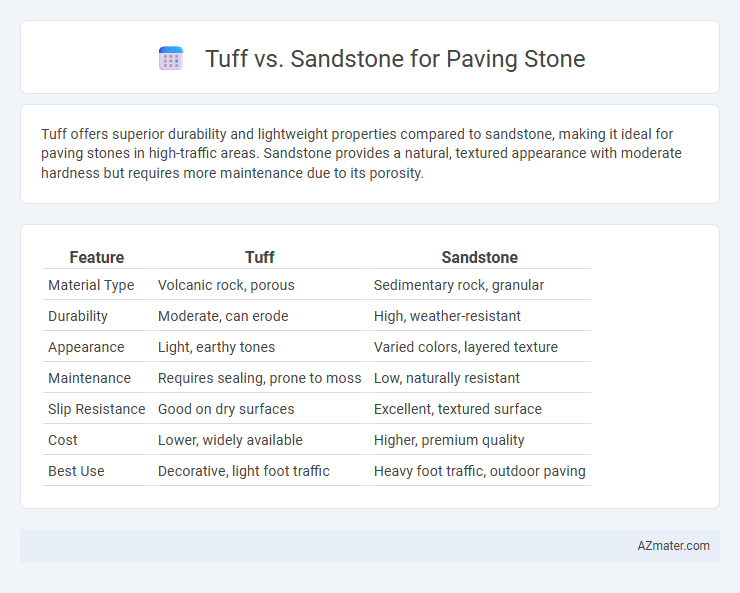
Tuff offers superior durability and lightweight properties compared to sandstone, making it ideal for paving stones in high-traffic areas. Sandstone provides a natural, textured appearance with moderate hardness but requires more maintenance due to its porosity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tuff | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Volcanic rock, porous | Sedimentary rock, granular |
| Durability | Moderate, can erode | High, weather-resistant |
| Appearance | Light, earthy tones | Varied colors, layered texture |
| Maintenance | Requires sealing, prone to moss | Low, naturally resistant |
| Slip Resistance | Good on dry surfaces | Excellent, textured surface |
| Cost | Lower, widely available | Higher, premium quality |
| Best Use | Decorative, light foot traffic | Heavy foot traffic, outdoor paving |
Understanding Tuff and Sandstone: Key Differences
Tuff and sandstone are distinct natural stones commonly used for paving, with tuff formed from volcanic ash and sandstone composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles cemented together. Tuff typically offers higher porosity and a softer texture, making it easier to cut but less durable under heavy traffic compared to the denser, harder sandstone. Sandstone's superior strength and weather resistance make it ideal for high-traffic paving applications, while tuff provides unique aesthetic qualities with its varied volcanic textures and colors.
Composition and Formation of Tuff vs Sandstone
Tuff is a volcanic rock formed from compacted volcanic ash, consisting primarily of fragmented volcanic glass, minerals, and small rock particles, resulting in a porous and lightweight material. Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles, typically quartz and feldspar, cemented together by silica, calcium carbonate, or iron oxides, creating a dense and durable stone. The contrasting formation processes--volcanic activity for tuff and sediment deposition for sandstone--directly influence their physical properties and suitability for paving stone applications.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color and Texture Comparison
Tuff offers a unique aesthetic appeal with its porous texture and warm earth tones ranging from soft beige to rusty reds, creating a natural, rustic look ideal for landscaping and garden paths. Sandstone provides a smoother surface and a broader color palette, including golden yellows, pinks, and browns, allowing for versatile design applications in both formal and casual paving scenarios. The choice between tuff and sandstone depends on the desired visual effect, with tuff emphasizing rugged natural charm and sandstone delivering refined elegance through its varied hues and fine grain.
Durability and Strength for Paving Applications
Tuff exhibits exceptional durability and moderate strength, making it suitable for paving applications with low to medium traffic, while sandstone offers higher compressive strength and better resistance to abrasion, ideal for heavy-traffic areas. The porosity of tuff can affect its long-term durability under harsh weather conditions, whereas sandstone's dense composition enhances its resilience against wear and freeze-thaw cycles. For optimal paving stone performance, sandstone is preferred where maximum strength and durability are critical, though tuff provides a cost-effective alternative for less demanding environments.
Slip Resistance and Surface Safety
Tuff offers superior slip resistance compared to sandstone due to its rougher, more porous texture that provides better traction on wet and dry surfaces. Sandstone, while aesthetically appealing with its smooth finish, can become slippery when wet, posing potential surface safety risks. Choosing tuff for paving stones enhances safety in high-traffic or outdoor areas where slip hazards are a concern.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Tuff exhibits superior weather resistance compared to sandstone, due to its volcanic origin which makes it denser and less porous, reducing water absorption and freeze-thaw damage. Sandstone, while aesthetically pleasing with its natural grain, tends to be more susceptible to erosion and surface wear under harsh weather conditions. Consequently, tuff paving stones generally offer greater longevity and lower maintenance in variable climates, making them a more durable choice for outdoor applications.
Maintenance Requirements: Tuff vs Sandstone
Tuff requires minimal maintenance due to its dense, non-porous nature, making it resistant to stains and weathering, ideal for low-upkeep paving stone applications. Sandstone, being more porous, demands regular sealing and cleaning to prevent water absorption, discoloration, and erosion, increasing overall maintenance efforts. Choosing Tuff over Sandstone reduces long-term upkeep costs and preserves aesthetic appeal in paving stone installations.
Installation Process and Workability
Tuff offers superior workability for paving stone installation due to its softer texture, allowing easier cutting and shaping compared to sandstone. The installation process with tuff is faster and less labor-intensive, as it requires less specialized equipment for fitting and adjustment. Sandstone, being denser and harder, demands more effort during cutting and precise handling, which can extend installation time and increase labor costs.
Cost Comparison: Tuff vs Sandstone Paving
Tuff paving stones generally offer a more cost-effective option compared to sandstone due to their abundance and easier quarrying process, leading to lower material and installation expenses. Sandstone, prized for its aesthetic appeal and durability, typically commands higher prices driven by quarrying difficulty, transportation, and specialized cutting techniques. When budgeting for paving projects, the initial savings with tuff must be weighed against potential long-term maintenance costs, while sandstone often presents a balance of longevity and visual value despite its higher upfront cost.
Best Use Cases: Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Tuff offers high porosity and lightweight properties, making it ideal for outdoor paving in areas with moderate foot traffic and good drainage requirements. Sandstone provides superior durability and a dense, textured surface, perfect for high-traffic patios and walkways where slip resistance and longevity are critical. Selecting the right paving stone depends on balancing environmental exposure, load demands, and aesthetic preference, with tuff excelling in softer landscapes and sandstone thriving in robust, heavily used settings.
Infographic: Tuff vs Sandstone for Paving Stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com