Slate offers a natural, fine-grained texture with excellent durability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for indoor and outdoor tiles. Basalt provides a dense, hard surface with superior strength and heat resistance, often preferred for high-traffic areas and modern architectural designs.
Table of Comparison
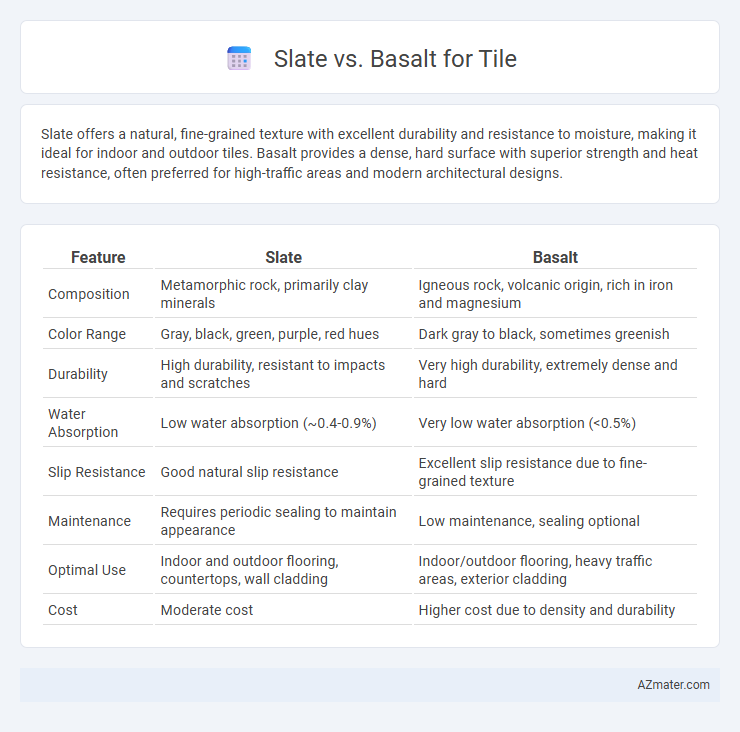
| Feature | Slate | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Metamorphic rock, primarily clay minerals | Igneous rock, volcanic origin, rich in iron and magnesium |
| Color Range | Gray, black, green, purple, red hues | Dark gray to black, sometimes greenish |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to impacts and scratches | Very high durability, extremely dense and hard |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption (~0.4-0.9%) | Very low water absorption (<0.5%) |
| Slip Resistance | Good natural slip resistance | Excellent slip resistance due to fine-grained texture |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic sealing to maintain appearance | Low maintenance, sealing optional |
| Optimal Use | Indoor and outdoor flooring, countertops, wall cladding | Indoor/outdoor flooring, heavy traffic areas, exterior cladding |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to density and durability |
Introduction to Slate and Basalt Tiles
Slate tiles are natural stone tiles formed from fine-grained, metamorphic rock known for their durability, natural cleft texture, and rich, earthy tones ranging from gray to green and purple. Basalt tiles originate from volcanic igneous rock, prized for their dense, hard composition, smooth surface, and dark, uniform coloring that ranges from black to charcoal gray. Both slate and basalt tiles are favored in interior and exterior applications for their strength, natural beauty, and resistance to moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Geological Origins and Formation
Slate originates from shale subjected to low-grade regional metamorphism, resulting in fine-grained, foliated rock characterized by excellent cleavage that makes it ideal for tile. Basalt forms from rapid cooling of basaltic lava at or near Earth's surface, creating dense, fine-grained igneous rock with uniform texture and high durability. The geological processes behind slate's foliated structure and basalt's crystalline uniformity significantly influence their respective uses and aesthetics in tile applications.
Physical Characteristics and Appearance
Slate features a fine-grained, foliated texture with natural clefts that create a textured, slip-resistant surface ideal for flooring, while basalt is a dense, fine-grained igneous rock offering a smooth, uniform appearance with high durability and low porosity. Slate tiles typically display a range of colors including gray, green, purple, and black with subtle variations and a matte finish, whereas basalt tiles are commonly dark gray to black with a consistent tone and a slightly glossy surface when polished. The physical hardness of basalt surpasses slate, making basalt more resistant to scratches and wear, but slate's layered structure provides better natural grip and aesthetic variety.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Slate and basalt are both durable natural stones commonly used for tile, but basalt exhibits superior strength due to its volcanic origin and fine-grained structure, making it more resistant to impact and wear. Slate, while durable, has a layered composition that can cause it to be more prone to chipping and splitting under heavy pressure. In terms of longevity, basalt's higher density and hardness contribute to better performance in high-traffic areas, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor tiling applications.
Slip Resistance and Safety
Slate tiles offer excellent natural slip resistance due to their textured surface, making them a safer choice for wet or high-traffic areas compared to smoother options. Basalt tiles, while denser and harder, typically have a smoother finish that can become slippery when wet unless treated with anti-slip coatings. Choosing slate enhances safety in environments where slip hazards are a concern, while basalt requires additional surface modification to meet similar slip resistance standards.
Installation Process and Ease
Slate tiles require careful handling during installation due to their natural cleft surface and varying thickness, necessitating skilled labor and precise cutting tools to achieve a smooth finish. Basalt tiles offer more uniform thickness and a smoother texture, simplifying the installation process and reducing the risk of uneven surfaces. Both materials benefit from professional installation, but basalt's consistent quality generally allows for faster and easier placement compared to slate.
Maintenance and Longevity
Slate tiles offer excellent durability and require minimal maintenance due to their dense, non-porous surface, resisting stains and scratches effectively. Basalt tiles provide superior longevity with their hard, volcanic origin, but they demand regular sealing to prevent moisture absorption and maintain their appearance. Both materials are long-lasting choices for flooring, though slate tends to be easier to maintain over time, while basalt requires more consistent upkeep to preserve its durability.
Cost and Value Analysis
Slate tiles typically cost between $5 to $10 per square foot, offering a natural, durable option with moderate maintenance requirements, while basalt tiles range from $7 to $15 per square foot, valued for their superior strength and sleek, modern appearance. Slate provides excellent value for budget-conscious projects seeking a rustic aesthetic, whereas basalt justifies its higher cost with enhanced longevity and resistance to wear, especially in high-traffic areas. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial investment against long-term durability and desired visual impact in tile applications.
Best Use Cases and Applications
Slate offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for bathroom floors, kitchen backsplashes, and outdoor patios where moisture exposure is high. Basalt provides a sleek, uniform appearance with excellent strength, suited for modern indoor flooring, wall cladding, and high-traffic commercial spaces. Both stones excel in heat resistance, but slate's natural cleft surface enhances slip resistance in wet areas, while basalt's fine-grained texture supports polished, contemporary design aesthetics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Slate tiles have a lower environmental impact due to their natural formation and minimal processing requirements, making them a sustainable choice for eco-conscious projects. Basalt tiles, while also natural, often require more intensive quarrying and energy consumption during production but offer durability and longer lifespan that can offset initial environmental costs. Both materials contribute to sustainability when sourced responsibly, with slate typically favored for its lower embodied energy and reduced carbon footprint.
Infographic: Slate vs Basalt for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com