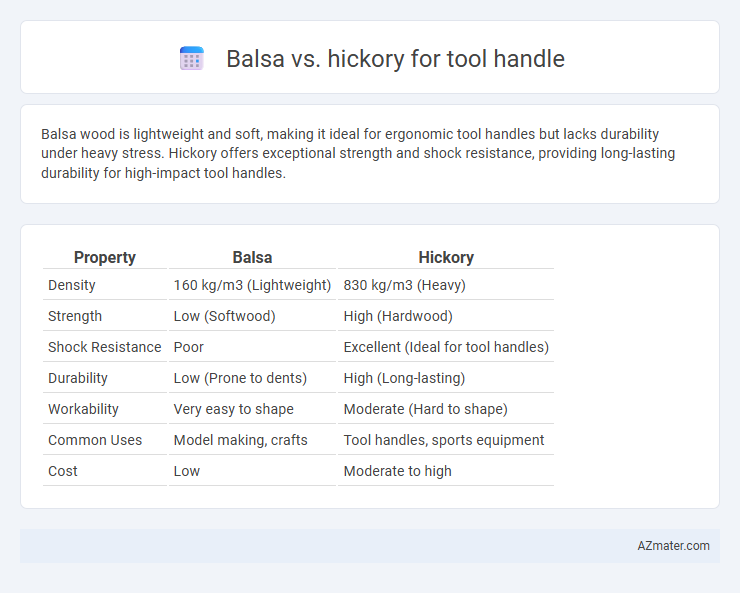
Balsa wood is lightweight and soft, making it ideal for ergonomic tool handles but lacks durability under heavy stress. Hickory offers exceptional strength and shock resistance, providing long-lasting durability for high-impact tool handles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Balsa | Hickory |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 160 kg/m3 (Lightweight) | 830 kg/m3 (Heavy) |
| Strength | Low (Softwood) | High (Hardwood) |
| Shock Resistance | Poor | Excellent (Ideal for tool handles) |
| Durability | Low (Prone to dents) | High (Long-lasting) |
| Workability | Very easy to shape | Moderate (Hard to shape) |
| Common Uses | Model making, crafts | Tool handles, sports equipment |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to high |
Introduction: Balsa vs Hickory for Tool Handles
Balsa and hickory are two distinct wood types commonly used for tool handles, each offering unique characteristics. Balsa is known for its lightweight and shock-absorbing properties, making it ideal for reducing user fatigue during prolonged tool use. Hickory, on the other hand, is prized for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to impact, providing long-lasting handles suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Wood Properties: Strength and Density
Hickory wood is renowned for its exceptional strength and high density, making it a preferred choice for durable and shock-resistant tool handles. Balsa wood, in contrast, has significantly lower density and strength, offering lightweight properties but reduced durability under repetitive impact. The superior tensile strength and hardness of hickory contribute to its ability to withstand heavy-duty usage, while balsa is more suitable for applications prioritizing lightness over resilience.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Hickory offers superior durability and longevity for tool handles compared to balsa due to its dense grain structure and high impact resistance. Balsa is significantly lighter but lacks the strength needed to withstand repeated heavy use, making it prone to dents and breaks under stress. Professionals often prefer hickory handles in demanding applications for their ability to endure prolonged wear and harsh conditions without compromising structural integrity.
Weight Considerations in Tool Performance
Balsa wood is extremely lightweight, offering superior shock absorption and reducing user fatigue during extended tool use, making it ideal for applications where weight is critical. Hickory, while heavier, provides exceptional strength and durability, ensuring long-lasting performance but potentially causing quicker fatigue due to increased weight. Selecting between balsa and hickory for tool handles requires balancing the need for lightweight comfort against robust impact resistance and longevity.
Shock Absorption and Vibration Control
Balsa wood offers superior shock absorption due to its low density and cellular structure, making it ideal for minimizing impact forces in tool handles. Hickory, though denser, provides excellent vibration control because of its stiffness and resilience, reducing user fatigue during prolonged use. The choice between balsa and hickory for tool handles depends on prioritizing either maximum shock absorption or effective vibration damping.
Workability: Cutting, Sanding, and Shaping
Balsa wood offers exceptional workability with cutting, sanding, and shaping due to its lightweight and soft texture, making it ideal for precise, intricate tool handle designs. Hickory, though denser and harder, provides strong resistance during machining processes and delivers a smooth finish when properly worked, enhancing durability in durable tool handles. Both woods suit different tool handle requirements, with balsa excelling in ease of shaping and hickory favored for robust handling and longevity.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Balsa wood is significantly more affordable and widely available due to its rapid growth and common use in lightweight applications, making it a cost-effective choice for tool handles. Hickory, known for its superior strength and durability, tends to be more expensive and less readily available, primarily sourced from mature hardwood forests. Market availability fluctuates with regional demand, but balsa remains a dominant option for budget-conscious consumers while hickory appeals to those requiring long-term reliability.
Safety Factors for Tool Handle Materials
Balsa offers lightweight properties but lacks the durability and impact resistance essential for safe tool handles, potentially increasing the risk of handle failure under stress. Hickory, renowned for its high strength, shock absorption, and toughness, provides superior safety factors by minimizing the likelihood of splintering or breaking during heavy use. Selecting hickory reduces operator injury risk and enhances tool longevity due to its excellent structural integrity and resilience.
Typical Applications: Best Uses for Each Wood
Balsa is ideal for lightweight tool handles requiring shock absorption, commonly used in model-making tools and delicate instruments. Hickory excels in heavy-duty applications such as hammer, axe, and garden tool handles due to its exceptional strength, impact resistance, and durability. Each wood's unique properties make balsa better suited for precision tasks, while hickory is preferred for rigorous, high-stress uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wood for Your Tool Handle
Balsa wood offers exceptional lightweight properties and shock absorption, making it ideal for tools requiring reduced user fatigue and precision. Hickory provides superior strength, durability, and impact resistance, suited for heavy-duty tools subjected to frequent use and high stress. Selecting the appropriate wood depends on the balance between weight preference and durability needs, with balsa favored for lightweight comfort and hickory chosen for lasting resilience.
Infographic: Balsa vs Hickory for Tool handle
 azmater.com
azmater.com