Birch veneer offers a tight grain and light color, ideal for smooth finishes and durability in cabinetry. Poplar veneer features a softer texture with a greenish hue, providing affordability and ease of staining for furniture projects.
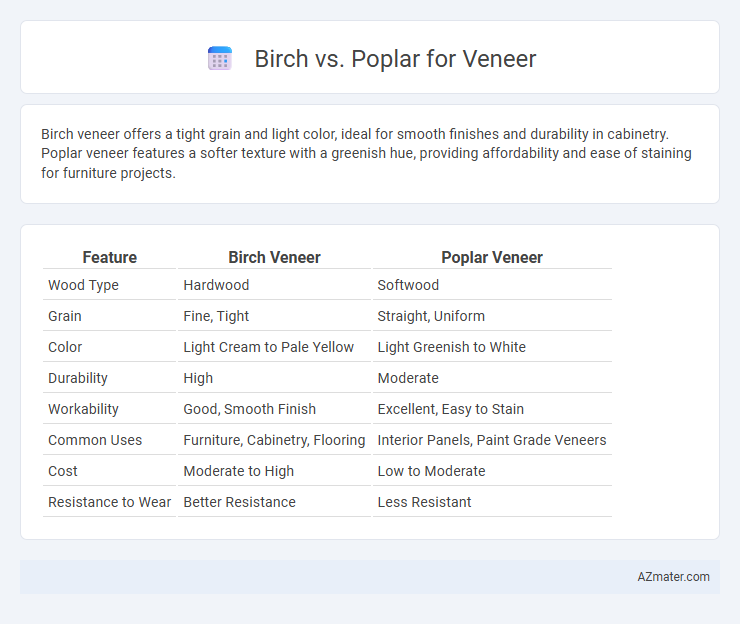
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Birch Veneer | Poplar Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Hardwood | Softwood |
| Grain | Fine, Tight | Straight, Uniform |
| Color | Light Cream to Pale Yellow | Light Greenish to White |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
| Workability | Good, Smooth Finish | Excellent, Easy to Stain |
| Common Uses | Furniture, Cabinetry, Flooring | Interior Panels, Paint Grade Veneers |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Resistance to Wear | Better Resistance | Less Resistant |
Introduction: Birch vs Poplar Veneer
Birch veneer offers a fine, uniform grain with a light, creamy color that enhances modern and Scandinavian design aesthetics, making it ideal for high-quality furniture and cabinetry. Poplar veneer, characterized by its soft texture and pale yellow to greenish hues, provides an affordable and versatile option commonly used in millwork and painted finishes. Both veneers differ significantly in durability and appearance, influencing their suitability for various woodworking projects and interior applications.
Botanical Origins of Birch and Poplar
Birch veneer originates from hardwood trees of the genus Betula, primarily found in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, known for their smooth bark and fine-grained wood. Poplar veneer comes from trees in the genus Populus, widespread across North America, Europe, and Asia, characterized by fast growth and softwood properties. The distinct botanical origins influence their grain patterns, durability, and typical applications in veneer manufacturing.
Appearance and Grain Differences
Birch veneer features a fine, even grain with a light cream to pale yellow color, offering a smooth, uniform appearance ideal for modern and Scandinavian-style furniture. Poplar veneer presents a more varied grain pattern, often interspersed with greenish or brown streaks, creating a distinctive, rustic look suited for casual and eclectic designs. The subtle but noticeable variations in grain texture and color intensity make birch veneers more consistent, while poplar provides unique character and natural variation.
Workability and Ease of Use
Birch veneer is highly valued for its excellent workability, offering consistent grain, smooth sanding, and easy cutting, making it ideal for detailed woodworking and fine finishes. Poplar veneer, while softer and more porous, is easier to shape and manipulate, but may require extra care during sanding and finishing to avoid splintering or uneven surfaces. Both woods provide versatility for veneer applications, with birch preferred for precision projects and poplar suited for budget-friendly, less intricate designs.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Birch veneer offers higher durability and strength compared to poplar, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry subjected to daily wear. Poplar veneer is softer with moderate strength, suitable for decorative applications but less resistant to dents and scratches. The dense grain structure of birch enhances its longevity, whereas poplar's lower density reduces its load-bearing capabilities in veneer products.
Cost and Availability Factors
Birch veneer is generally more expensive than poplar due to its denser grain and higher demand in fine woodworking and cabinetry, offering superior durability and a smoother finish. Poplar veneer costs are lower, making it a budget-friendly option with wide availability, especially in North America, but it tends to have a softer texture and less attractive grain. Availability of birch is more limited in certain regions, leading to longer lead times compared to the readily accessible poplar veneer.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Birch veneers offer a more sustainable option due to faster growth rates and higher regeneration capacity compared to poplar, which often requires more intensive management to maintain. Birch's greater durability and less chemical processing extend product lifespan, reducing environmental waste. Poplar's lower density results in less wood per veneer sheet, increasing the frequency of harvesting and impacting carbon sequestration negatively.
Common Applications for Each Veneer
Birch veneer is widely used in furniture making, cabinetry, and interior paneling due to its smooth texture and light color, which allows for easy staining and finishing. Poplar veneer is commonly applied in millwork, painted cabinetry, and decorative plywood because of its uniform grain and affordability, making it ideal for projects requiring a consistent surface. Both veneers serve key roles in interior design, with birch favored for visible, high-quality finishes and poplar chosen for cost-effective, paint-compatible applications.
Pros and Cons of Birch Veneer
Birch veneer offers a smooth, fine grain and light color, making it ideal for modern and clean interior designs. Its durability and resistance to wear provide a long-lasting surface, but birch veneer can be prone to yellowing over time and may require regular maintenance to preserve its appearance. Compared to poplar veneer, birch is generally harder and more stable, though it tends to be more expensive and less flexible for intricate applications.
Pros and Cons of Poplar Veneer
Poplar veneer offers a lightweight, affordable option with a smooth texture and consistent grain, making it ideal for painted finishes and modern interiors. It tends to be softer and less durable compared to birch, showing dents and wear more easily under heavy use. While poplar's greenish-brown hues provide unique coloration, its color variability can challenge uniform staining in veneer applications.
Infographic: Birch vs Poplar for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com