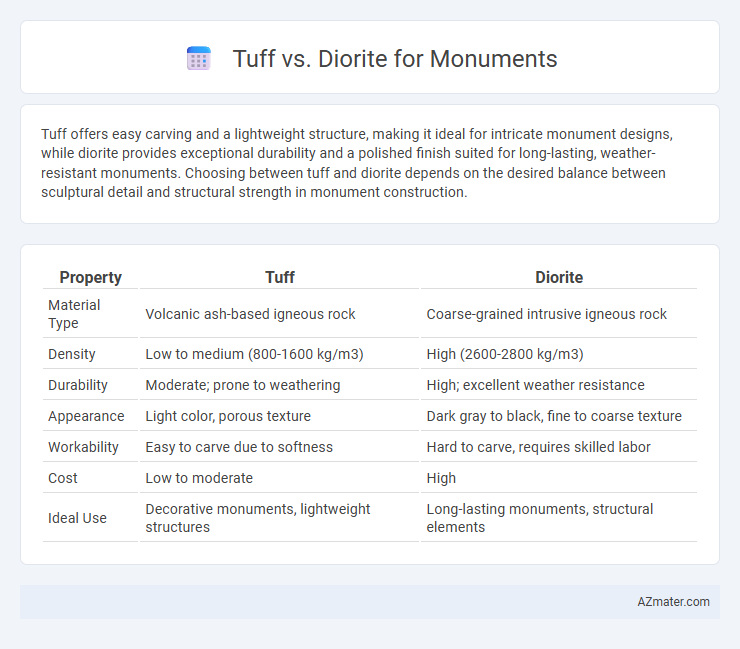
Tuff offers easy carving and a lightweight structure, making it ideal for intricate monument designs, while diorite provides exceptional durability and a polished finish suited for long-lasting, weather-resistant monuments. Choosing between tuff and diorite depends on the desired balance between sculptural detail and structural strength in monument construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tuff | Diorite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Volcanic ash-based igneous rock | Coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock |
| Density | Low to medium (800-1600 kg/m3) | High (2600-2800 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to weathering | High; excellent weather resistance |
| Appearance | Light color, porous texture | Dark gray to black, fine to coarse texture |
| Workability | Easy to carve due to softness | Hard to carve, requires skilled labor |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Ideal Use | Decorative monuments, lightweight structures | Long-lasting monuments, structural elements |
Introduction: Understanding Tuff and Diorite
Tuff, a volcanic rock composed of compacted ash and fragmented material, offers lightweight durability and ease of carving, making it popular for monuments. Diorite, an intrusive igneous rock with a coarse-grained texture and high hardness, provides exceptional strength and weather resistance, suitable for long-lasting commemorative structures. Understanding the physical properties, mineral composition, and aesthetic appeal of both tuff and diorite is essential for selecting the ideal material in monument construction.
Geological Origins of Tuff and Diorite
Tuff is a volcanic rock formed from consolidated volcanic ash ejected during explosive eruptions, characterized by its relatively porous texture and lightweight composition. Diorite, an intrusive igneous rock, crystallizes slowly beneath the Earth's surface from cooling magma, resulting in a coarse-grained, durable structure with interlocking feldspar and hornblende crystals. The contrasting geological origins of tuff and diorite influence their physical properties and suitability for monuments, with tuff offering ease of carving and diorite providing superior hardness and longevity.
Physical Properties Comparison
Tuff exhibits lower density and compressive strength compared to Diorite, making it lighter but less durable for heavy load-bearing monuments. Diorite's coarse-grained texture and high hardness provide superior resistance to weathering, ideal for long-lasting and detailed architectural features. While Tuff's porosity allows easier carving, Diorite offers greater longevity due to its lower porosity and higher mechanical strength.
Aesthetic Qualities in Monument Design
Tuff offers a softer, porous texture with earthy hues ideal for creating rustic and weathered monument designs, enhancing historical or natural aesthetics. Diorite, known for its coarse-grained, speckled appearance and durability, provides a polished, elegant finish suited for modern or high-contrast memorials. The choice between Tuff and Diorite impacts the monument's visual appeal, balancing organic warmth against refined sophistication.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Tuff offers moderate durability with its volcanic ash composition, making it lighter but more porous and susceptible to weathering and erosion over time. Diorite is highly durable due to its coarse-grained igneous structure, exhibiting excellent resistance to weathering, making it ideal for long-lasting monuments exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Choosing diorite ensures superior longevity and preservation in monuments subjected to extreme weather, while tuff is better suited for less demanding applications.
Workability and Carving Potential
Tuff offers superior workability for monuments due to its softer texture, allowing intricate carving and detailed designs with less effort compared to the harder, denser Diorite. Diorite's coarse-grained composition provides durability but limits fine detail carving, making it ideal for larger, more robust structures rather than delicate sculpting. Choosing Tuff enhances artistic expression in monuments, while Diorite ensures long-lasting strength with moderate carving potential.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tuff offers easier maintenance due to its softer composition, allowing for straightforward cleaning and repair, but it is more susceptible to weathering and erosion over time compared to diorite. Diorite's dense and durable nature ensures exceptional longevity and resistance to environmental wear, making it ideal for monuments intended to last centuries with minimal upkeep. Choosing diorite reduces long-term restoration costs and preserves inscriptions and details better than tuff under harsh climatic conditions.
Environmental Impact of Quarrying
Quarrying tuff generally has a lower environmental impact than diorite due to its softer composition, requiring less energy-intensive extraction and processing. Diorite quarrying involves extensive blasting and crushing, leading to higher carbon emissions and habitat disruption. Choosing tuff for monuments can reduce ecological footprints by minimizing land degradation and energy consumption during quarrying.
Historical and Modern Uses in Monuments
Tuff, a porous volcanic rock, has been extensively used in ancient monuments such as the Roman Colosseum due to its lightweight nature and ease of carving, making it ideal for intricate architectural designs and large-scale construction. Diorite, a dense, durable igneous rock with a speckled appearance, was favored in ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia for statues and sarcophagi because of its hardness and resistance to weathering, ensuring longevity in monumental art. In modern monuments, tuff's versatility allows for decorative facades and restoration projects, whereas diorite remains prized for commemorative sculptures and foundations requiring exceptional durability and aesthetic appeal.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Monument
Tuff offers a lightweight, easily carved option with a porous texture ideal for intricate monument details, while Diorite provides superior durability and a polished, dense surface that withstands harsh weather conditions better. Selecting between Tuff and Diorite depends on balancing aesthetic preferences with longevity requirements, as Diorite's hardness ensures monument preservation over time. For monuments requiring fine, detailed craftsmanship in less exposed environments, Tuff is suitable, but for enduring outdoor structures, Diorite is the optimal choice.
Infographic: Tuff vs Diorite for Monument
 azmater.com
azmater.com