Alder offers a softer, warm-toned wood that is easier to carve and stains well, making it ideal for rustic or traditional cabinets. Birch is a harder, more durable wood with a fine grain and light color, providing a smooth finish suited for modern or contemporary cabinetry.
Table of Comparison
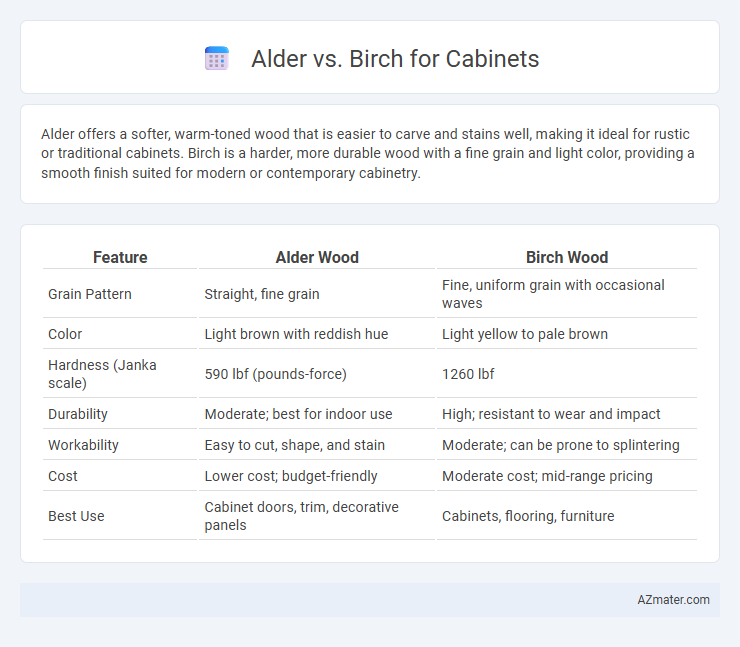
| Feature | Alder Wood | Birch Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Pattern | Straight, fine grain | Fine, uniform grain with occasional waves |
| Color | Light brown with reddish hue | Light yellow to pale brown |
| Hardness (Janka scale) | 590 lbf (pounds-force) | 1260 lbf |
| Durability | Moderate; best for indoor use | High; resistant to wear and impact |
| Workability | Easy to cut, shape, and stain | Moderate; can be prone to splintering |
| Cost | Lower cost; budget-friendly | Moderate cost; mid-range pricing |
| Best Use | Cabinet doors, trim, decorative panels | Cabinets, flooring, furniture |
Introduction to Alder vs Birch for Cabinets
Alder and birch are popular wood choices for cabinets, each offering unique characteristics suited for different design preferences. Alder wood is known for its smooth texture and warm, reddish-brown tones that darken over time, making it ideal for rustic or traditional cabinetry. Birch features a fine grain and lighter color with subtle variations, providing a clean, modern look while maintaining durability and resistance to wear.
Overview of Alder Wood Characteristics
Alder wood is valued in cabinetry for its fine, straight grain and uniform texture, providing a smooth and consistent surface ideal for staining and finishing. Its moderate hardness, with a Janka rating around 590, makes it durable yet easy to work with for intricate cabinet designs. Alder's natural light brown to reddish hues offer a warm, inviting appearance, complementing both traditional and modern kitchen styles.
Overview of Birch Wood Characteristics
Birch wood is highly valued for cabinetry due to its fine grain and smooth texture, offering a clean and uniform appearance that enhances modern and traditional designs. Its light color ranges from creamy white to pale yellow with subtle reddish hues, providing a versatile backdrop for various stains and finishes. Birch is a durable hardwood that resists warping, making it a reliable choice for long-lasting cabinet construction.
Visual Appearance: Grain and Color Comparison
Alder wood features a smooth, consistent grain with a warm, reddish-brown hue that darkens over time, ideal for traditional and rustic cabinet styles. Birch wood displays a fine, uniform grain with a light, creamy color that enhances modern and contemporary cabinetry designs. The natural color variation in alder provides rich warmth, while birch offers a brighter, more neutral aesthetic for versatile kitchen decor.
Durability and Strength: Alder vs Birch
Birch cabinets offer superior durability and strength compared to alder, making them more resistant to dents and scratches in high-traffic kitchens. Alder wood is softer and easier to work with, providing a smooth finish but compromising long-term durability under heavy use. Choosing birch ensures a sturdier cabinet that withstands wear and tear, ideal for families or busy cooking environments.
Workability and Finishing Properties
Alder wood offers superior workability with its soft texture, making it easier to machine, carve, and shape for cabinet construction compared to the harder, denser Birch. Both woods accept stains and finishes well, but Alder provides a smoother, more uniform surface that enhances paint adhesion and results in a refined finish. Birch's tight grain pattern lends to a polished appearance, though it can be prone to uneven stain absorption, requiring careful preparation for optimal finishing.
Cost Comparison: Alder and Birch Cabinets
Alder cabinets typically cost between $100 to $150 per square foot, making them moderately priced compared to other hardwood options, while birch cabinets range from $90 to $140 per square foot, often offering a more budget-friendly alternative. The cost variation depends on factors such as wood grade, finishing, and customizations, with alder being favored for its distinct grain and warmer tones, and birch prized for its smooth texture and light color suitable for various stains. Both wood types provide durability and aesthetic appeal, but birch cabinets usually offer slightly better value for cost-conscious kitchen remodels.
Maintenance and Longevity
Alder wood cabinets require minimal maintenance, benefiting from their smooth texture and resistance to warping, making them ideal for stable indoor environments. Birch cabinets offer excellent durability with a harder surface, allowing them to withstand daily wear and resist dents, thus providing longer longevity in high-traffic kitchens. Both woods perform well with regular cleaning and occasional refinishing, but birch's robustness generally ensures a longer lifespan under intensive use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alder wood for cabinets has a lower environmental impact due to its faster growth rate and abundance in managed forests, making it a more sustainable choice than birch. Birch, while durable and attractive, often comes from slower-growing trees, which can contribute to deforestation if not sourced responsibly. Choosing alder supports sustainable forestry practices by promoting the use of a renewable resource with efficient carbon sequestration.
Which Wood is Best for Your Cabinets?
Alder offers a smooth grain and warm reddish-brown tones, making it ideal for rustic and traditional cabinets, while birch has a tighter, more uniform grain with lighter color, suited for contemporary and painted finishes. Alder is softer and easier to work with, providing cost efficiency, whereas birch boasts greater durability and resistance to dents, enhancing cabinet longevity. Choosing between alder and birch depends on your priority for aesthetic style, budget, and the desired cabinet durability in your space.
Infographic: Alder vs Birch for Cabinet
 azmater.com
azmater.com