring maximum door longevity and impact resistance, Douglas fir is generally the preferred material.
Finishing Options and Maintenance
Douglas fir offers a smooth grain that readily accepts stains and clear finishes, providing a rich, warm appearance that enhances its natural reddish-brown hue, while being moderately resistant to wear and easy to maintain with regular cleaning and occasional refinishing. Ash presents a more pronounced grain pattern that stains evenly, allowing for a variety of finishing options including oils, varnishes, and paints, with a durable surface that can withstand frequent handling but may require more frequent touch-ups to preserve its lighter, natural look. Both woods benefit from protective coatings to extend lifespan, but Douglas fir's tighter grain structure generally offers superior resistance to moisture-related issues compared to ash.
Cost Analysis: Douglas Fir vs Ash
Douglas fir doors typically cost less per board foot than ash due to the species' faster growth rate and wider availability, making it a budget-friendly option for quality wooden doors. Ash, known for its exceptional hardness and attractive grain, commands a higher price driven by its durability and aesthetic appeal in premium door applications. When considering long-term value, Douglas fir offers cost efficiency for standard projects, while ash justifies its higher initial investment with superior resistance to wear and longer lifespan in high-traffic areas.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Douglas fir offers exceptional strength and stability, making it ideal for exterior doors exposed to varying weather conditions and heavy use, while its fine grain delivers an attractive finish. Ash wood provides excellent shock resistance and a light, appealing color, making it suitable for interior doors where durability and aesthetics are priorities. For high-traffic entryways, Douglas fir is recommended due to its superior durability, whereas ash is preferred for decorative interior doors requiring a balance of toughness and visual appeal.
Infographic: Douglas fir vs Ash for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com