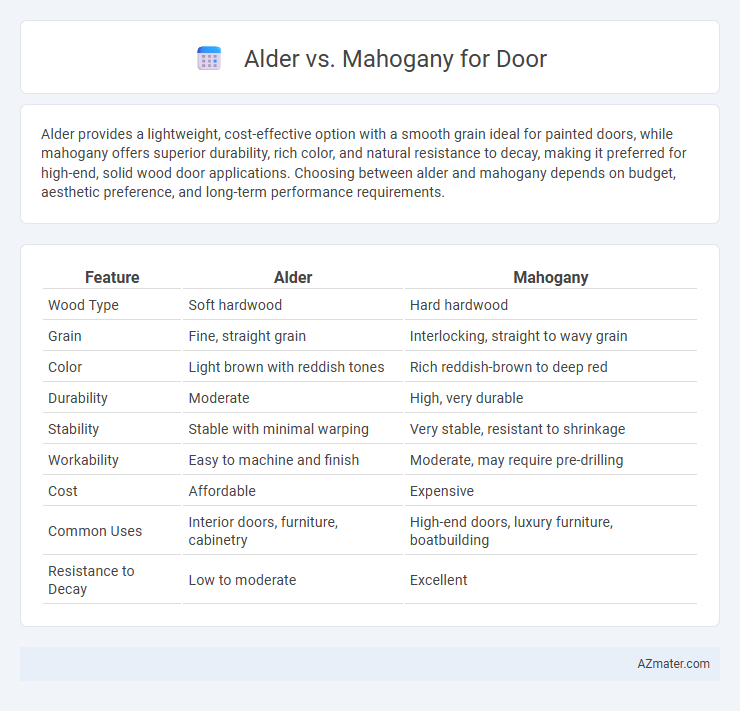
Alder provides a lightweight, cost-effective option with a smooth grain ideal for painted doors, while mahogany offers superior durability, rich color, and natural resistance to decay, making it preferred for high-end, solid wood door applications. Choosing between alder and mahogany depends on budget, aesthetic preference, and long-term performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Alder | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Soft hardwood | Hard hardwood |
| Grain | Fine, straight grain | Interlocking, straight to wavy grain |
| Color | Light brown with reddish tones | Rich reddish-brown to deep red |
| Durability | Moderate | High, very durable |
| Stability | Stable with minimal warping | Very stable, resistant to shrinkage |
| Workability | Easy to machine and finish | Moderate, may require pre-drilling |
| Cost | Affordable | Expensive |
| Common Uses | Interior doors, furniture, cabinetry | High-end doors, luxury furniture, boatbuilding |
| Resistance to Decay | Low to moderate | Excellent |
Introduction to Alder and Mahogany for Doors
Alder is a soft hardwood known for its fine grain and warm, reddish-brown hues, making it a popular choice for interior doors that require a smooth finish and easy stainability. Mahogany, a dense tropical hardwood, is prized for its rich, deep reddish-brown color and exceptional durability, offering a luxurious appearance and excellent resistance to warping and insects, ideal for both interior and exterior doors. Both woods provide distinct aesthetic and functional qualities, with alder favored for affordability and versatility, while mahogany stands out for premium strength and long-lasting beauty.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Alder wood features a fine, uniform grain with a lighter color, ranging from creamy white to light brown, making it easier to stain or paint for a smooth finish. Mahogany, known for its dense, straight grain and rich reddish-brown hue, offers exceptional durability and resistance to wear, ideal for high-traffic doors. The softer nature of alder makes it more susceptible to dents and scratches compared to the harder, more resilient mahogany.
Durability and Longevity
Alder wood offers moderate durability and is softer, making it prone to dents and scratches, which may reduce its longevity for high-traffic door applications. Mahogany, known for its exceptional hardness and resistance to decay, provides superior durability and can last for decades without significant wear. Choosing mahogany over alder ensures a more resilient door that withstands daily use and environmental stress better.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Alder wood offers a smooth, uniform appearance with subtle, fine grain patterns that create a warm, rustic charm ideal for traditional or farmhouse-style doors. In contrast, mahogany features a richer, deeper reddish-brown hue with pronounced, interlocking grain patterns that provide a luxurious and elegant look suited for classic or formal entryways. Both hardwoods showcase unique visual textures, but mahogany's distinctive grain and color depth typically convey higher-end craftsmanship and durability.
Workability and Ease of Fabrication
Alder wood offers superior workability and ease of fabrication compared to mahogany, making it a preferred choice for intricate door designs and detailed woodworking. Its softer texture allows for smoother cutting, shaping, and sanding, reducing labor time and tool wear. Mahogany, while durable and strong, tends to be denser and harder, requiring more effort and specialized tools for precise fabrication.
Cost and Availability
Alder doors typically cost less than mahogany, making them a budget-friendly option for homeowners seeking durability and a warm appearance. Mahogany, known for its rich color and superior hardness, is more expensive due to its premium quality and limited availability, often sourced from tropical regions. Availability favors alder as it grows more abundantly, while mahogany's restricted supply can lead to longer wait times and higher prices.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Alder doors require minimal maintenance, as their soft wood is less prone to cracking but may need periodic sealing or staining to prevent surface damage and maintain appearance. Mahogany doors are highly durable with natural resistance to rot and insects, demanding less frequent treatment but benefit from occasional oiling or refinishing to preserve their rich color and smooth finish. Both woods need protection from prolonged moisture exposure to extend door lifespan and ensure optimal performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alder wood is considered more sustainable than mahogany due to its faster growth rate and availability from responsibly managed plantations, resulting in a lower environmental impact. Mahogany, often sourced from slow-growing tropical forests, faces concerns over deforestation and illegal logging, making it less eco-friendly. Choosing alder for doors supports a reduced carbon footprint and promotes sustainable forestry practices.
Best Applications for Each Wood Type
Alder doors are best suited for interior applications due to their smooth texture, affordability, and ease of staining or painting, making them ideal for living spaces, bedrooms, and interior panel doors. Mahogany, known for its exceptional durability, rich color, and resistance to rot, excels in exterior door applications where weather resistance and high-end aesthetic appeal are essential, such as entry doors and exterior-facing shutters. Both woods perform well in their specialized roles, with alder favoring refined indoor environments and mahogany preferred for long-lasting, high-traffic exterior uses.
Choosing the Right Wood: Alder vs Mahogany for Your Door
Alder wood offers a smooth, consistent grain and affordability, making it ideal for painted doors and contemporary designs, while mahogany features a rich, deep reddish-brown color with exceptional durability and natural resistance to decay, suited for high-end, traditional doors. Choosing between alder and mahogany depends on desired aesthetics, budget, and the door's exposure to environmental elements. Mahogany's superior hardness and stability make it a preferred choice for exterior doors requiring long-lasting performance.
Infographic: Alder vs Mahogany for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com