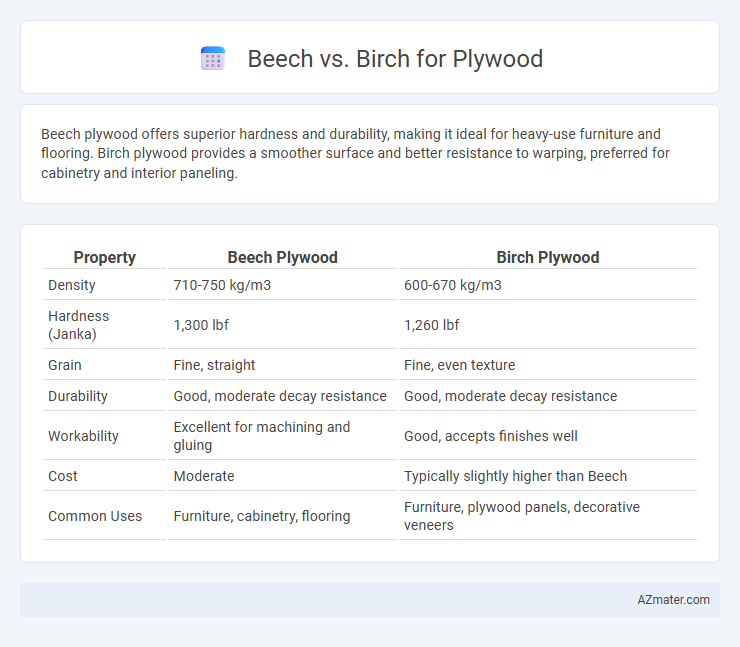
Beech plywood offers superior hardness and durability, making it ideal for heavy-use furniture and flooring. Birch plywood provides a smoother surface and better resistance to warping, preferred for cabinetry and interior paneling.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Beech Plywood | Birch Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 710-750 kg/m3 | 600-670 kg/m3 |
| Hardness (Janka) | 1,300 lbf | 1,260 lbf |
| Grain | Fine, straight | Fine, even texture |
| Durability | Good, moderate decay resistance | Good, moderate decay resistance |
| Workability | Excellent for machining and gluing | Good, accepts finishes well |
| Cost | Moderate | Typically slightly higher than Beech |
| Common Uses | Furniture, cabinetry, flooring | Furniture, plywood panels, decorative veneers |
Introduction to Beech and Birch Plywood
Beech plywood is renowned for its durability, fine grain, and smooth surface, making it ideal for furniture and interior applications requiring strength and aesthetic appeal. Birch plywood offers a lighter color with a uniform texture, prized for its versatility, resistance to warping, and consistent quality in cabinetry and construction projects. Both types provide excellent stability and bonding strength, but beech tends to deliver superior hardness while birch emphasizes flexibility and ease of finishing.
Botanical Origins: Beech vs Birch
Beech plywood originates from the Fagus genus, primarily Fagus sylvatica, characterized by its dense, hard wood with a fine grain pattern ideal for smooth finishes. Birch plywood comes from multiple Betula species, notably Betula pendula and Betula pubescens, known for their light color and consistent grain, providing excellent strength and stability. Both woods are deciduous hardwoods but differ in botanical classification, texture, and natural resistance, influencing their use in various plywood applications.
Wood Grain and Appearance Differences
Beech plywood features a fine, tight grain with a uniform texture and a light pinkish-brown hue, providing a smooth and consistent appearance ideal for furniture and cabinetry. Birch plywood exhibits a slightly more pronounced grain with subtle variations and a pale cream to light yellow color, offering a natural, warm look preferred for decorative applications. Both woods are valued for their strength and durability, but beech presents a more uniform aesthetic while birch offers distinctive grain patterns that enhance visual interest.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Beech plywood offers superior strength due to its dense hardwood composition, making it highly resistant to impact and structural stress. Birch plywood, while slightly lighter, provides excellent durability and dimensional stability, often favored for fine woodworking and cabinetry. Both woods exhibit strong resistance to warping and wear, but beech generally outperforms birch in load-bearing applications.
Workability and Machining Ease
Beech plywood exhibits superior workability due to its fine grain and uniform texture, allowing clean cuts and smooth sanding with minimal splintering. Birch plywood is also highly machinable, offering excellent resistance to wear and providing a consistent finish, but it can be slightly harder on cutting tools compared to beech. Both woods respond well to CNC routing and drilling, yet beech is preferred for precise, detailed woodworking projects because of its easier machining properties.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Beech plywood generally costs more than birch plywood due to its denser grain and higher durability, making it a preferred choice for furniture and flooring applications. Birch plywood is widely available and tends to be more affordable, benefiting from its extensive use in construction and cabinetry. Cost and availability vary by region, with birch often dominating markets due to easier sourcing and faster growth cycles compared to beech.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Beech plywood supports sustainable forestry practices due to its fast growth rates and potential for responsible sourcing, while birch plywood stands out for its higher durability, enabling longer product life cycles and reduced replacement needs. Both types contribute to lower environmental impact when certified by FSC or PEFC, promoting biodiversity and reduced carbon emissions during manufacturing. Choosing birch or beech plywood from sustainable sources ensures minimal ecological footprint and supports regenerative forest management.
Common Applications of Beech vs Birch Plywood
Beech plywood is commonly used in furniture making, cabinetry, and flooring due to its smooth finish and durability, offering excellent resistance to wear and tear. Birch plywood, favored in architectural millwork, drawer construction, and paneling, provides a strong, stable surface with a fine grain that accepts paint and veneers well. Both types are popular choices for interior applications where strength and aesthetic appeal are essential.
Moisture Resistance and Stability
Beech plywood offers moderate moisture resistance suitable for indoor applications but tends to absorb water if exposed to prolonged humidity. Birch plywood provides superior moisture resistance due to its tighter grain and denser composition, making it more stable in damp conditions and less prone to warping. Stability in birch plywood ensures better durability in environments with fluctuating humidity compared to the relatively softer and less stable beech plywood.
Choosing the Right Plywood for Your Project
Beech plywood offers superior strength, fine grain, and excellent resistance to wear, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry that require durability and a smooth finish. Birch plywood is favored for its consistent texture, light color, and flexibility, which suits decorative applications and curved components. Selecting between Beech and Birch plywood depends on the project's structural demands, aesthetic preferences, and budget considerations.
Infographic: Beech vs Birch for Plywood
 azmater.com
azmater.com