Beech plywood offers superior hardness and durability compared to poplar plywood, making it ideal for furniture and flooring applications. Poplar plywood is lighter, more affordable, and easier to work with, suitable for interior paneling and lightweight structures.
Table of Comparison
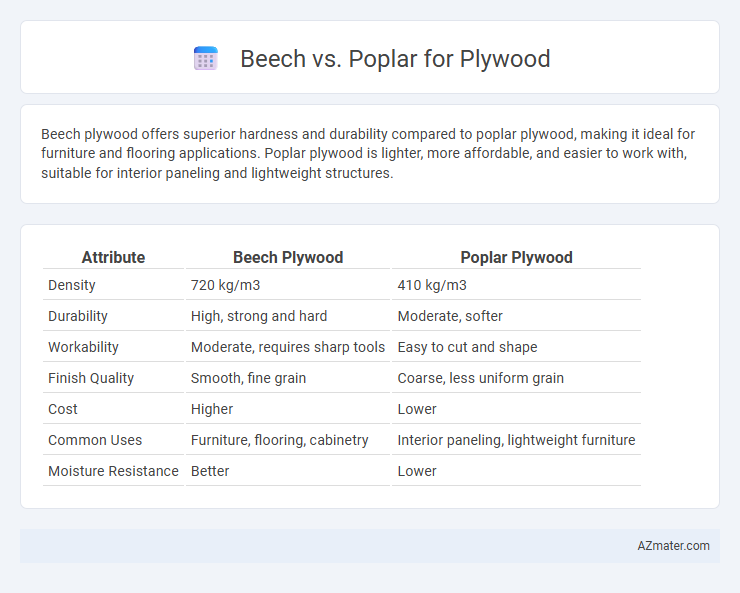
| Attribute | Beech Plywood | Poplar Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 720 kg/m3 | 410 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High, strong and hard | Moderate, softer |
| Workability | Moderate, requires sharp tools | Easy to cut and shape |
| Finish Quality | Smooth, fine grain | Coarse, less uniform grain |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses | Furniture, flooring, cabinetry | Interior paneling, lightweight furniture |
| Moisture Resistance | Better | Lower |
Introduction: Beech vs Poplar for Plywood
Beech plywood offers excellent strength, stability, and a fine, uniform grain, making it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and flooring applications that demand durability and a smooth finish. Poplar plywood is lightweight, easy to work with, and cost-effective, featuring a straight grain and pale hue suitable for interior projects, painting, and decorative uses. Choosing between beech and poplar plywood depends on the balance between structural performance and budget constraints in specific woodworking tasks.
Botanical Overview: Beech and Poplar Trees
Beech (Fagus spp.) is a deciduous hardwood tree known for its dense and fine-grained wood, commonly used in high-quality plywood due to its strength and smooth finish. Poplar (Populus spp.), a fast-growing deciduous hardwood, features a lighter, softer wood with a more open grain pattern, making it a cost-effective choice for plywood applications requiring moderate durability. Both species are widely cultivated in temperate regions, with Beech thriving in Europe and Poplar prevalent across North America and Asia.
Wood Density and Strength Comparison
Beech plywood typically exhibits a higher wood density ranging from 720 to 740 kg/m3, providing superior strength and durability compared to poplar plywood, which has a density between 400 and 500 kg/m3. The greater density of beech contributes to enhanced load-bearing capacity and resistance to impact, making it ideal for applications requiring robust structural performance. Poplar plywood, while lighter, offers moderate strength suitable for less demanding uses, often favored for its ease of machining and cost-effectiveness.
Workability and Machinability
Beech plywood offers superior workability with its fine, tight grain that allows for smooth cutting, sanding, and shaping without tearing or splintering. Poplar plywood provides excellent machinability due to its softer texture, making it easier to drill, plane, and route while reducing wear on tools. Both species respond well to adhesives and finishes, but beech's denser composition results in a more durable and stable final product.
Durability and Lifespan
Beech plywood offers higher durability and a longer lifespan compared to poplar plywood due to its denser hardwood structure, making it more resistant to wear and impact. Poplar plywood, being a softer wood, tends to be less durable and more prone to dents and damage over time, resulting in a shorter lifespan. Choosing beech plywood is ideal for applications requiring robust, long-lasting material, while poplar suits projects where lightweight and cost-effectiveness are prioritized over durability.
Visual Appearance and Grain
Beech plywood features a fine, tight grain with a uniform texture, creating a smooth and consistent surface ideal for furniture and cabinetry that demands a classic, clean look. Poplar plywood displays a more varied, open grain pattern with occasional knots and streaks, offering a rustic and casual aesthetic suitable for decorative projects and painted finishes. Both woods accept stains and finishes well, but beech tends to highlight the natural wood grain more prominently, enhancing visual elegance.
Cost and Availability
Beech plywood typically costs more than poplar plywood due to its higher density and durability, making it a preferred choice for high-quality furniture and cabinetry. Poplar plywood offers greater availability and affordability, often sourced from fast-growing poplar trees, making it a budget-friendly option for interior construction and temporary structures. The wider market presence and quicker growth cycle of poplar contribute to its dominance in cost-effective plywood applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Beech plywood is often favored for its durability and strength but involves higher environmental costs due to slower growth rates and intensive logging practices. Poplar plywood, sourced from fast-growing trees, offers a more sustainable choice with lower carbon footprints and quicker forest regeneration rates. Choosing poplar plywood supports better forest management and reduces habitat disruption compared to beech.
Applications in Plywood Manufacturing
Beech plywood is favored for its high strength, durability, and fine grain, making it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and flooring applications requiring structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Poplar plywood, being lighter and more affordable, is commonly used in interior applications such as paneling, drawer bodies, and decorative elements where cost-efficiency and ease of machining are priorities. Both wood types influence plywood's performance in terms of workability, finish quality, and resistance to wear, determining their suitability across different manufacturing needs.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Beech and Poplar
Beech plywood offers superior hardness, durability, and fine grain, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry requiring strength and a smooth finish. Poplar plywood is lighter, more affordable, and easier to work with, suited for projects prioritizing cost-efficiency and ease of machining. Selecting between beech and poplar plywood depends on balancing the need for sturdiness and aesthetic appeal against budget constraints and workability preferences.
Infographic: Beech vs Poplar for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com