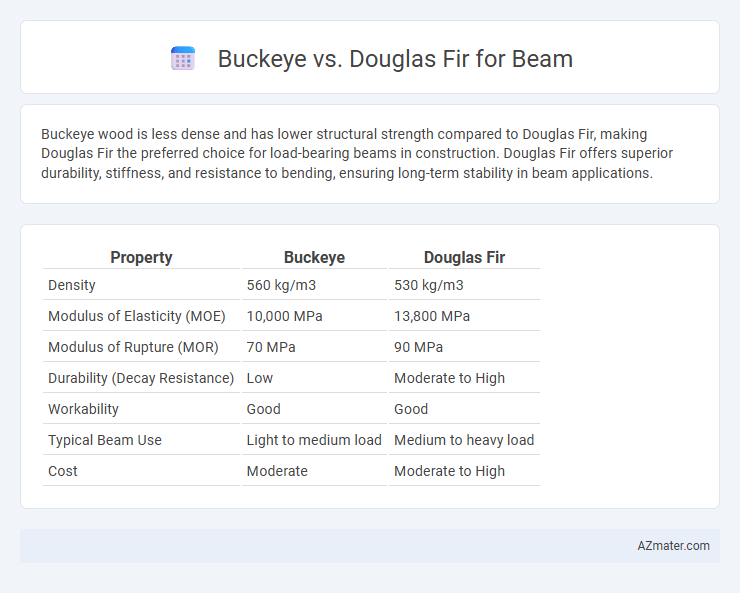
Buckeye wood is less dense and has lower structural strength compared to Douglas Fir, making Douglas Fir the preferred choice for load-bearing beams in construction. Douglas Fir offers superior durability, stiffness, and resistance to bending, ensuring long-term stability in beam applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Buckeye | Douglas Fir |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 560 kg/m3 | 530 kg/m3 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (MOE) | 10,000 MPa | 13,800 MPa |
| Modulus of Rupture (MOR) | 70 MPa | 90 MPa |
| Durability (Decay Resistance) | Low | Moderate to High |
| Workability | Good | Good |
| Typical Beam Use | Light to medium load | Medium to heavy load |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to High |
Introduction to Buckeye and Douglas Fir Beams
Buckeye beams are valued for their lightweight yet strong characteristics, making them suitable for structural applications requiring ease of handling and moderate load-bearing capacity. Douglas Fir beams, renowned for their exceptional strength, stiffness, and durability, are widely used in heavy construction and framing due to their superior load resistance and resistance to decay. Both Buckeye and Douglas Fir offer unique benefits, with Buckeye preferred for lighter, more flexible designs and Douglas Fir favored for projects demanding high structural integrity.
Wood Characteristics: Buckeye vs Douglas Fir
Buckeye wood is lightweight, soft, and has a fine, uniform texture, making it less ideal for structural beams due to its low strength and durability. Douglas Fir, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, dense grain, and excellent dimensional stability, is a preferred choice for load-bearing beams in construction. The natural resistance of Douglas Fir to decay and its rigidity significantly outperform the softer, less durable properties of Buckeye in structural applications.
Strength and Structural Performance
Buckeye wood exhibits moderate strength with a specific gravity of approximately 0.55, making it suitable for light structural applications but less ideal for heavy load-bearing beams compared to Douglas Fir. Douglas Fir, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and a specific gravity around 0.50-0.55, offers superior structural performance with excellent stiffness and load-bearing capacity often preferred in construction for beams. The mechanical properties of Douglas Fir, including its high modulus of elasticity (around 12 GPa) and bending strength (up to 92 MPa), significantly outperform Buckeye, making it a better choice for critical structural components.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Buckeye wood offers moderate durability with resistance to decay suitable for indoor beams but lacks the longevity of Douglas Fir, which is renowned for its high strength and natural resistance to rot and insect damage. Douglas Fir's dense grain and resin content contribute to exceptional durability, making it a preferred choice for structural beams in both interior and exterior applications. In comparison, Buckeye performs adequately in dry, protected environments but does not match the lifespan or robustness of Douglas Fir under harsh or load-bearing conditions.
Workability and Ease of Installation
Buckeye wood offers excellent workability due to its fine, even grain and moderate hardness, allowing for easy cutting, shaping, and fastening when used as a beam. Douglas Fir, while slightly harder and denser than Buckeye, remains a popular choice for beams because of its strength-to-weight ratio and smooth surface, facilitating straightforward installation with common tools. Both species provide reliable performance in beam applications, but Buckeye's softer texture may reduce labor time during installation.
Resistance to Pests and Decay
Buckeye wood exhibits moderate resistance to pests and decay but is generally less durable than Douglas Fir, which is renowned for its natural resistance to fungal decay and insect attacks. Douglas Fir contains resinous compounds that enhance its durability, making it a preferred choice for structural beams in environments prone to moisture and pest exposure. Buckeye's lower density and softer texture make it more susceptible to fungal decay and wood-boring insects, requiring additional treatment to ensure longevity in beam applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Buckeye beams typically have a lower cost due to its regional abundance, especially in the Midwestern United States, making it a budget-friendly option for local construction projects. Douglas Fir, widely available across North America, tends to have a higher price point but offers greater strength-to-weight ratio and durability, justifying the investment for structural applications. Availability of Buckeye is limited outside its native regions, whereas Douglas Fir benefits from established supply chains and consistent availability in lumber markets nationwide.
Aesthetics and Visual Appeal
Buckeye beams present a unique, light-toned grain with pronounced swirls and knots that create a rustic yet elegant aesthetic, making them ideal for spaces seeking natural character and warmth. Douglas Fir beams showcase a clean, straight grain with a rich golden-red hue that enhances modern and traditional interiors through a smooth, consistent appearance. Both woods offer distinct visual appeals, with Buckeye adding artistic texture and Douglas Fir providing classic, uniform beauty.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Buckeye wood offers a sustainable option for beams due to its fast growth rate and abundant availability, reducing the pressure on old-growth forests. Douglas fir is prized for its strength and durability but often requires careful sourcing to ensure it comes from responsibly managed forests, minimizing environmental impact. Choosing certified sustainably harvested timber, whether Buckeye or Douglas fir, significantly lowers carbon footprints and supports forest conservation efforts.
Best Applications for Buckeye and Douglas Fir Beams
Buckeye beams excel in indoor applications requiring moderate strength and fine aesthetics, such as decorative ceiling accents and light structural supports in residential settings. Douglas Fir beams offer superior load-bearing capacity and natural resistance to decay, making them ideal for heavy-duty construction projects like commercial buildings, outdoor decks, and bridges. The choice between Buckeye and Douglas Fir beams depends on the specific structural demands and environmental exposure of the project.
Infographic: Buckeye vs Douglas Fir for Beam
 azmater.com
azmater.com