Alder offers moderate strength and easy workability, making it suitable for interior construction and furniture. Hemlock provides greater durability and structural integrity, ideal for framing and exterior construction projects.
Table of Comparison
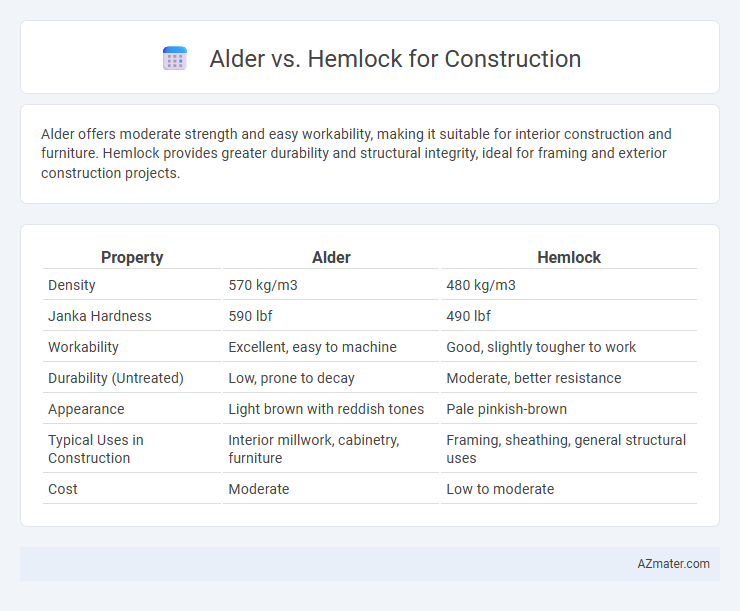
| Property | Alder | Hemlock |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 570 kg/m3 | 480 kg/m3 |
| Janka Hardness | 590 lbf | 490 lbf |
| Workability | Excellent, easy to machine | Good, slightly tougher to work |
| Durability (Untreated) | Low, prone to decay | Moderate, better resistance |
| Appearance | Light brown with reddish tones | Pale pinkish-brown |
| Typical Uses in Construction | Interior millwork, cabinetry, furniture | Framing, sheathing, general structural uses |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Alder and Hemlock in Construction
Alder and Hemlock are both prominent softwoods used in construction, each offering distinct properties that influence their applications. Alder is valued for its fine, even grain and moderate hardness, making it suitable for interior trim, cabinetry, and furniture construction where aesthetics and workability are prioritized. Hemlock, known for its strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to warping, is commonly used in structural framing, paneling, and outdoor applications requiring durability and load-bearing capacity.
Botanical and Physical Characteristics
Alder wood, sourced from the Alnus genus, features a fine, straight grain with uniform texture, offering moderate hardness and excellent workability ideal for furniture and interior construction. Hemlock, from the Tsuga genus, displays a coarse, straight grain with a slightly rough texture, known for its strength, stiffness, and resistance to warping, making it suitable for framing and structural applications. Both species provide durable timber options, but alder's smoother finish and softer density contrast with hemlock's greater load-bearing capacity and dimensional stability.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Alder wood is moderately strong with a Janka hardness of 590, making it suitable for indoor construction but less durable under heavy load or exposure. Hemlock, with a Janka hardness around 480 and good dimensional stability, offers moderate strength but excels in resistance to wear, making it preferred for framing and structural applications. Both woods require proper treatment against moisture and pests, yet Hemlock's higher natural resistance to decay enhances its durability in construction scenarios.
Workability and Ease of Use
Alder wood offers excellent workability due to its fine, even texture and consistent grain, making it easy to cut, shape, and finish with standard woodworking tools. Hemlock, while also workable, tends to be slightly tougher and can splinter more easily, requiring sharper blades and more careful handling during construction. Both woods provide good nailing and screwing properties, but alder's smoother surface and uniform density give it an edge in ease of use for detailed carpentry projects.
Resistance to Decay and Pests
Alder wood exhibits moderate resistance to decay with limited natural protection against pests, making it less durable in high-moisture environments. Hemlock, while also moderately resistant, demonstrates slightly better natural defense against fungal decay and insect damage due to its denser grain structure. For construction requiring longevity and pest resistance, Hemlock provides a more reliable option compared to Alder.
Cost and Availability
Alder wood is generally more affordable than hemlock, making it a cost-effective option for construction projects with budget constraints. Hemlock, while slightly more expensive, offers greater availability across North America due to its widespread growth in the Pacific Northwest. Both woods are commonly used in framing and interior finishes, but alder's lower price point and ready availability in furniture-grade lumber make it a preferred choice for cost-sensitive construction applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Alder wood, known for its rapid growth and renewability, offers a more sustainable option compared to Hemlock, which grows slower and is less abundant, impacting forest ecosystems over time. Alder's lower density results in reduced energy consumption during processing, supporting eco-friendly construction practices. Hemlock, while durable, may contribute to habitat disturbance when harvested unsustainably, making certified Alder a preferable choice for environmentally conscious builders.
Common Construction Applications
Alder wood is commonly used for interior applications such as cabinetry, furniture, and millwork due to its fine grain, ease of staining, and moderate hardness. Hemlock is favored in structural framing and general construction for its strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to warping and splitting. Both woods are valued for their workability, but alder excels in finish work while hemlock is preferred for load-bearing frameworks.
Maintenance and Longevity
Alder wood offers moderate durability with maintenance requirements including regular sealing to prevent moisture damage, making it suitable for interior construction but less ideal for outdoor use. Hemlock provides greater resistance to decay and insect damage, resulting in lower maintenance needs and longer lifespan, especially in structural applications exposed to varying weather conditions. Choosing hemlock over alder enhances the longevity of construction projects with reduced upkeep and better performance under environmental stress.
Choosing Between Alder and Hemlock: Key Considerations
When choosing between alder and hemlock for construction, consider alder's moderate strength and smooth grain, making it ideal for indoor applications like furniture and cabinetry. Hemlock offers greater durability and resistance to decay, suitable for structural elements and outdoor projects. Cost, availability, and the specific load-bearing requirements of the construction project also play critical roles in selecting the appropriate wood.
Infographic: Alder vs Hemlock for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com