Sintered stone offers superior durability, non-porosity, and resistance to stains compared to bluestone, making it a premium choice for paving in high-traffic areas. Bluestone provides a natural, textured surface with excellent slip resistance but requires more maintenance due to its porous nature.
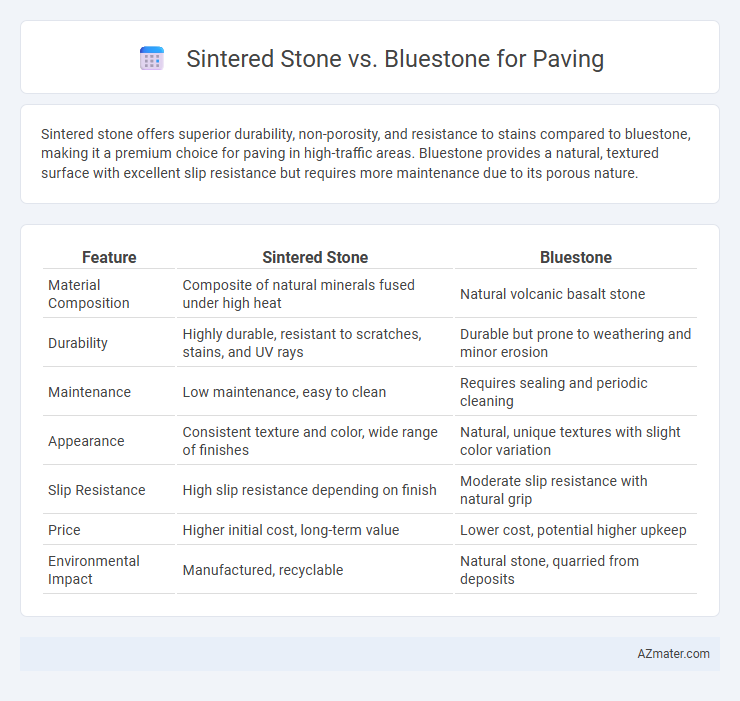
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sintered Stone | Bluestone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Composite of natural minerals fused under high heat | Natural volcanic basalt stone |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to scratches, stains, and UV rays | Durable but prone to weathering and minor erosion |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires sealing and periodic cleaning |
| Appearance | Consistent texture and color, wide range of finishes | Natural, unique textures with slight color variation |
| Slip Resistance | High slip resistance depending on finish | Moderate slip resistance with natural grip |
| Price | Higher initial cost, long-term value | Lower cost, potential higher upkeep |
| Environmental Impact | Manufactured, recyclable | Natural stone, quarried from deposits |
Introduction: Sintered Stone vs Bluestone for Paving
Sintered stone offers superior durability and low porosity, making it highly resistant to stains and weathering compared to bluestone, which is a natural sedimentary rock known for its unique color variations and rustic appearance. Bluestone's natural texture provides excellent slip resistance, ideal for outdoor paving, whereas sintered stone's engineered composition ensures uniformity and easier maintenance. Both materials perform well in paving applications, but sintered stone excels in longevity and versatility, while bluestone delivers natural aesthetic appeal.
What is Sintered Stone?
Sintered stone is an engineered surface made by compressing natural minerals and raw materials under extreme heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, durable, and non-porous material ideal for paving. This manufacturing process enhances its resistance to scratches, stains, and UV rays, making sintered stone highly suitable for outdoor applications compared to bluestone, a natural sedimentary rock. Unlike bluestone, sintered stone offers consistent color and texture, ensuring long-lasting aesthetic appeal and minimal maintenance for paved surfaces.
What is Bluestone?
Bluestone is a dense, durable natural stone primarily composed of sandstone or basalt, commonly used in outdoor paving for its weather resistance and slip-resistant surface. Sourced mainly from regions like Pennsylvania and New England in the United States, bluestone offers a distinctive blue-gray hue that enhances landscape aesthetics. Compared to sintered stone, bluestone provides a natural texture and organic variation, ideal for traditional and rustic paving designs.
Appearance and Design Versatility
Sintered stone offers a sleek, uniform appearance with a wide range of colors and patterns achieved through advanced manufacturing processes, making it highly versatile for contemporary design applications. Bluestone, a natural stone, features unique textures and earthy tones that provide a rustic and organic look, appealing to traditional and naturalistic outdoor settings. The consistent surface of sintered stone allows for precise fabrication and large-format slabs, while bluestone's irregularities and color variations enhance its character and natural appeal.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Sintered stone offers superior strength and durability compared to bluestone, with its engineered composition providing enhanced resistance to impact, scratches, and weathering. Bluestone, while naturally tough and dense, is more prone to chipping and requires regular sealing to maintain its longevity in paving applications. The high compressive strength of sintered stone makes it ideal for high-traffic areas, whereas bluestone suits moderate use where natural aesthetics are prioritized alongside durability.
Porosity and Water Resistance
Sintered stone exhibits low porosity, typically below 0.1%, making it highly resistant to water absorption and ideal for paving in wet environments. Bluestone, a natural sedimentary rock, has higher porosity ranging from 1% to 5%, which can lead to increased water retention and potential surface damage over time. The superior water resistance of sintered stone ensures durability and reduced maintenance compared to bluestone in paving applications.
Slip Resistance and Safety
Sintered stone offers superior slip resistance compared to bluestone due to its denser, non-porous surface structure that enhances grip, making it safer for wet or high-traffic areas. Bluestone, while naturally textured, can become slippery when polished or wet, requiring additional treatments or finishes to improve safety. Choosing sintered stone for paving prioritizes long-term slip resistance and durability, essential for minimizing accidents in public or residential outdoor spaces.
Maintenance Requirements
Sintered stone requires minimal maintenance due to its non-porous surface that resists stains, scratches, and weathering, making it ideal for high-traffic paving areas. Bluestone, while durable, is more porous and demands regular sealing to prevent staining and damage from freeze-thaw cycles. Routine cleaning with mild detergents helps prolong the lifespan of both materials, but sintered stone offers more consistent low-maintenance benefits over time.
Cost and Value
Sintered stone typically offers higher upfront costs than bluestone due to its advanced manufacturing process and enhanced durability. Bluestone provides a cost-effective option with natural variations that contribute to its aesthetic appeal, but may require more maintenance over time. Evaluating long-term value, sintered stone's resistance to stains, scratches, and weathering often results in lower replacement and upkeep expenses, making it a worthwhile investment for high-traffic paving applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sintered stone, produced through a high-pressure, high-temperature process using natural minerals, offers superior durability and low porosity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing environmental waste. Bluestone, a natural quarried stone, typically requires more energy-intensive extraction and processing, contributing to higher carbon emissions and landscape disruption. Choosing sintered stone for paving supports sustainability by combining long lifespan with lower environmental impact compared to traditional bluestone.
Infographic: Sintered stone vs Bluestone for Paving
 azmater.com
azmater.com