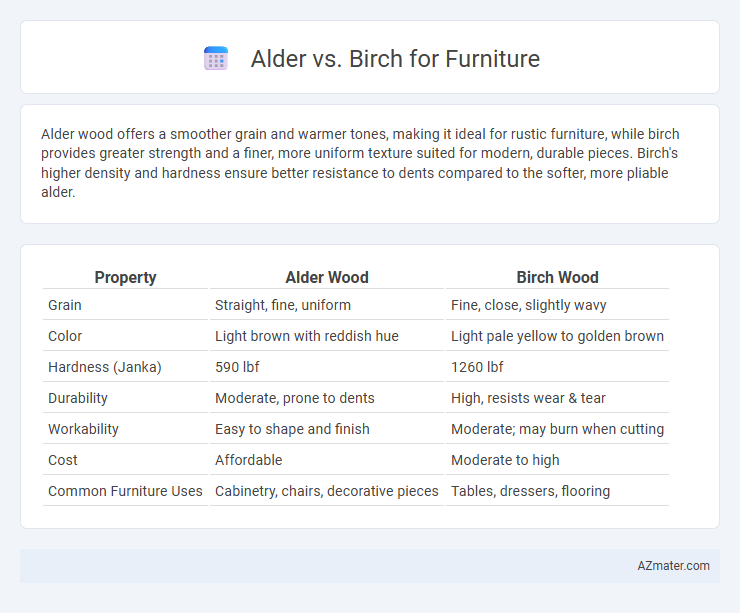
Alder wood offers a smoother grain and warmer tones, making it ideal for rustic furniture, while birch provides greater strength and a finer, more uniform texture suited for modern, durable pieces. Birch's higher density and hardness ensure better resistance to dents compared to the softer, more pliable alder.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alder Wood | Birch Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Grain | Straight, fine, uniform | Fine, close, slightly wavy |
| Color | Light brown with reddish hue | Light pale yellow to golden brown |
| Hardness (Janka) | 590 lbf | 1260 lbf |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to dents | High, resists wear & tear |
| Workability | Easy to shape and finish | Moderate; may burn when cutting |
| Cost | Affordable | Moderate to high |
| Common Furniture Uses | Cabinetry, chairs, decorative pieces | Tables, dressers, flooring |
Introduction to Alder and Birch Wood
Alder wood, known for its fine grain and light reddish-brown color, offers a smooth surface that is easy to stain and shape, making it a popular choice for furniture. Birch wood features a pale cream color with a slightly wavy grain pattern, providing durability and a clean, modern look ideal for both traditional and contemporary furniture designs. Both woods are hardwoods but differ in hardness and color stability, influencing their selection according to aesthetic and functional furniture requirements.
Key Characteristics of Alder Wood
Alder wood is prized in furniture making for its smooth grain, consistent texture, and light reddish-brown color, contrasting with birch's typically pale cream tone. It is softer and easier to work with than birch, allowing for detailed carving and a warm, rustic finish ideal for cabinetry and rustic furniture styles. Alder tends to absorb stains evenly, enhancing its natural grain, while birch offers higher durability and a tighter grain pattern suited for more contemporary or heavy-use pieces.
Key Characteristics of Birch Wood
Birch wood is renowned for its fine grain, pale color, and high durability, making it ideal for furniture that requires both strength and an attractive finish. Compared to alder, birch exhibits greater resistance to wear and offers a more uniform texture, which allows for smooth staining and finishing. Its hardness and stability make birch a preferred choice for furniture pieces that endure frequent use, such as chairs and tables.
Appearance and Grain Comparison
Alder wood exhibits a smooth, fine grain with a consistent texture and a warm, reddish-brown hue that deepens over time, making it ideal for rustic or traditional furniture styles. Birch features a tighter, more uniform grain pattern with a light cream to pale yellow color, offering a clean, modern look that brightens interior spaces. While alder ages gracefully to a richer tone, birch maintains its lighter color, influencing the visual warmth and style of furniture pieces.
Strength and Durability Differences
Alder wood is softer and less dense than birch, resulting in moderate strength and durability suitable for light-use furniture. Birch offers higher hardness and greater resistance to wear and dents, making it more durable for heavy-use or high-traffic furniture applications. The superior strength of birch provides better long-term performance compared to alder in furniture construction.
Workability and Ease of Crafting
Alder wood offers superior workability with its consistent grain and softer texture, making it easier to cut, shape, and sand compared to birch. Birch, while harder and more durable, tends to have a tighter grain that can cause more wear on tools and requires more precision during crafting. Woodworkers often prefer alder for intricate designs or furniture requiring smooth finishes due to its ease of shaping and staining versatility.
Cost and Availability
Alder wood is generally more affordable and widely available compared to birch, making it a cost-effective choice for furniture manufacturing. Birch tends to be pricier due to its harder texture and distinct grain pattern, which adds to its desirability and aesthetic value. Both woods are sustainably harvested, but alder's abundance in North America enhances its accessibility for large-scale furniture production.
Best Furniture Types for Alder
Alder wood is highly favored for furniture types such as cabinets, dressers, and rustic-style tables due to its smooth grain and warm, reddish-brown hue that enhances natural aesthetics. It offers moderate durability and softness, making it easier to carve detailed designs, ideal for decorative pieces and intricate woodwork. Compared to birch, alder is less dense and more prone to dents, but its affordability and workability make it best suited for indoor furniture requiring detailed craftsmanship and a softer finish.
Best Furniture Types for Birch
Birch wood is highly valued for furniture types such as cabinets, dressers, and children's furniture due to its fine grain and light color, which provide a smooth finish and excellent paint adherence. Its durability and resistance to dents make it ideal for high-use pieces like desks and dining tables. Compared to alder, which is softer and more prone to dents, birch offers greater structural strength and longevity for functional and decorative furniture.
Which Wood to Choose: Alder or Birch?
Alder wood is softer and features a consistent, warm grain, making it ideal for rustic or casual furniture with ease of staining and finishing. Birch wood is harder and denser, offering greater durability and a smooth, fine grain ideal for modern, sleek furniture pieces. Choose alder for affordability and ease of workability, while birch is best for strength and long-lasting furniture quality.
Infographic: Alder vs Birch for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com