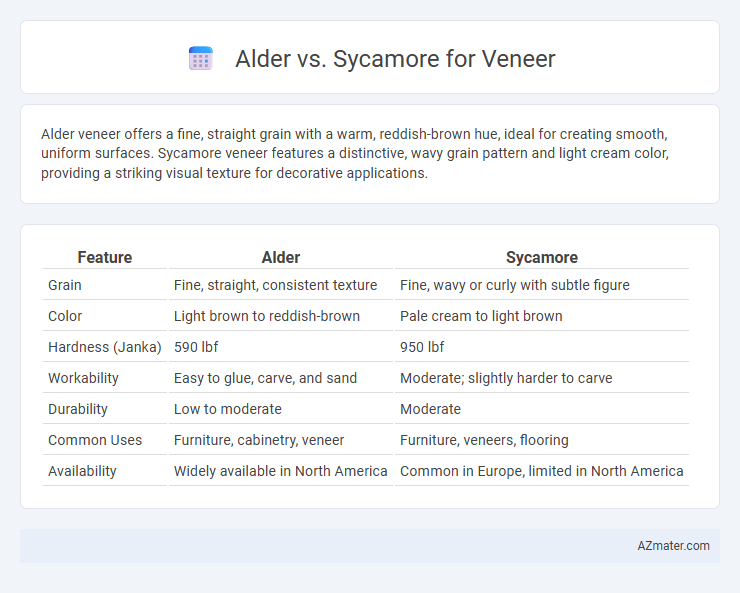
Alder veneer offers a fine, straight grain with a warm, reddish-brown hue, ideal for creating smooth, uniform surfaces. Sycamore veneer features a distinctive, wavy grain pattern and light cream color, providing a striking visual texture for decorative applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Alder | Sycamore |
|---|---|---|
| Grain | Fine, straight, consistent texture | Fine, wavy or curly with subtle figure |
| Color | Light brown to reddish-brown | Pale cream to light brown |
| Hardness (Janka) | 590 lbf | 950 lbf |
| Workability | Easy to glue, carve, and sand | Moderate; slightly harder to carve |
| Durability | Low to moderate | Moderate |
| Common Uses | Furniture, cabinetry, veneer | Furniture, veneers, flooring |
| Availability | Widely available in North America | Common in Europe, limited in North America |
Introduction to Alder and Sycamore Veneer
Alder veneer offers a fine, uniform grain with a rich, warm reddish-brown color, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry that require a smooth, elegant finish. Sycamore veneer features a light, creamy color with a distinctive wavy or bird's eye grain pattern, prized for its unique visual texture and suitability in high-end interior applications. Both veneers are valued for their workability and smooth sanding properties, but alder is favored for its consistent appearance while sycamore is chosen for its striking figure.
Botanical Overview of Alder and Sycamore
Alder, belonging to the genus Alnus, is a deciduous hardwood tree commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere, known for its fine, even texture and consistent grain that makes it ideal for smooth veneer finishes. Sycamore, from the genus Platanus, features a distinctive coarse, interlocking grain pattern with a creamy to light brown hue, providing a contrasting textured veneer option favored for its unique visual appeal. Both species offer durability and workability, but Alder's uniformity suits refined applications while Sycamore's irregular grain enhances decorative surfaces.
Color and Grain Characteristics
Alder veneer features a warm, reddish-brown hue with a fine, straight grain that often displays subtle cathedrals and smooth texture, making it ideal for a cozy, inviting aesthetic. Sycamore veneer presents a lighter cream to pale brown color with distinctive, intricate birdseye and curly grain patterns that create a more dynamic and decorative appearance. The color consistency in alder provides a uniform look, while sycamore's varied grain patterns offer a unique, visually striking surface for high-end furniture and cabinetry.
Workability and Machining Properties
Alder veneer is highly regarded for its excellent workability, offering smooth, consistent cuts and easy sanding due to its fine, even grain and moderate hardness. Sycamore veneer, while slightly harder and denser, presents a more challenging machining process but yields a striking, figured appearance with good resistance to splitting and chipping. Both woods machine well, but alder is preferred for projects requiring intricate detailing and faster production times.
Durability and Stability Comparison
Alder veneer offers moderate durability with a fine, even grain that provides consistent stability in indoor applications, making it less prone to warping under controlled humidity. Sycamore veneer demonstrates superior durability due to its dense, tight grain structure, resulting in enhanced resistance to wear and environmental changes, which promotes greater long-term stability. When comparing both, Sycamore is preferable for high-traffic or variable conditions, while Alder suits projects emphasizing aesthetic uniformity with moderate durability demands.
Veneer Application Suitability
Alder veneer is highly suited for fine furniture and cabinetry due to its smooth grain and warm, consistent color, which enhances detailed finishes and staining options. Sycamore veneer offers a distinctive wavy grain pattern ideal for decorative paneling and high-end architectural applications, providing visual depth and unique texture. Both veneers excel in projects requiring precise cutting and finishing, but alder's softness allows easier machining, while sycamore's hardness offers greater durability in heavy-use environments.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Alder veneer is prized for its renewable growth rate and lower environmental impact due to sustainable forestry practices, making it a more eco-friendly choice compared to sycamore. Sycamore veneer, while visually appealing with its unique grain patterns, often comes from slower-growing trees, which can contribute to higher ecological footprints when harvested unsustainably. Choosing alder supports efforts to reduce deforestation and promote sustainable wood sourcing in veneer production.
Cost Differences and Market Availability
Alder veneer typically costs less than sycamore veneer, making it a budget-friendly option for woodworking projects. Alder is widely available and sourced mainly from the Pacific Northwest, ensuring steady market supply. Sycamore veneer tends to be pricier due to its unique grain patterns and limited regional availability, often sourced from eastern North America, resulting in higher demand and more fluctuating prices.
Aesthetic Appeal in Finished Products
Alder veneer offers a warm, reddish-brown hue with a smooth, consistent grain pattern that enhances the natural beauty of finished furniture, making it ideal for traditional and rustic designs. Sycamore veneer, known for its lighter color and highly figured grain with unique curls and waves, provides a striking visual texture that suits contemporary and artistic applications. The choice between alder and sycamore veneers significantly impacts the aesthetic appeal, with alder delivering subtle elegance and sycamore adding distinctive character and visual interest.
Choosing the Right Veneer for Your Project
Alder veneer offers a smooth grain and warm tones, making it ideal for projects requiring a uniform appearance and easy stain absorption, which enhances color depth. Sycamore veneer features a distinctive, wavy pattern with varied shading, providing a striking visual texture well-suited for decorative applications and furniture focal points. Selecting between alder and sycamore veneers depends on the desired aesthetic and project requirements, where alder suits subtle elegance and sycamore excels in unique, eye-catching designs.
Infographic: Alder vs Sycamore for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com