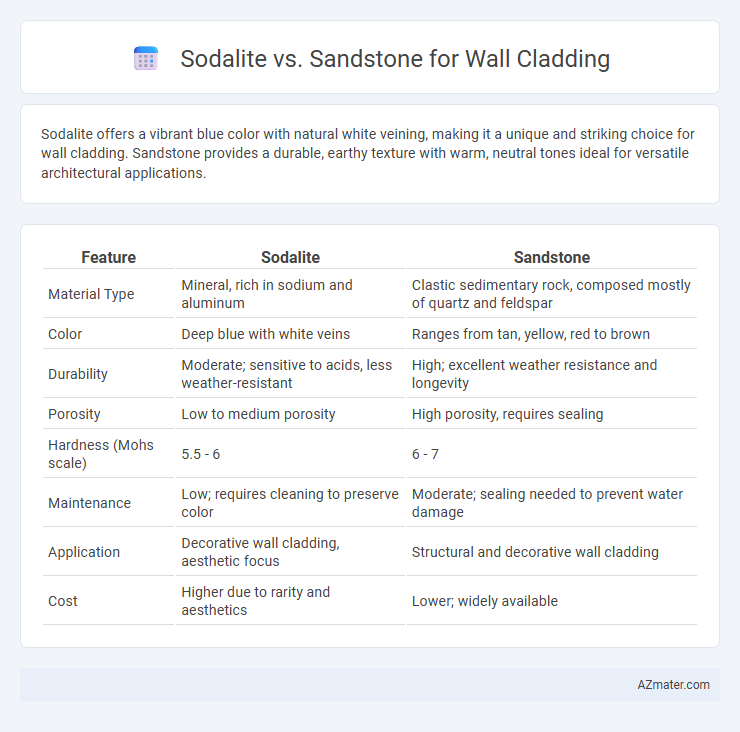
Sodalite offers a vibrant blue color with natural white veining, making it a unique and striking choice for wall cladding. Sandstone provides a durable, earthy texture with warm, neutral tones ideal for versatile architectural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sodalite | Sandstone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Mineral, rich in sodium and aluminum | Clastic sedimentary rock, composed mostly of quartz and feldspar |
| Color | Deep blue with white veins | Ranges from tan, yellow, red to brown |
| Durability | Moderate; sensitive to acids, less weather-resistant | High; excellent weather resistance and longevity |
| Porosity | Low to medium porosity | High porosity, requires sealing |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 5.5 - 6 | 6 - 7 |
| Maintenance | Low; requires cleaning to preserve color | Moderate; sealing needed to prevent water damage |
| Application | Decorative wall cladding, aesthetic focus | Structural and decorative wall cladding |
| Cost | Higher due to rarity and aesthetics | Lower; widely available |
Introduction to Sodalite and Sandstone
Sodalite is a rich blue, tectosilicate mineral commonly used in wall cladding for its striking color and durability, often sourced from Brazil, Canada, and Russia. Sandstone, a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized mineral particles, is valued for its natural earth tones, texture, and weather resistance, with major quarries in India, Australia, and the United States. Both materials offer distinct aesthetic and functional benefits, making them popular choices in architectural and interior design applications.
Geological Origins and Composition
Sodalite, an intrusive igneous rock rich in sodium, forms from magma cooling deep within the Earth's crust and is characterized by its vibrant blue color due to its sodium aluminum silicate composition. Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of quartz and feldspar grains cemented together, originating from the lithification of sand deposited by water or wind over millions of years. The fundamental difference in geological origin results in sodalite having a denser, crystalline structure, whereas sandstone features a granular texture with variable porosity affecting durability and aesthetic applications in wall cladding.
Aesthetic Differences: Color and Texture
Sodalite wall cladding showcases deep blue hues with white veining, creating a striking and luxurious appearance that adds vibrancy and elegance to any space. Sandstone offers a warm, earthy palette ranging from beige to reddish tones with a naturally granular, matte texture that evokes a rustic and timeless charm. The bold, polished finish of sodalite contrasts with the soft, textured surface of sandstone, making each suitable for different architectural styles and aesthetic preferences.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Sodalite offers moderate strength and durability, making it suitable for interior wall cladding but less ideal for high-impact or exterior applications due to its relative softness and susceptibility to weathering. Sandstone exhibits higher durability and compressive strength, with excellent resistance to abrasion and environmental conditions, making it a preferred choice for both interior and exterior wall cladding projects. The inherent hardness and porosity differences mean sandstone generally outperforms sodalite in long-term structural integrity and maintenance.
Installation Process and Techniques
Sodalite wall cladding requires precise cutting techniques due to its crystalline structure, often necessitating diamond blade saws to prevent chipping and ensure clean edges. Sandstone, being softer and more porous, allows for easier cutting and shaping with standard masonry tools, but requires careful sealing after installation to prevent moisture absorption. Both materials benefit from mechanical anchoring systems, although sandstone's lower density may require more frequent fixation points to maintain structural integrity.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Sodalite wall cladding offers superior durability and low maintenance due to its dense mineral composition, resisting weathering and staining more effectively than sandstone. Sandstone requires regular sealing and more frequent cleaning to prevent erosion and discoloration caused by its porous nature. Over time, sodalite maintains its aesthetic appeal and structural integrity longer, making it a cost-effective choice for long-term exterior applications.
Cost Analysis: Sodalite vs Sandstone
Sodalite wall cladding typically costs more than sandstone due to its rarer availability and vibrant blue hues, commanding premium prices in the market. Sandstone, being abundant and easier to quarry, offers a more budget-friendly option with a broader range of earthy tones, often reducing overall project expenses. When comparing total installation costs, sandstone also benefits from lower labor and maintenance expenses, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale wall cladding projects.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Sodalite offers a more sustainable option for wall cladding due to its lower extraction impact and higher durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements compared to sandstone. Sandstone often involves energy-intensive quarrying processes that contribute to greater carbon emissions and environmental degradation. Choosing sodalite supports eco-friendly construction practices by minimizing resource depletion and promoting long-term environmental balance.
Best Applications for Each Stone
Sodalite is best suited for interior wall cladding due to its vibrant blue hues and fine-grained texture, making spaces visually striking and elegant. Sandstone excels in exterior wall cladding with its durability and natural weather resistance, providing a rustic and warm appearance ideal for facades and garden walls. Both stones offer unique aesthetic and functional qualities, with sodalite preferred for decorative indoor settings and sandstone favored for robust outdoor applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Wall Cladding Material
Sodalite offers a unique deep blue color and high durability, making it ideal for decorative and visually striking wall cladding applications. Sandstone provides natural earth tones with excellent weather resistance and ease of installation, suitable for traditional and rustic architectural styles. Selecting the right wall cladding material depends on design preference, environmental exposure, and maintenance requirements to ensure long-lasting performance and aesthetic appeal.
Infographic: Sodalite vs Sandstone for Wall Cladding
 azmater.com
azmater.com