Alder wood offers a durable, fine-grained texture ideal for drawer sides, while poplar provides a lightweight, affordable, and easily workable option with moderate strength. For increased longevity and smooth drawer operation, alder is preferred in high-quality cabinetry, whereas poplar suits budget-conscious projects.
Table of Comparison
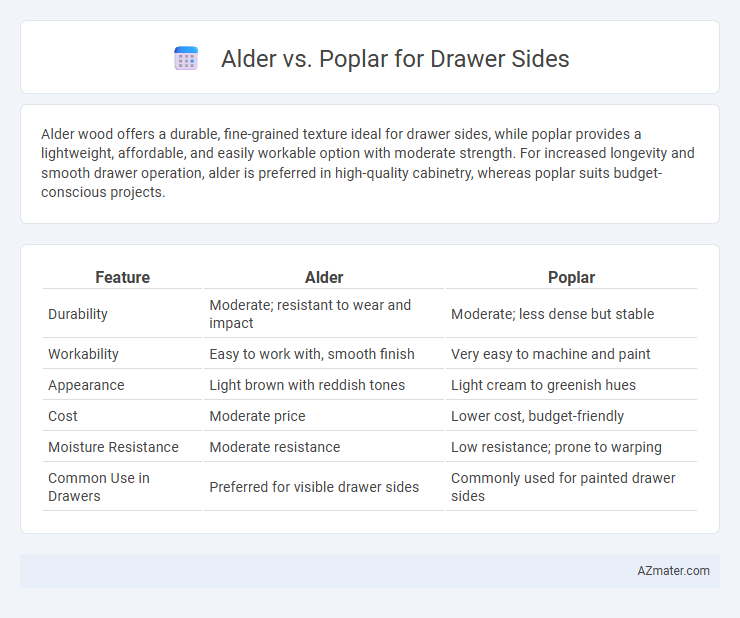
| Feature | Alder | Poplar |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate; resistant to wear and impact | Moderate; less dense but stable |
| Workability | Easy to work with, smooth finish | Very easy to machine and paint |
| Appearance | Light brown with reddish tones | Light cream to greenish hues |
| Cost | Moderate price | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate resistance | Low resistance; prone to warping |
| Common Use in Drawers | Preferred for visible drawer sides | Commonly used for painted drawer sides |
Introduction to Alder and Poplar Woods
Alder wood features a fine, straight grain with a smooth texture, making it a popular choice for drawer sides due to its stability and ease of finishing. Poplar wood is lightweight and dense, with a uniform texture and subtle grain patterns, offering good workability and resistance to warping in drawer construction. Both woods provide durable, cost-effective options for cabinetry, though alder tends to have a warmer tone compared to the pale, creamy color of poplar.
Physical Properties Comparison
Alder wood exhibits a Janka hardness rating of approximately 590, making it moderately hard and resistant to dents compared to Poplar's lower rating of around 410, which results in a softer and more easily marked surface. Alder offers a stable grain with fine texture, providing a smooth finish ideal for drawer sides, whereas Poplar's coarser texture and tendency to warp under humidity variations reduce its dimensional stability. Moisture content absorption rates in Alder are generally lower, contributing to better resistance against swelling and shrinking over time compared to Poplar, enhancing its durability in cabinetry applications.
Durability and Strength Differences
Alder wood is generally softer and less dense than poplar, making it more prone to dents and scratches but easier to work with for drawer sides. Poplar offers superior strength and durability due to its higher density, making it more resistant to wear and better suited for heavy-use drawers. When choosing between the two, poplar is preferred for long-lasting structural integrity, while alder provides a smoother finish ideal for aesthetic-focused applications.
Workability and Machinability
Alder wood offers excellent workability with smooth cutting and good nail-holding properties, making it ideal for detailed drawer sides. Poplar provides superior machinability due to its uniform texture and softness, allowing for precise shaping and easy sanding. Both woods perform well in woodworking projects, but poplar's consistent grain reduces the risk of tear-out during complex machining.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Alder wood features a smooth, fine grain with a consistent texture that presents a warm, reddish-brown hue, making it ideal for drawer sides requiring a clean and elegant appearance. Poplar offers a straighter, more uniform grain with subtle streaks of green or brown, providing a lighter, more neutral tone that blends well in contemporary or casual cabinetry styles. Both woods are soft hardwoods, but alder's richer color and uniform fine grain often appeal to those seeking a classic, polished look.
Cost and Availability
Alder wood is generally more affordable and widely available compared to poplar, making it a cost-effective choice for drawer sides. Poplar, while slightly more expensive, offers consistent availability due to its rapid growth and abundant supply in North America. Both woods provide good workability, but alder's balance of cost and availability often makes it preferred for budget-conscious cabinetry projects.
Finishing and Staining Results
Alder wood offers a smooth texture and absorbs stain evenly, resulting in rich, warm tones that enhance drawer sides with a refined appearance. Poplar, while more affordable, tends to have a blotchy finish due to its variable grain, requiring a pre-conditioner for uniform staining and often producing muted colors. Choosing Alder ensures a consistent, high-quality stain finish, whereas Poplar is better suited for painted surfaces or light staining applications on drawer sides.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alder wood is sourced from fast-growing deciduous trees, making it a more sustainable choice due to its shorter harvest cycles and smaller carbon footprint compared to poplar. Poplar is also considered eco-friendly because it grows quickly and can be cultivated on less fertile land, reducing deforestation pressure on prime forests. Both woods have low environmental impact, but alder's slightly better durability helps extend product life, supporting sustainability in drawer construction.
Best Uses for Drawer Sides
Alder wood offers durability and smooth workability, making it ideal for drawer sides in cabinetry requiring fine finishing and moderate strength. Poplar, being lightweight and stable, suits drawer sides in furniture where cost-efficiency and ease of painting are prioritized. Both woods provide sufficient structural integrity, but alder excels in visible drawer components, while poplar is preferred for hidden or painted drawer interiors.
Conclusion: Which Wood is Better for Drawer Sides?
Alder wood offers a smoother finish and superior workability, making it ideal for drawer sides requiring fine detail and uniform texture. Poplar provides greater durability and resistance to dents, which is advantageous for high-traffic or heavy-use drawers. Choosing between alder and poplar depends on the balance between aesthetic preference and functional durability for the specific drawer project.
Infographic: Alder vs Poplar for Drawer Side
 azmater.com
azmater.com